
Artificial Intelligence : Renaissance of Technology
Aiding ABC’s of the Industry
All About AI:
According to the Cambridge dictionary, the meaning of AI is, “the study of how to produce machines that have some of the qualities that the human mind has, such as the ability to understand language, recognize pictures, solve problems, and learn”. When a machine is able to make an intelligent decision, it can be referred to as being intelligent, but artificially. We mostly see people using the terms of machine learning, deep learning, and AI synonymously. However, Deep Learning is a subset of Machine Learning, and Machine Learning is a subset of AI.
The Evolution of AI:
The seeds of modern AI were planted by classical philosophers who attempted to describe the process of human thinking as the mechanical manipulation of symbols. In 1836, Cambridge University mathematician Charles Babbage and Augusta Ada Byron, Countess of Lovelace, invented the first design for the programmable machine. In the 1940s, Princeton mathematician John Von Neumann conceived the architecture for the stored-program computer — the idea that a computer’s program and the data it processes can be kept in the computer’s memory. And Warren McCulloch and Walter Pitts laid the foundation for Neural Networks.

The AI surge began with six major design goals as follows:
1. Teach machines to reason in accordance to perform sophisticated mental tasks like playing chess, proving mathematical theorems, and others.
2. Knowledge representation for machines to interact with the real world as humans do — machines needed to be able to identify objects, people, and languages. Programming language Lisp was developed for this very purpose.
3. Teach machines to plan and navigate around the world we live in. With this, machines could autonomously move around by navigating themselves.
4. Enable machines to process natural language so that they can understand language, conversations and the context of speech.
5. Train machines to perceive the way humans do– touch, feel, sight, hearing, and taste.
6. General Intelligence that included emotional intelligence, intuition, and creativity.
All these goals set the foundation to build a machine with human capabilities. Millions of dollars were invested in bringing their vision to life. However, soon, the US government realized the absence of powerful computing technologies needed to implement AI. The funds were withdrawn, and the journey took the first halt in the late 80s.

The field of AI research was founded at a workshop held on the campus of Dartmouth College during the summer of 1956. The modern field of artificial intelligence is widely cited as starting in 1956 during a summer conference at Dartmouth College.
Top 4 Most Popular Ai Articles:
3. Real vs Fake Tweet Detection using a BERT Transformer Model in few lines of code
Sponsored by the Defence Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA), the conference was attended by 10 luminaries in the field, including AI pioneers Marvin Minsky, Oliver Selfridge and John McCarthy, who is credited with coining the term Artificial Intelligence.
In 1973, it became obvious that they had grossly underestimated the difficulty of the project. The US and British government stopped funding for the undirected research and the difficult years of AI started also termed as “AI Winters”.
Seven years later, a visionary initiative by the Japanese Government inspired governments and industry to provide AI with billions of dollars, but by the late 80s the investors became disillusioned and withdrew funding again.
Increases in computational power and an explosion of data sparked an AI renaissance in the late 1990s that has continued to present times.

