Microsoft Azure Machine Learning x Udacity — Lesson 5 Notes
Detailed Notes for Machine Learning Foundation Course by Microsoft Azure & Udacity, 2020 on Lesson 5 — Applications of Machine Learning
In this lesson, you will learn about the most important applications of ML, including deep learning, similarity learning, text classification, feature learning, and anomaly detection.
Similarity Learning
- Closely related to classification and regression
- Uses a different type of objective function
- Often used in recommendation systems
- Often used in solving verification problems (speech, face, etc)
Similarity Learning as a Classification Problem:
- Maps pairs of entities to a finite number of similarity levels (ranging from 0/1 or any number of levels)
Similarity Learning as a Regression Problem:
- Maps pairs of entities to numerical values
Ranking Similarity Learning:
- A variation from the regression approach where the supervision is weakened from an exact measure to ordering measure. This is a better approach to real-life large-scale problems.

Recommender Systems
A typical application of Similarity Learning. The aim of a recommender system is to recommend one or more items to users of the system, e.g. movies, restaurants, books, songs. A user might be a person, a group of persons, or another entity with item preferences.
Content-base Recommender: makes use of features for both users and items. Users can be described by properties such as age or gender. Items can be described by properties such as the author or the manufacturer. Typical examples of content-based recommendation systems can be found on social matchmaking sites.
- Makes use of features for both users and items
- User properties: age, gender, region, etc
- Item properties: author, manufacturer, etc
Collaborative Filtering Recommender: uses only identifiers of the users and the items. It is based on a matrix of ratings given by the users to the items. The main source of information about a user is the list of the items they’ve rated and the similarity with other users who have rated the same items.
- Uses only identifiers for users and items (not properties)
- Calculates recommender properties, or ratings, from a matrix, Creates a very large matrix of preferences between users and items, and based on those we get information from that particular matrix of ratings.
- Ratings can be either explicit or implicit
Text Classification
The process of translating the text into some kind of numerical representation is commonly referred to as Text Embedding. Text embeddings come into two major forms:
- Word Embedding: transform every single word in our text into a numerical vector that has a number of features or a certain dimension, for example, 100 features, and then use that representation down the line in the model training process. Embedding enables us to gain a deeper understanding of the structure of the text and hence, unlock some of the more complex scenarios. There is also a twist to word embedding, which is called Sentence Embedding, where word embeddings are combined for all the words in the sentence to create a single embedding at the sentence level. Once we have this resulting numerical representation, usually in the form of vectors, then we can basically feed that data into a wide range of classification algorithms.
- Scoring: calculate some kind of score that is related to the importance of that particular word in the text. The scoring approach is a simpler one and enables us to understand the global properties of the text like for example, sentiment. However, it does not allow us to perform the more complex tasks on texts like, for example, machine learning translation.
Training a Classification Model with Text:
We start off with a set of documents, their associated labels, and train a model that would classify every single component with respect to a certain rule based on a description.
The first step is to normalize those documents. For example, identify parts of speech, remove some components, do the lemmatization, etc. There are several tasks of text normalization that you can apply.
The next part is to apply feature extraction. Feature extraction is a two-step process. We define a vocabulary of the texts which is identifying individual words based on their frequencies and recording them as a vocabulary.
Once you have that vocabulary, you can vectorize your documents using various approaches like word embedding or scoring, e.g. TF-IDF.
Finally, a Machine Learning model will be obtained capable of classifying documents.
Predicting a Classification from Text:
Take in the test set and apply the same processes that were previously applied to the training set i.e, text normalization, feature extraction, and embeddings. It is important to use the same vocabulary used for the test set because otherwise, the predictions will be inaccurate.
The test set is then fed into the classification model which produces labels for the new text.
Feature Learning
Feature Engineering is one of the core techniques that can be used to increase the chances of success in solving Machine Learning problems. As a part of feature engineering, Feature Learning (also called Representation Learning) is a technique that can be used to derive new features in your dataset.
Existing features are sometimes not good enough and having the right input features is an important prerequisite for training high-quality ml models. Hence, feature engineering is used to transform sets of inputs into new, more useful inputs to solve a particular problem.
