LONG SHORT TERM MEMORY:
Understanding of LSTM can be a bit challenging, I recommend you to take one step at a time and move to next part only when you are comfortable with the previous one. By the end of this article you will have a good understanding of LSTM and when they should be preferred over RNN.
Long short term memory (LSTM) is a special type of Recurrent Neural Network (RNN), RNN is a type of Neural Network in which output from the previous step are fed as input to the current step. RNN is used mainly in time series forecasting problems.
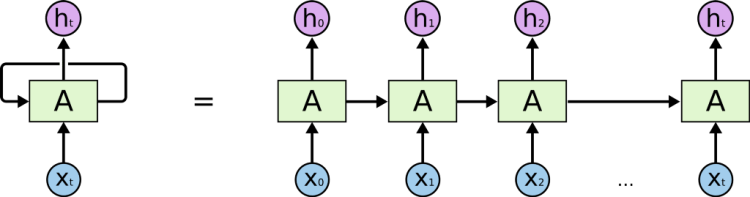
The major appeal behind RNN is the usage of previous values to predict the present values, but RNN suffers from a drawback , as the number of previous value increases RNN tends to perform poorly. It could be clear with the help of an example: “The fishes are in the water” , if we want to predict the last word from the sentence which is water, we can predict it from the given sentence and no further context is needed, in these cases the gap is small and RNN performs well. RNN performs well in short-term dependency.

