
AI and Machine Learning are two buzz words that everyone hears almost every day. But when we see the job requirements there is a miss alignment between what we actually see in the news and what companies require. Why is that? Let’s get it by learning what lies under the hood.
How a machine can have intelligence! Let’s get it through some history and a comparison with human anatomy.
In 1950 Alan Turing published an article named “Computing Machinery and Intelligence”. He started his article with this quote:
I propose to consider the question, can a machine think?
In 1970 when scientists thought of something like Speech Recognition or Image Recognition they had to do maths on paper with pencils and they made books of lookup tables. Which took an immense amount of manpower and time. Then they though if they could somehow make the machine learn all the data then it can make calculations on its own.
A computer scientist Geoffrey Hinton almost 40 years ago, was obsessed with figuring out how the human mind works. He studied physiology, the anatomy of our brain, psychology, and then got into more of a computer science approach to modeling the brain, called Neural Network in Artificial Intelligence.
Needless to say that Artificial Intelligence has been inspired by human anatomy. The reason why Geoffrey Hinton is called the godfather of AI in modern times because, Artificial intelligence is mostly about artificial neural networks and deep learning. But this is not how it always was. In fact, for most of its six-decade history, the field was dominated by symbolic artificial intelligence, also known as “classical AI,” “rule-based AI,” and “good old-fashioned AI.”

AI is a huge section to combine in a small diagram. But I tried to picture it this way:
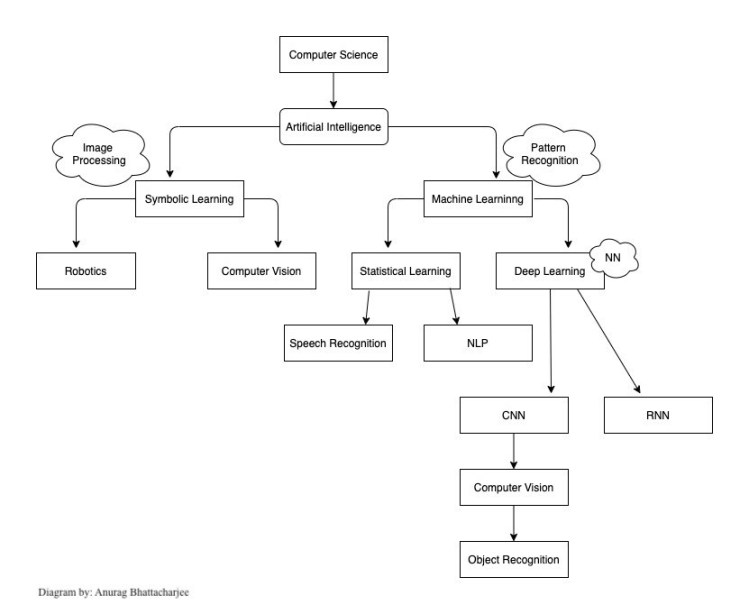
Now, there are basically two approaches for a Machine to be Intelligent.
- Symbolic Based:
Symbols play a big role in the human imagination.
Suppose I tell you that, I am writing this article lying on my sofa with my laptop on my lap. I am holding a pen on my right hand and swinging it to think about how to arrange this article well.
I am sure you have made an image of my situation on your mind and if you know me personally you may have pictured me as well. Being able to communicate with symbols is one of the main things that make human intelligent.
The early pioneers of AI believed that
“every aspect of learning or any other feature of intelligence can in principle be so precisely described that a machine can be made to simulate it.”
Trending AI Articles:
3. Real vs Fake Tweet Detection using a BERT Transformer Model in few lines of code
Many of the concepts and tools you find in computer science are the results of these efforts. Symbolic AI programs are based on creating explicit structures and behavior rules.
An example of symbolic AI tools is object-oriented programming. OOP languages allow you to define classes, specify their properties, and organize them in hierarchies. You can create instances of these classes (called objects) and manipulate their properties. Class instances can also perform actions, also known as functions, methods, or procedures. Each method executes a series of rule-based instructions that might read and change the properties of the current and other objects.
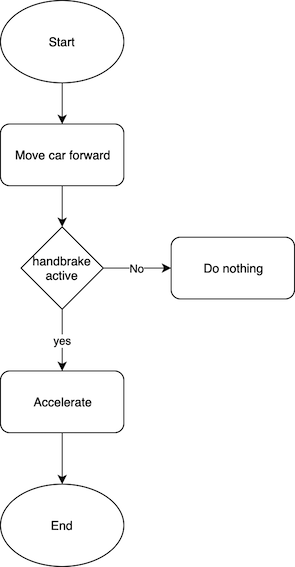
In the early days of AI Computer Vision and robotics were tried to get implied using symbolic AI. As, you can see a flowchart of a robot car designed with symbolic AI. Let,s take an example of Computer Vision. Say you have a picture of your cat and want to create a program that can detect images that contain your cat. You create a rule-based program that takes new images as inputs, compares the pixels to the original cat image, and responds by saying whether your cat is in those images.
So, this was a symbolic approach to solve a computer vision problem. Now with the evolve of Neural Network, Computer Vision is being designed with Neural Network more previously Deep Learing.
One of the main differences between machine learning and traditional symbolic reasoning is where the learning happens. In machine- and deep-learning, the algorithm learns rules as it establishes correlations between inputs and outputs. In symbolic reasoning, the rules are created through human intervention. That is, to build a symbolic reasoning system, first humans must learn the rules by which two phenomena relate, and then hard-code those relationships into a static program.
Researchers realized that it’s really hard to handcraft all the rules and they need algorithms to extract information from data.
2. Data-Based (Machine Learning):
Machine learning is more of a data-driven side of Artificial Intelligence. It’s all about recognizing patterns from a huge amount of data.
Just like how we human practice more we get better at anything, i.e. Playing music, Singing, playing a game, coding etc. machine also gets better when it keeps dealing with various kind of data with different patterns.
Statistical Learning:
In this part, a machine performs on the statistics data or supervised learning. The more we introduce it with various languages, emotion etc. of a human speech, the more fluently it recognizes a new speech.
Now, Human can talk and recognize when someone talks, that is the part of Speech Recognition.
Human can read and write a text, that is part of NLP.
Let’s see a quick example diagram of NLP.