The need for a massive amount of data and enormous computing power disrupted the progress in the 80s. The 21st century, however, brought the concept quickly back to life proving Moore’s law. The heavy processing power that tiny silicons hold today has made AI feasible in the current context, also enabling to build improved algorithms.
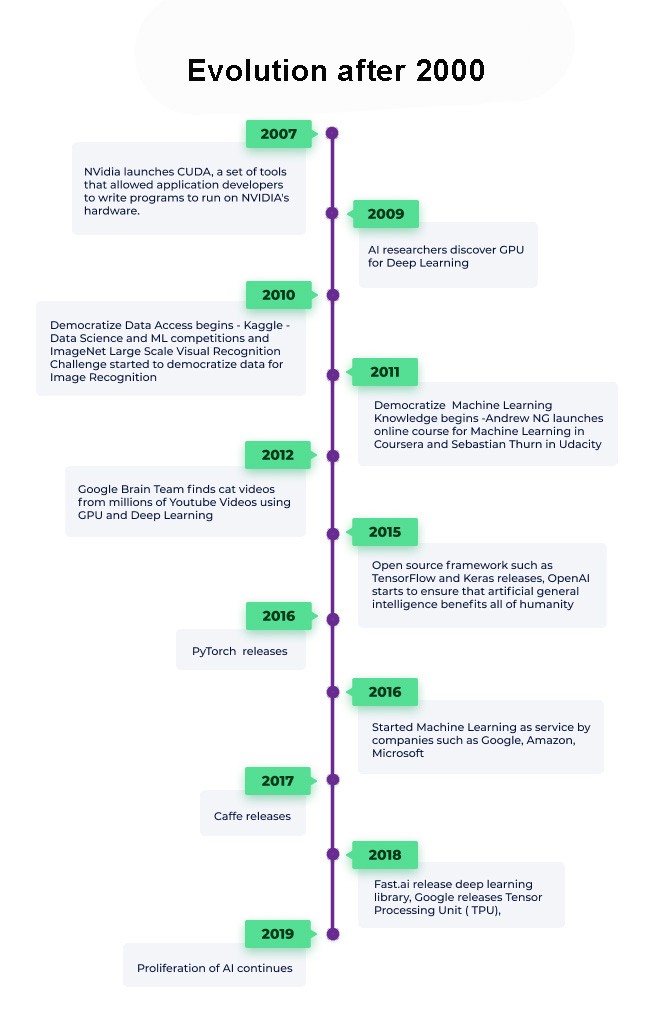
The latest focus on AI has given rise to breakthroughs in Natural Language Processing, Computer Vision, Robotics, Machine Learning, Deep Learning and more. Moreover, AI is becoming ever more tangible, powering cars, diagnosing disease and cementing its role in popular culture.
Branches of AI :
This era is of AI and here are the branches of AI so that we can understand the wide reach of AI.
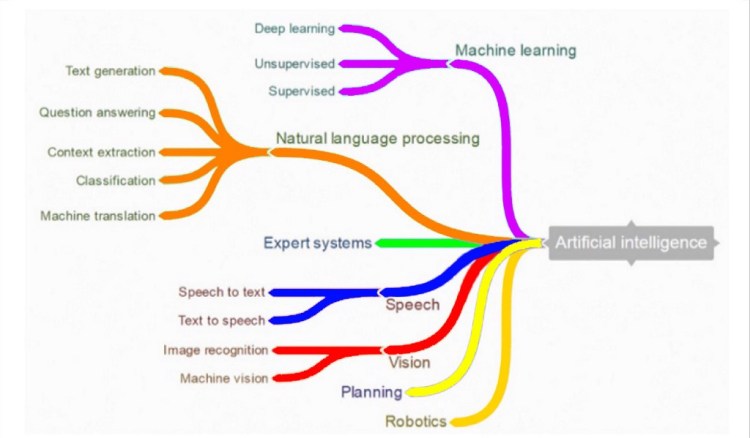
Types of AI:-
Reactive Machines:
The most basic types of AI systems are purely reactive and have the ability neither to form memories nor to use past experiences to inform current decisions. Deep Blue, IBM’s chess-playing supercomputer, which beat international grandmaster Garry Kasparov in the late 1990s, is the perfect example of this type of machine.
This type of intelligence involves the computer perceiving the world directly and acting on what it sees. It doesn’t rely on an internal concept of the world.
Limited memory:
Limited Memory AI, can make informed and improved decisions by studying the past data from its memory. Such an AI has a short-lived or a temporary memory that can be used to store past experiences and hence evaluate future actions. These observations are added to the Self-Driving Cars’ pre-programmed representations of the world, which also include lane markings, traffic lights and other important elements, like curves in the road. They’re included when the car decides when to change lanes, to avoid cutting off another driver or being hit by a nearby car.
Theory of Mind:
We might stop here, and call this point the important divide between the machines we have and the machines we will build in the future. In psychology, this is called “theory of mind” — the understanding that people, creatures and objects in the world can have thoughts and emotions that affect their own behavior. If AI systems are indeed ever to walk among us, they’ll have to be able to understand that each of us has thoughts and feelings and expectations for how we’ll be treated. And they’ll have to adjust their behavior accordingly.
Self-Awareness:
The final step of AI development is to build systems that can form representations about themselves. This is, in a sense, an extension of the “theory of mind”. The next stage of AI, where machines have their own consciousness and become self-aware. This type of AI is a little far-fetched given the present circumstances. However, in the future, achieving a stage of superintelligence might be possible. Geniuses like Elon Musk and Stephen Hawkings have consistently warned us about the evolution of AI specifically in this domain which is machines having self-awareness also termed as ‘Wide AI’.
AI aiding the ABC’s of the industry!!
A — Automotive
B — Bioscience
C — Creative Services
D — Data
E — Education
F — Finance
G — Gaming
H — Healthcare
I — Internet of Things
The above are the industries and domains where AI is widely used and accepted by many. Though many think that one day AI will take jobs of humans and they will overpower the humans but if this technology used widely can lead to a tangent growth of a nation and along with various nations together can do wonders.
Authors:
1. Mangesh Chincholkar
2. Rohan Sarkar
are part of CORE TEAM of HEXABERRY DATA SCIENCE COMMUNITY.
Authors can be reached at:
1. Hexaberry.datasciencecommunity@gmail.com
2. info@hexaberrytechnologies.com
3. https://www.instagram.com/hdsc.official
4. https://www.facebook.com/Hexaberry-Data-Science-Community-HDSC-105656644481089
Sources:
https://www.lftechnology.com/blog/ai/ai-evolution/
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Artificial_intelligence
https://searchenterpriseai.techtarget.com/definition/AI-Artificial-Intelligence
https://theconversation.com/understanding-the-four-types-of-ai-from-reactive-robots-to-self-aware-beings-67616
Don’t forget to give us your ? !




Artificial Intelligence : Renaissance of Technology was originally published in Becoming Human: Artificial Intelligence Magazine on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