Supervised Approach:
New features are learned using data that has already been labeled.
Examples:
- Datasets that have multiple categorical features with high cardinality
- Image classification
Unsupervised Approach:
Based on learning the new features without having labeled input data. With this approach, labels are actually not needed in the existing data because new features can be learned using the following algorithms and used as inputs for model training.
The typical form of feature leaning is Clustering. A cluster identifier can act as a new feature when assigned to a bunch of rows when splitting the data into different clusters.
Other algorithms:
- Principle Component Analysis
- Independent component Analysis
- Autoencoder
- Matrix Factorization
Applications of Feature Learning
Image Classification with Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs):
One of the applications of feature learning is Image Classification where Deep Learning models with their hidden layers are capable of automatically learning features from images.
A convolutional neural network is a special case of a deep learning neural network that has a combination of hidden layers that have some very specific abilities in learning hidden features. A typical convolutional neural network will consist of a stack of two types of hidden layers. One is the convolution layer, the other one is the max-pooling layer. Finally, the output uses a densely connected layer to produce the final classification.
You can use the convolutional layers to:
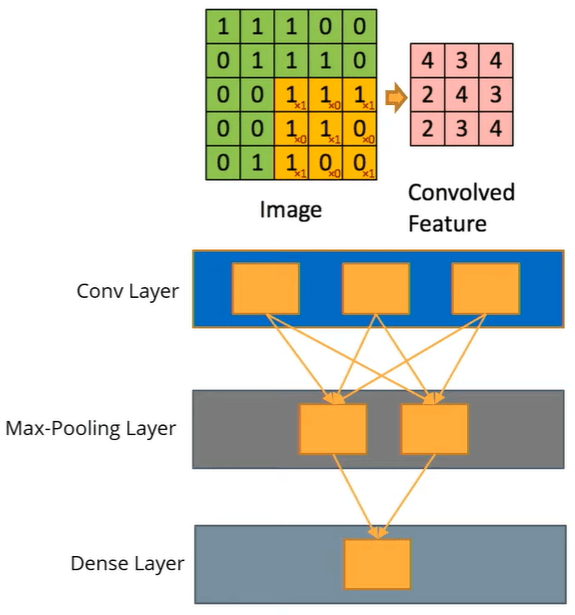
- Learn local patterns: they are translation invariant i.e, once the model learns to recognize a certain type of local pattern somewhere in the image, it can also recognize it somewhere else in the image. That makes the approach so powerful.
- Down-sample and make Translation-Invariant: the Max-Pooling layer is applied to down-sample the data using a special kernel and results in a representation that is translation invariant. The max-pooling layer is the one that enables such a classification approach to recognize a human face, even if the picture is taken from different angles.
- Densely connect all outputs to learn classification: multiple stacks of convolutional and max-pooling layers applied with a very large number of nodes in those hidden layers are all connected together to form a classification model.
Trending AI Articles:
1. Machine Learning Concepts Every Data Scientist Should Know
3. AI Fail: To Popularize and Scale Chatbots, We Need Better Data
Image Search with Autoencoders:
Another application of feature learning is an Image Search where the same approach is used as CNNs but to search for images.
An autoencoder is a very special type of neural network that is used for unsupervised learning. The most important feature of the autoencoder is that it is trained to reproduce its own inputs as accurately as possible.
It typically starts with a very large number of inputs. Each layer becomes progressively narrower than the previous one until the minimum layer width is reached. Afterward, layers start to have increasingly larger widths until the last one, which must have the same number of outputs as there are inputs in the first layer.
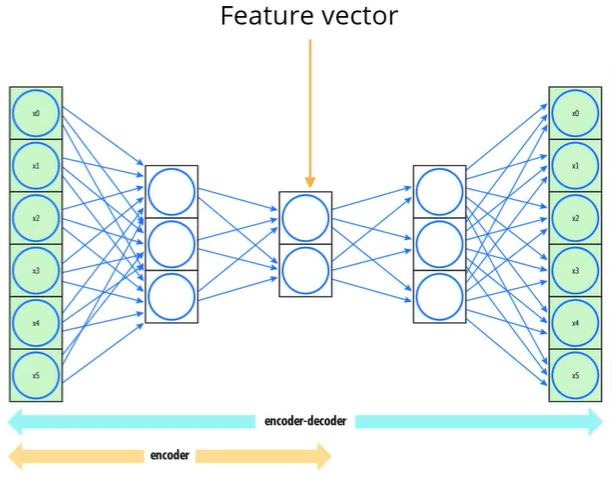
The middle layer has the smallest width and is of particular importance for two reasons:
- It marks the border between the two internal components of the autoencoder — the Encoder: left of that particular layer, and the Decoder: the right of that particular layer.