In case of long term dependency the performance of RNN is not good and RNN becomes unable to learn to connect information. “I grew up in German.. I speak fluent German” , in the above language model if we want to predict the last word we need more previous layer and the gap grows so RNN fails.
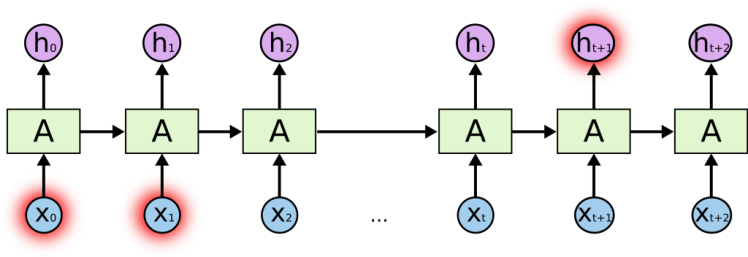
To overcome the shortcomings of RNN, especially those of vanishing gradient,LSTM was introduced, LSTM was designed to avoid long term dependency problem, remembering information for long period of time is their default behaviour.
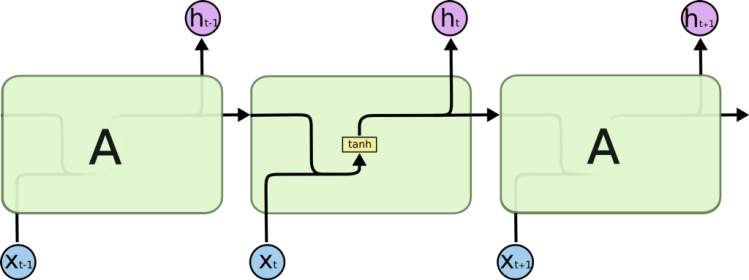
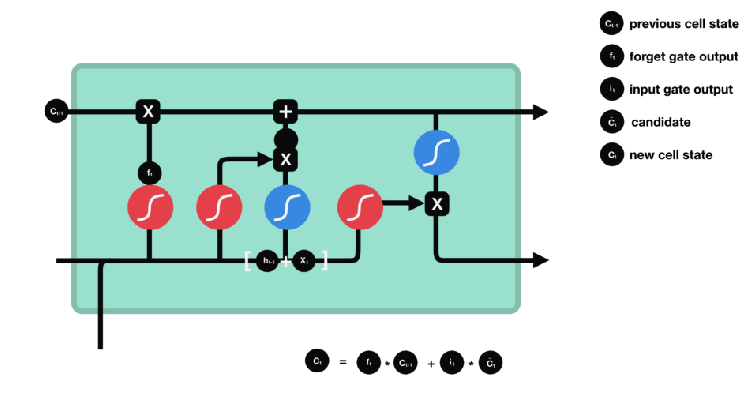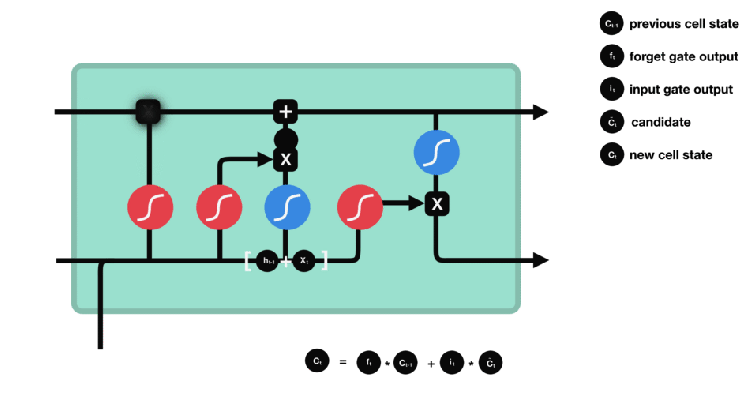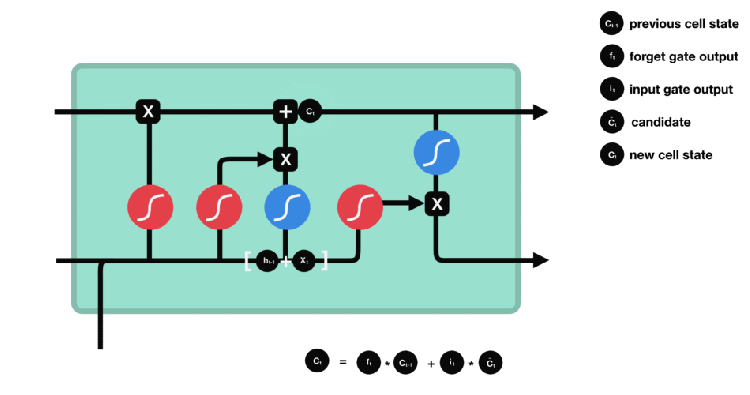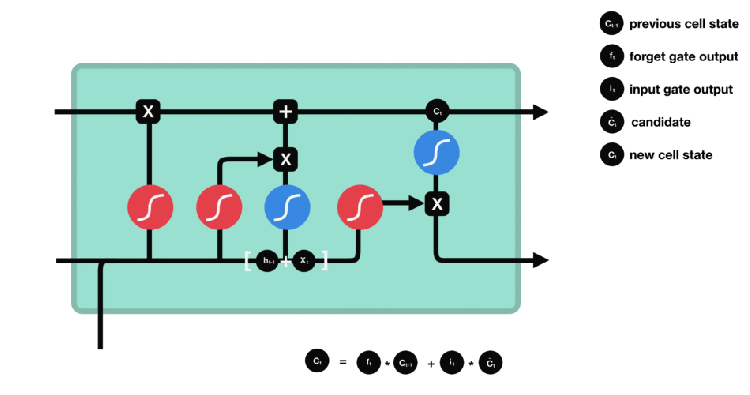
RNN only has a single tanh layer in its structure, while LSTM structure consist of 4 intersecting layers.
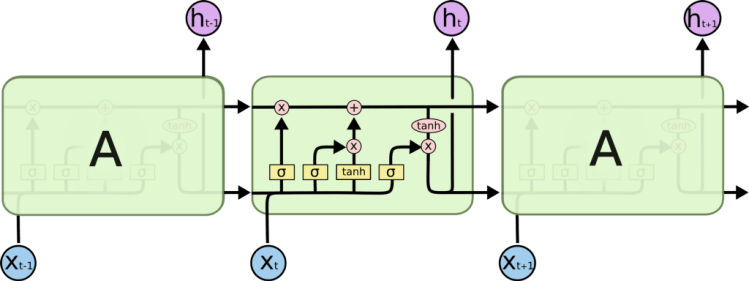
Deeper in to LSTM:
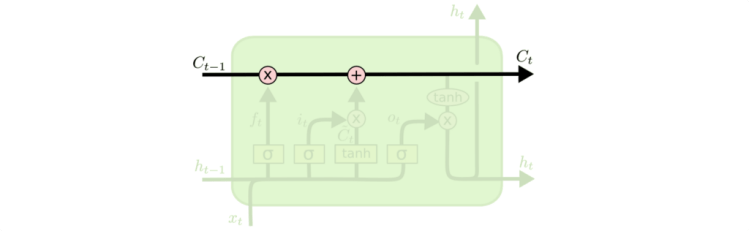
The line which runs straight through in the above diagram with very lminor interaction is called as the cell state.

