
Reading: PANet — Path Aggregation Network, 1st Place in COCO 2017 Challenge (Instance Segmentation)
1st Place in COCO 2017 Instance Segmentation, 2nd Place in COCO 2017 Object Detection, Outperforms Mask R-CNN, FCIS, G-RMI, & RetinaNet
In this story, Path Aggregation Network (PANet), by The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Peking University, SenseTime Research, and YouTu Lab, Tencent, is presented. In PANet:
- Bottom-up path augmentation is used to shorten the information path between lower layers and topmost feature.
- Adaptive feature pooling is used to link feature grids at all feature levels.
- Fully connected fusion is used to improve the mask prediction.
- Finally, it win the 1st place in COCO 2017 Challenge Instance Segmentation task, and 2nd place in Object Detection task without large-batch training.
This is a paper in 2018 CVPR with over 300 citations. (Sik-Ho Tsang @ Medium)
Outline
- PANet: Network Architecture
- Bottom-Up Path Augmentation
- Adaptive Feature Pooling
- Fully-connected Fusion
- Ablation Study on COCO
- Results on COCO
- Results on Cityscape and MVD
1. PANet: Network Architecture
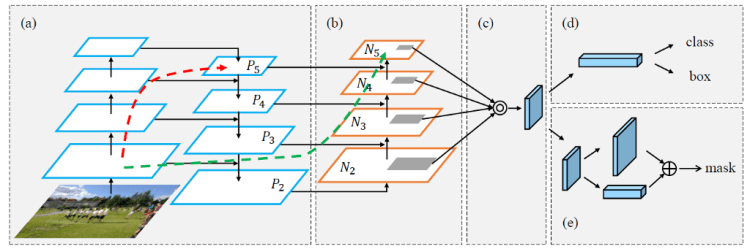
- (a) The FPN backbone.
- (b) First, to shorten information path and enhance feature pyramid with accurate localization signals existing in low-levels, bottom-up path augmentation is created.
- A path is built with clean lateral connections from the low level to top ones. Therefore, there is a “shortcut” (dashed green line in the above figure), which consists of less than 10 layers, across these levels.
- In comparison, the CNN trunk in FPN gives a long path (dashed red line in the above figure) passing through even 100+ layers from low layers to the topmost one.
- (c) Then, Adaptive feature pooling, which is a simple component, is used to aggregate features from all feature levels for each proposal.
- (d) Box Branch.
- (e) To capture different views of each proposal, mask prediction is augmented with tiny fully-connected (fc) layers. By fusing predictions from these two views, information diversity increases and masks with better quality are produced.
Trending AI Articles:
1. Natural Language Generation:
The Commercial State of the Art in 2020
4. Becoming a Data Scientist, Data Analyst, Financial Analyst and Research Analyst
2. Bottom-Up Path Augmentation
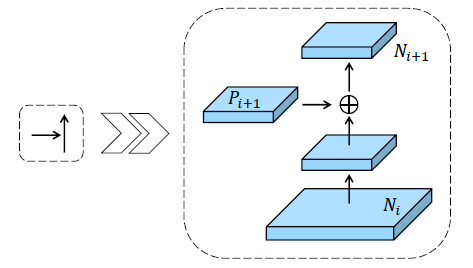
- {N2, N3, N4, N5} denote the newly generated feature maps corresponding to {P2, P3, P4, P5}.
- N2 is simply P2 without any processing.
- Each building block takes a higher resolution feature map Ni and a coarser map Pi+1 through lateral connection and generates the new feature map Ni+1.
- Each feature map Ni first goes through a 3×3 convolutional layer with stride 2 to reduce the spatial size.
- Then each element of feature map Pi+1 and the down-sampled map are added through lateral connection.
- The fused feature map is then processed by another 3×3 convolutional layer to generate Ni+1 for following sub-networks.
