Deep Learning
An Overview
What is Deep Learning?
Deep learning is a subset of machine learning, which in turn is a subset of Artificial intelligence.
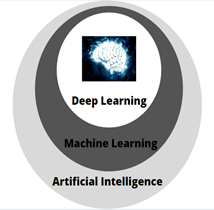
Artificial intelligence involves traditional methods to learn from data, whereas machine learning involves teaching the computer to recognize pattern from the data. Deep learning is a machine learning technique that learns features directly from the data by using an architecture called “neural networks”.
Why deep learning?
No matter how complex the traditional machine learning algorithm gets, it will still be machine-like and can perform only designated tasks. They are very domain specific. Hence, to overcome these disadvantages we go for more advanced branch of machine learning which is deep learning. Moreover, Deep learning provides us with the advantage of learning by itself from raw data!

Many of the deep learning algorithms already existed for many years, but it is now, that they are gaining popularity. In general, three technical forces are driving advances in machine learning: advance hardware and great computational power, abundance of data and availability of open source software like TensorFlow and PyTorch etc.
Neural Networks
Neural Networks form the base of deep learning and the fundamental building block of the neural network is a neuron. The neural networks take data as their input, train themselves using the data and present useful predictions as their outputs.
Any neural network is made up of three essential components — Input layer, Several hidden layers and an output layer.
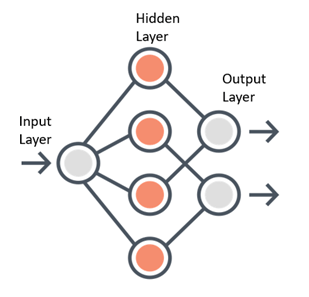
Learning of a Neural Network
Learning process of a Neural Network includes two parts — Forward propagation and Back propagation.
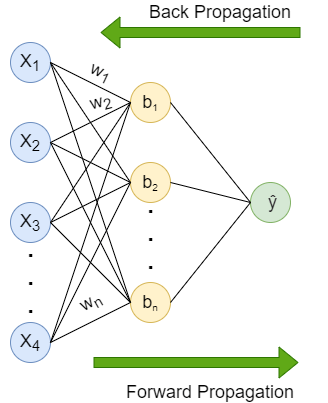
Forward propagation is the flow of information from the input layer to the output layer. Input layer consists of several neurons which are connected to the next layer through channels, which are assigned numerical values know as weights(wᵢ) (At the beginning of the process the weights are randomly assigned and later updated). The data fed into the input layer(xᵢ) is multiplied by these weights and then fed into the next layer. All the neurons in the hidden layer are associated with a value know was bias(bᵢ) which is then added to the input sum. This weighted sum is then passed through the non- linear function called the activation function(σ). This function decides whether a particular neuron can contribute to the next layer. Finally the output layer gives the probability, the neuron with the highest probability is final output(ŷ). This process is represented in mathematical form as:
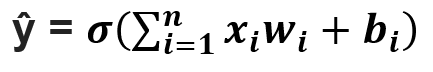
(Don’t be afraid of the big equation, it is just the mathematical representation of the above explanation, read the explanation along with the equation again and you are good to go!)
Trending AI Articles:
1. Machine Learning Concepts Every Data Scientist Should Know
3. AI Fail: To Popularize and Scale Chatbots, We Need Better Data
Back propagation is same as the forward propagation but in reverse direction. The information is passed from the output layer to the input layer. After the last layer gives a prediction, it is evaluated by a loss function. The loss function helps quantify the deviation from the expected output, meaning it gives a value that depicts the difference between the predicted output and the actual output. This information is sent back to the hidden layer to adjust the weights and bias to get a more accurate prediction. The weights and bias are updated using the gradient descent algorithm(optimizer).
Note: Weights and Biases are known as the Model parameters whereas the learning rate is known as the Model Hyperparameter.
Important Terminologies
Let’s see some important terms quickly:
- Weights: Basically it tells us how important a channel(link between the two neurons) is. The higher the value the more important it is.
- Bias: It allows to shift the activation function to the right or left (as adding a scalar value to a function shifts the graph to the right or left)
- Activation function: Introduces non- linearity in the network and also decides whether a neuron can contribute to the next layer. Step function, Linear function, Sigmoid function etc. are some examples of the activation function.