So, we make models with the help of some algorithms and feeding the algorithm data. The more robust our model become the more accurate our machine becomes on recognizing a speech.
Now, there is also Neural Network. Neural network is inspired by Human Brain.
Human Brain is made of zillions of neurons. These neurons capture data, process them, and store relevant information.
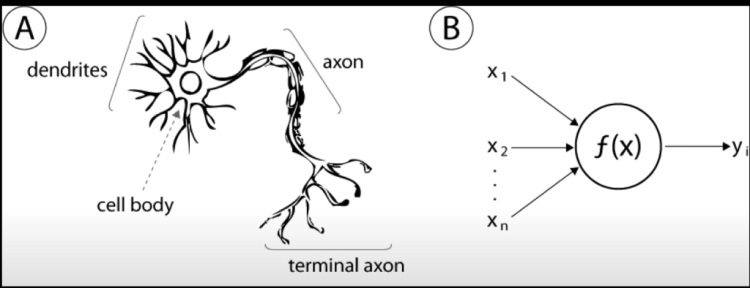

As, we can see from the comparison, a neuron in Neural network also gets data (x1, x2, …, xn) process them through a function and store an output just like a human brain does with its dendrites (inputs), cell body (f(n)) and axon (output).
A combination of several neurons makes a neural network. And when the neural networks are far more complicated and work on different levels it’s called deep learning.

