
In this blog, we are going to look at RNN ie. Recurrent Neural Network. I’ll be sharing the theory and then we’ll solve a real-time problem using RNN.
RNN is used for sequential data such as Time series data, Heartbeat data.
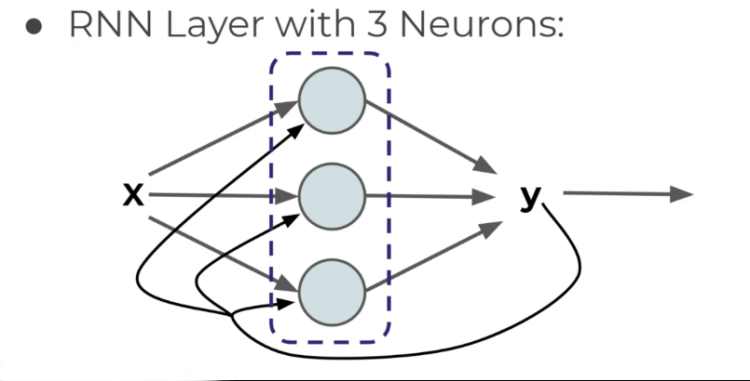
About RNN
If anyone asks you 1,2,3,4,5, ??? You can easily tell the next number. But RNN needs to know the previous history of outputs. One easy way to do this is to simply feed it’s output back into itself as an output.



Cells that are functions of inputs from previous time steps are also known as memory cells. Rnn is also flexible in their inputs and outputs, for both sequences and single vector values.
Vanishing Gradients
For complex data, we need deep layer. The issue can arise during backpropagation. Backpropagation goes backwards from output to the input layer, propagating the error gradient. For deeper networks issues can arise from backpropagation, vanishing and exploding gradients. As you go back to the lower layers gradients often get smaller, eventually causing weights to never change at lower levels. The opposite can also occur, gradients explode on the way back, causing issues.
Now let’s start some hands-on with RNN.
Trending AI Articles:
3. Real vs Fake Tweet Detection using a BERT Transformer Model in few lines of code
About Dataset
Release: Advance Monthly Sales for Retail and Food Services
Units: Millions of Dollars, Not Seasonally Adjusted
Frequency: Monthly
The value for the most recent month is an advance estimate that is based on data from a subsample of firms from the larger Monthly Retail Trade Survey. The advance estimate will be superseded in the following months by revised estimates derived from the larger Monthly Retail Trade Survey. The associated series from the Monthly Retail Trade Survey is available at https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/MRTSSM448USN
Information about the Advance Monthly Retail Sales Survey can be found on the Census website at https://www.census.gov/retail/marts/about_the_surveys.html
Suggested Citation: U.S. Census Bureau, Advance Retail Sales: Clothing and Clothing Accessory Stores [RSCCASN], retrieved from FRED, Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis; https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/RSCCASN, November 16, 2019.
Advance Retail Sales: Clothing and Clothing Accessory Stores
Now let’s jump into coding.
Import all the necessary libraries.
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.sequence import TimeseriesGenerator
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, LSTM
from tensorflow.keras.callbacks import EarlyStopping
Loading the dataset
dataset = pd.read_csv(‘RSCCASN.csv’, index_col=’DATE’, parse_dates=True)
Checking info of the dataset
dataset.info()
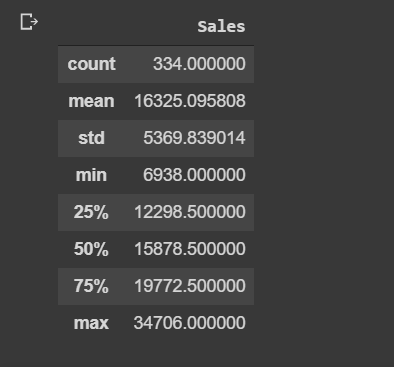
Checking description of the data
Checking first 5 columns of the dataset
dataset.head()

Now let’s split the dataset into training and testing
test_sp=len(dataset)-18
train = dataset.iloc[:test_sp]
test = dataset.iloc[test_sp:]
Apply MinMaxScaler to fit and transform the training and testing data
scaler = MinMaxScaler()
scaler.fit(train)
scaled_train = scaler.transform(train)
scaled_test = scaler.transform(test)

Apply TimeSeriesGenerator to predict the sales beyond the dataset date and time.
length = 12
generator = TimeseriesGenerator(scaled_train,scaled_train,length=length, batch_size=1)
Create LSTM model
model = Sequential()
model.add(LSTM(100, activation=’relu’, input_shape=(length, 1)))
model.add(Dense(1))
model.compile(optimizer=’adam’, loss=’mse’)
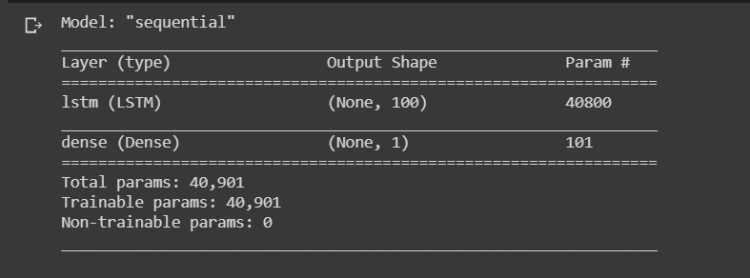
Summary of our model
model.summary()
Apply EarlyStoping to prevent the model from overfitting
early_stop = EarlyStopping(monitor=’val_loss’,patience=2)
validation_generator = TimeseriesGenerator(scaled_test,scaled_test,length=length, batch_size=1)
model.fit_generator(generator,epochs=10,
validation_data=validation_generator,
callbacks=[early_stop])
Now let’s predict the output from our model and tally with the data value
n_features = 1
test_predictions = []
first_eval_batch = scaled_train[-length:]
current_batch = first_eval_batch.reshape((1, length, n_features))
for i in range(len(test)):
# get prediction 1 time stamp ahead ([0] is for grabbing just the number instead of [array])
current_pred = model.predict(current_batch)[0]
# store prediction
test_predictions.append(current_pred)
# update batch to now include prediction and drop first value
current_batch = np.append(current_batch[:,1:,:],[[current_pred]],axis=1)
prediction = scaler.inverse_transform(test_predictions)
test['Predictions'] = prediction
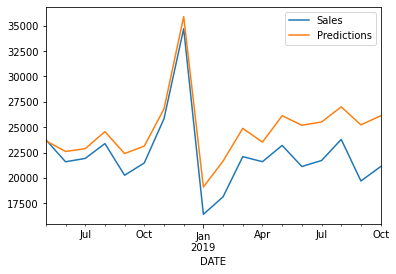
test

In the above screenshot, you can view the predicted value and dataset value together.
For complete source code, you can access my Github repository here.
I hope you like this blog. Feel free to share your thoughts in the comment section and you can also connect with me in:-
Linkedin — https://www.linkedin.com/in/shreyak007/
Github — https://github.com/Shreyakkk
Twitter — https://twitter.com/Shreyakkkk
Happy Learning.
Thank You.
Don’t forget to give us your ? !




A to Z About Recurrent Neural Network (RNN). was originally published in Becoming Human: Artificial Intelligence Magazine on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