3. Adaptive Feature Pooling
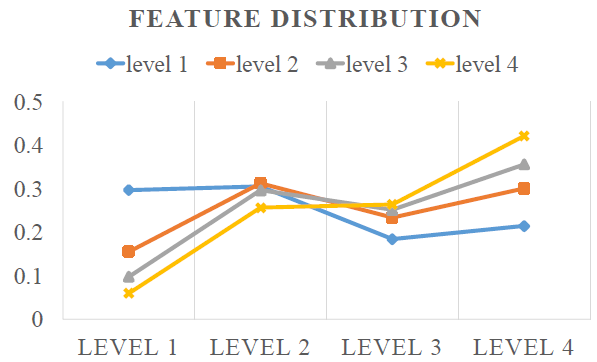
- High-level features are generated with large receptive fields and capture richer context information.
- Low-level features are with many fine details and high localization accuracy.
- Levels 1–4 represent low-to-high levels.
- The blue line represents small proposals that were assigned to level 1 originally in FPN. Surprisingly, nearly 70% of features are from other higher levels.
- The yellow line represents large proposals that were assigned to level 4 in FPN. Again, 50%+ of the features are pooled from other lower levels.
- This observation clearly indicates that features in multiple levels together are helpful for accurate prediction.
- First, for each proposal, we map them to different feature levels, as denoted by dark grey regions in the first figure (b).
- Following Mask R-CNN, ROIAlign is used to pool feature grids from each level. Then a fusion operation (element-wise max or sum) is utilized to fuse feature grids from different levels.
- Below is the adaptive feature pooling for box branch:

4. Fully-connected Fusion
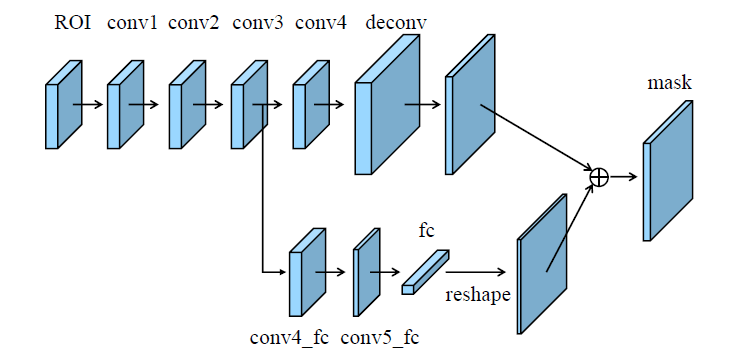
- fc layers yield different properties compared with FCN.
- fc layers are location sensitive since predictions at different spatial locations are achieved by varying sets of parameters. So they have the ability to adapt to different spatial locations.
- At the above figure, the main path is a small FCN, which consists of 4 consecutive convolutional layers and 1 deconvolutional layer. It predicts a binary pixel-wise mask similar as Mask R-CNN.
- A short path is created from layer conv3 to a fc layer. There are two 3×3 convolutional layers where the second shrinks channels to half to reduce computational overhead.
- This fc layer is used to predict a class-agnostic foreground/background mask. The mask size is 28×28 so that the fc layer produces a 784×1×1 vector. This vector is reshaped to the same spatial size as the mask predicted by FCN.
- To obtain the final mask prediction, mask of each class from FCN and foreground/background prediction from fc are added.

5. Ablation Study on COCO
- COCO: 115k images for training and 5k images for validation (new split of 2017). 20k images are used in test-dev and 20k images are used as test-challenge. 80 classes with pixel-wise instance mask annotation.
5.1. Individual Components
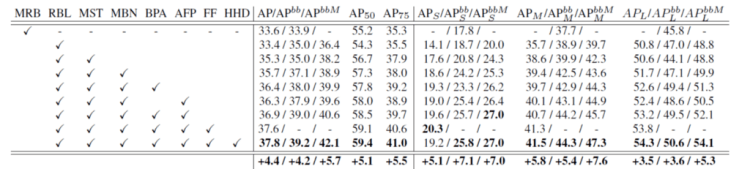
- MRB: Mask R-CNN Baseline in the original paper.
- RBL: Reimplemented Baseline.