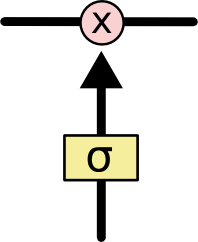
Now here comes the key behind LSTM, useful information can be added to the cell state and irrelevant ones can be removed from the cell state with the help of gates which cconsists of a sigmoid layer.

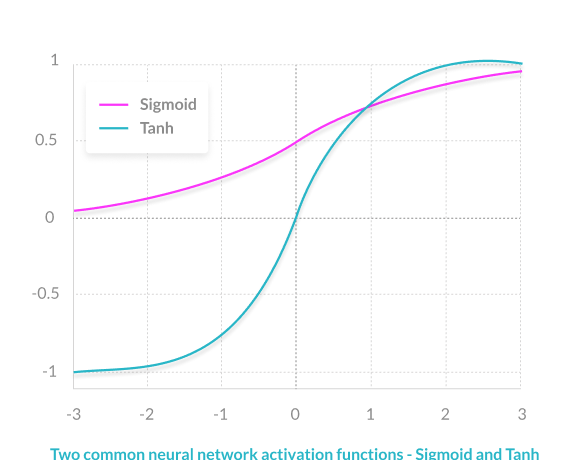
In general sigmoid layer outputs a value between 0 and 1 , a value of 0 means the value is rejected or irrelevant information , while a value of 1 means useful information or in other words 0 means “Let nothing through it” while 1 means “Leave everything through it”.
FORGET GATE LAYER:
Forget gate take cares which information to throw away or it takes care of removing the unnecssary information .
Trending AI Articles:
1. Neural networks for algorithmic trading. Multimodal and multitask deep learning
2. Back-Propagation is very simple. Who made it Complicated ?
The forget gate looks at ht-1 and xt and output a value between 0 and 1 , a value of 0 means “don’t let anything to pass through” while a value of 1 means “Completely allow everything to pass through”.

INPUT GATE LAYER:

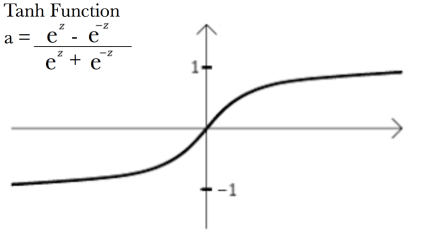
The input layer consist of 2 parts tanh and a sigmoid layer, the sigmoid decides which value we will update and the tanh layer creates a new set of vectors Ct. Tanh function outputs a value between -1 to 1.
The old cell state Ct-1 is updated in to new cell state Ct by multiplying ft with Ct-1, this takes care of the things we need to forget earlier, then we add it∗Ct to it.

For output we run a sigmoid layer and then we multiply it with tanh layer.

Don’t forget to give us your ? !




LONG SHORT TERM MEMORY: PART 1 was originally published in Becoming Human: Artificial Intelligence Magazine on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
Via https://becominghuman.ai/long-short-term-memory-part-1-3caca9889bbc?source=rss—-5e5bef33608a—4
source https://365datascience.weebly.com/the-best-data-science-blog-2020/long-short-term-memory-part-1