- This layer produces a Feature Vector i.e, a compressed representation of the input (compression as in dimensionally reduced as opposed to reduced in size).
Autoencoders translate those images into n-dimensional vectors, where n is the width of the middle layer. Then, these vectors can be compared with each other using some distance metric like the well-known Euclidean distance.
Once the autoencoder is trained, the encoder can be used to embed inputs into feature vectors. Finally, apply a distance measure to identify similar input images. If that distance is below a certain threshold, there is a high probability that the new image contains the encoded image(s).
Anomaly Detection
Anomaly detection is a machine learning technique concerned with finding data points that deviate significantly from the norm. These anomalies can be of interest, since they may be the result of bad data, unusual behavior, or important exceptions to the typical trends. Usually, the number of abnormalities is much smaller than normal entities.
Supervised Approach:
Binary classification problem where entities must be classified as either normal or anomaly. These classes are highly imbalanced and are based on using a training dataset that has already been labeled as normal/anomaly.
Unsupervised Approach:
A problem of identifying two major groups (clusters) of entities — the normal ones and the abnormal ones (anomalies).
Based on using a training dataset which has no normal/anomaly labels available. The task of the algorithm is to create a model which would be able to define anomalies and then classify the data between anomalies and normal entities.
Applications of Anomaly Detection:
- Condition monitoring (industrial maintenance) and failure prevention
- Fraud detection (banking, telecommunications, etc)
- Intrusion detection (networking)
- Anti-virus and anti-malware protection
- Data preparation (outlier identification)
Forecasting
Forecasting is a special case of Machine Learning problems in which given a set of ordered data points predict the next data points in the series.
Forecasting is a class of problems that deals with predictions in the context of orderable datasets. These orderable datasets can be time-series datasets, but they don’t have to be — forecasting can be applied to other types of orderable sets as well.
Types of Forecasting Algorithms:
- ARIMA — AutoRegressive Integrated Moving Average: initially designed provide some description for a random time-based processing i.e. time-series.
- Multivariate Regression: the problem of forecasting can also be modeled as a regression problem, where the task is to predict a numerical value for the very next iteration of your time series. With the multivariate regression approach, the algorithm can also take into account other properties of the entities that occur in the time series to improve the predictive accuracy of your model.
- Prophet: a time series based algorithm that was specifically designed to be capable of taking into account the strong seasonal effects.
- ForecastTCN — Temporal Convolutional Network: a very special, one-dimensional convolutional network. It is one-dimensional because this approach is based on time-series. According to the latest scientific research, ForecastTCN is capable of exhibiting a longer memory than other similar approaches.
- Recurrent Neural Network: The recurrent architecture is basically referring to a class of networks that have additional connections between the nodes. The spectacular property of RNNs is that they can effectively learn time-based patterns and have revolutionized areas like speech recognition, text-to-speech synthesis, and machine translation. Types of RNNs are Long-Short Term Memory (LSTMs), Gated Recurrent Unit (GRUs), etc.
Lesson Summary
In this lesson, you’ve learned the fundamentals of deep learning, including:
- The differences between classical machine learning and deep learning
- The benefits and applications of Deep Learning
- How to train your first neural network model
Next, you learned about some of the most important specialized cases of model training, including:
- Similarity learning and the basic features of a recommendation engine
- Text classification and the fundamentals of processing text in machine learning
- Feature learning, an essential task in feature engineering
- Anomaly detection
- Time-series forecasting
Don’t forget to give us your ? !




Microsoft Azure Machine Learning x Udacity — Lesson 5 Notes was originally published in Becoming Human: Artificial Intelligence Magazine on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