- MST: Multi-Scale Training. Using different scales of images with longer edges from 400 to 1400 for training.
- MBN: Multi-GPU synchronized Batch Normalization. BN across multiple GPU. Mean and variance based on all samples in one batch across all GPUs.
- BPA: Bottom-up Path Augmentation. With or without AFP, bottom-up path augmentation consistently improves mask AP and box ap APbb by more than 0.6 and 0.9 respectively.
- AFP: Adaptive Feature Pooling. With or without BPA, adaptive feature pooling consistently improves performance.
- FF: Fully-connected Fusion. It yields 0.7 improvement in terms of mask AP.
- HHD: Heavier HeaD. 4 consecutive 3×3 convolutional layers shared by box classification and box regression, instead of two fc layers.
5.2. Adaptive Feature Pooling
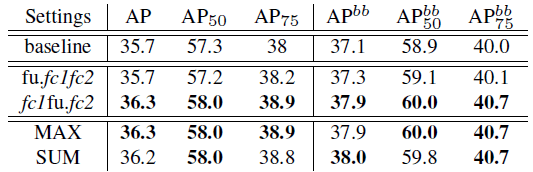
- The place of AFP either between ROIAlign and fc1, represented by “fu.fc1fc2” or between fc1 and fc2, represented by “fc1fu.fc2” are tested. Also, feature fusing, max and sum operations are tested.
- Finally, max is used as fusion operation and it is behind the first parameter layer in the framework.
5.3. Fully-connected Fusion (FF)
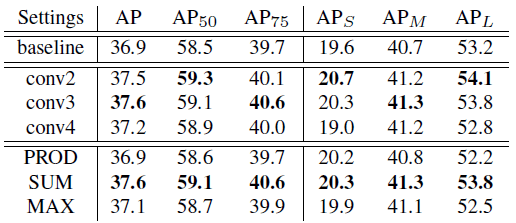
- The layer to start the new branch and the way to fuse predictions from the new branch and FCN.
- The above table clearly shows that staring from conv3 and taking sum for fusion produces the best results.
6. Results on COCO
6.1. Instance Segmentation
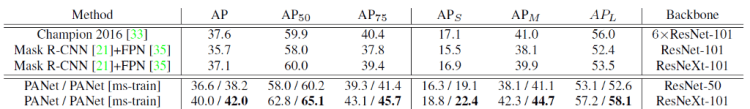
- PANet with ResNet-50 trained on multi-scale images and tested on single-scale images already outperforms Mask R-CNN and Champion in 2016 FCIS, where the latter used larger model ensembles and testing tricks.
- Same as Mask R-CNN, trained and tested with image scale 800, PANet outperforms the single-model state-of-the-art Mask R-CNN with nearly 3 points under the same initial models.
6.2. Object Detection
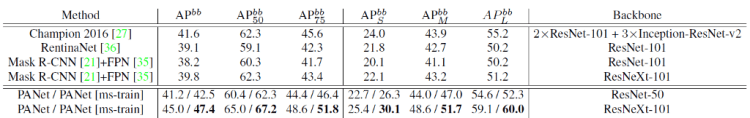
- PANet with ResNet-50, trained and tested on single-scale images, outperforms, by a large margin, all other single-model ones including RetinaNet and Mask R-CNN, even using much larger ResNeXt-101.
- With multi-scale training and single-scale testing, PANet with ResNet-50 outperforms Champion in 2016 G-RMI, which used larger model ensemble and testing tricks.
6.3. COCO 2017 Challenge
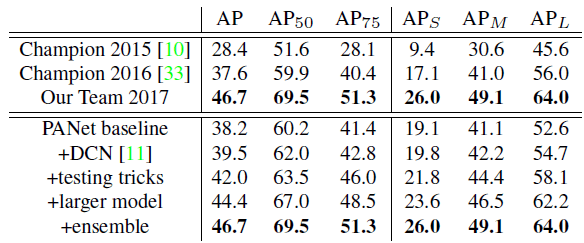
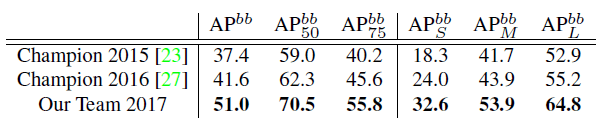
- As shown in above tables, compared with 2016 champions, PANet achieves 9.1% absolute and 24% relative improvement on instance segmentation.