Deep Learning has several sectors like CNN (Convolution Neural Network), RNN (Recurrent Neural Network).
These all depend on recognizing patterns from data. While human can recognize 2/3 dimensions from data for a machine it can be 9–10.
And when it’s come to calculation computers can beat humans. Because intelligence can’t beat calculations.
Example: World Chess grandmaster Garry Kimovich Kasparov least against an IBM program in a classic chess game under tournament rules.
Auto driving car by google uses laser and other sensors to make a 3d model of the road so that it doesn’t make an accident.
Now that we have learned a bit of history and brief knowledge about AI. Let’s have a quick look at why the news that we see about AI and what companies require in their job requirements are misaligned.
Let’s first see how these AI, ML has become a buzz word.
In 1996, engineers used to mine data from databases for knowledge discovery. Data Mining: The practice of examining large databases in order to generate new information.
In 2001 William S. Cleveland took it to another level. He thought that if we can make Computer to do the calculations of data we can make more in less time. So, Data Science = Computing + Data Mining/Statistics.
From, 2003 the websites has changed from static to more dynamic where we can upload data. In 2003 My Space, 2004 facebook, 2005 youtube. It enabled us to contribute to the internet and leave our footprint in digital landscape. That’s called internet.
That was lot of Data and too much to handle by regular technologies.That introduced Big Data. And also gave us important perspectives like getting insights and analytics from data. So, that’s when we started getting better results from the machine and started seeing the result of AI in our day to day life. and thus AI and ML news is everywhere.
But, we often see big companies posts job for Data Analyst, Data Scientist, Machine Learning Engineer, Deep Learning Engineer, etc. What do these actually mean? Before going to the hierarchy of need, let’s see a diagram that describes the steps of Data science.
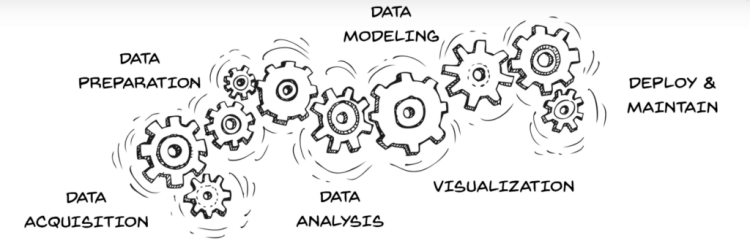
Now these, steps are needed for a complete data analysis and getting meaningful results. So’ now let’s see the steps according to the hierarchy of need.

So as we can, the basic steps that we saw in the diagram for NLP the skeleton are mostly the same. We have to collect data, process the data, and get a better output. But, the intelligence lies here in between.
In big companies, they have a dedicated team for each step who tries to make it better, optimize it, and maximize its performance. In smaller companies, there can be less team and that team is responsible for 2–3 steps of the procedure. In startups, it may be only a person who does all of that on a small scale. So it actually varies what a role can be working on the Data Science field.
I hope this article helped to get an overview or maybe a bird’s eye view of this sector of Computer Science. I would like to hear from you, what do you think about it.
References:
Video:
1. What is Artificial Intelligence? In 5 minutes by Raj Ramesh
2. Understanding Artificial Intelligence and Its Future | Neil Nie | TEDxDeerfield
3. This Canadian Genius Created Modern AI ( Geoffrey Hinton )
4. But what is a Neural Network? | Deep learning, chapter 1
5. What REALLY is Data Science? Told by a Data Scientist by Joma Tech
6. Artificial Intelligence In 5 Minutes | What Is Artificial Intelligence? | AI Explained | Simplilearn
7. CogX 2018 — Symbolic Methods Coming Back
Article:
1. Data Engineer VS Data Scientist
2. The AI Hierarchy of Needs
3. A Beginner’s Guide to Data Engineering — Part I by Robert Chang
4. What is symbolic artificial intelligence?
5. Symbolic Reasoning (Symbolic AI) and Machine Learning
Don’t forget to give us your ? !




A brief introduction to AI was originally published in Becoming Human: Artificial Intelligence Magazine on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
Via https://becominghuman.ai/a-brief-introduction-to-ai-22ca582493f6?source=rss—-5e5bef33608a—4
source https://365datascience.weebly.com/the-best-data-science-blog-2020/a-brief-introduction-to-ai