- While for object detection, 9.4% absolute and 23% relative improvement is yielded.
7. Results on Cityscape and MVD
7.1. Results on Cityscape
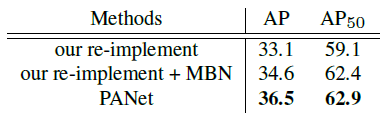
- Based on the re-implemented baseline, multi-GPU synchronized batch normalization is added to help network converge better. It improves the accuracy by 1.5 points.
- With the full PANet, the performance is further boosted by 1.9 points.
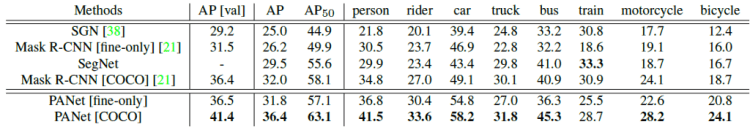
Trained on “fine-only” data, PANet outperforms Mask R-CNN with “fine-only” data by 5.6 points. It is even comparable with Mask R-CNN pre-trained on COCO.
- By pre-training on COCO, PANet outperforms Mask R-CNN with the same setting by 4.4 points.
7.2. Results on MVD
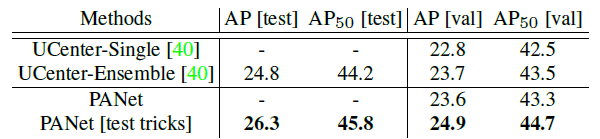
- MVD is a relatively new and large-scale dataset for instance segmentation. It provides 25,000 images on street scenes with fine instance-level annotations for 37 semantic classes.
- Compared with UCenter — winner on this dataset in LSUN 2017 instance segmentation challenge, PANet with one ResNet-50 tested on single-scale images already performs UCenter comparably with the ensemble result with pre-training on COCO.
- With multi-scale and horizontal flip testing, which are also adopted by UCenter, PANet performs even better.
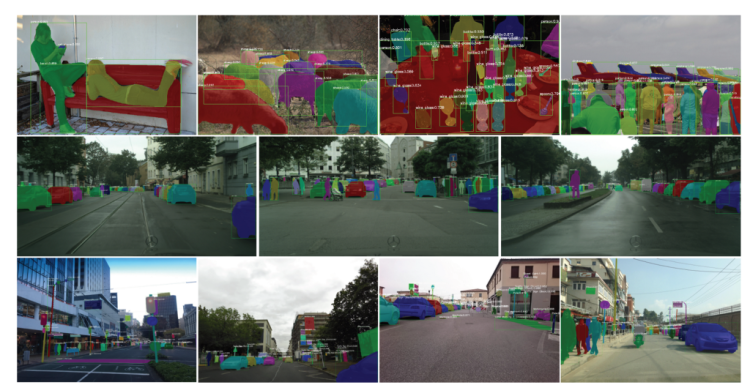
It has been a long time not reading paper about instance segmentation.
This is the 7th story in this month.
Reference
[2018 CVPR] [PANet]
Path Aggregation Network for Instance Segmentation
Instance Segmentation
[SDS] [Hypercolumn] [DeepMask] [SharpMask] [MultiPathNet] [MNC] [InstanceFCN] [FCIS] [Mask R-CNN] [MaskLab] [PANet] [DCNv2]
My Other Previous Readings
Don’t forget to give us your ? !




Reading: PANet — Path Aggregation Network, 1st Place in COCO 2017 Challenge (Instance Segmentation) was originally published in Becoming Human: Artificial Intelligence Magazine on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