- Loss function: Loss function are the mathematical ways of measuring how wrong the predictions made by the neural network are. Depending on the project you are working on you can use different loss functions like squared error, binary cross entropy, multi- class cross- entropy etc.
- Optimizer: Update the weights and bias in response to the output of the loss function. The loss function acts like a guide to the optimizer which tells whether it moves in the right or wrong direction. The goal of the optimizer is to minimize the loss function. The most popular optimizer is gradient descent.
- Learning rate: Learning rate ensures that changes made to the weights are at the right pace. Taking too large steps or too small steps can mean that the algorithm will never find optimum values for the weights.
- Epochs: One epoch is when the entire dataset is passed forward and backward through the neural network only once. Generally, we use more than one epoch. Passing the dataset multiple times to the network helps the model to generalize better. But too many epochs may cause the problem of overfitting(model makes prediction specific to the dataset rather than making more general predictions).
- Batches, Batch sizes: Datasets includes millions of examples, passing the entire dataset at once becomes extremely difficult. Hence, we divide the dataset in smaller chunks or batches and then feed it to the neural network. Number of examples in one batch is the batch size.
- Iterations: Size of the dataset divided by batch size gives us the number of iterations. E.g. If you have a dataset of 39,000 training examples and you divide the dataset into batches of 600, then you will have 39,000/600 = 65 iterations to complete one epoch.
Note: There is no right combination of number of hidden layers, activation function, number of epochs etc. which will give maximum accuracy to your model. You will have to experiment and find out what suits best for your project!
Regularization
One of the main goal of deep learning is to build a model that will perform well not only on training data but also on new inputs. Overfitting is a situation when the model performs exceptionally well on the training data but not on testing data. It probably learns “too much” from the training data. Regularization is a technique to avoid overfitting. Some regularization technique are — Dropout, Augmentation, Early Stopping.
Dropout: Let’s say we have a neural network with two hidden layers. During each iteration, dropout randomly selects some nodes and removes them along with their connections as shown in the diagram(red nodes are dropped).
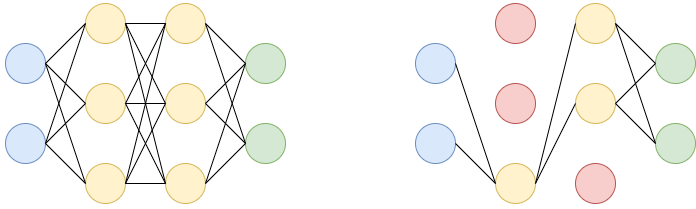
So each iteration has different sets of nodes which result in different sets of output which help in better generalizing the model as it captures more random features.
Augmentation: Another cause of overfitting is having too few examples to learn from. Augmentation refers to creating more training data from existing data by applying various transformations. This helps the model to expose to more aspects of the data and generalize better.
Early Stopping: When training over sufficient data, we often observe that the training error decreases with time but the error begins to rise again. Thus we can obtain a better model if we stop training when an increase in error is observed, this is known as early stopping.
Neural Network Architecture
The three most common type of neural networks are:
Fully connected feed forward neural network
Fully connected indicates that each neuron in preceding layer is connected to every other neuron in the following layer, in only forward direction(no backward connections or loops).
Recurrent Neural Network(RNN)
Fully connected or plain neural networks cannot handle sequential data. Processing of sequential data, may require information from the earlier stage of processing and plain neural networks don’t share parameters across time. RNN has the ability to look for a given feature everywhere in the sequence, rather than in just a certain area. RNN uses feedback loop in the hidden layer.
Convolutional Neural Network(CNN)
CNN is a deep neural network architecture which is used specifically for tasks like image classification, processing audios, videos etc. Hidden layers of CNN include convolutional layer, pooling layer, fully connected layer, normalization layer instead of traditional activation functions.
Create a deep learning model
There are five fundamental steps involved in every deep learning project. They can be extended to many other steps, but at the very core there are five.
- Gathering data
- Preprocessing the data
- Training the model
- Evaluation
- Optimization
Don’t forget to give us your ? !




Deep Learning- An Overview was originally published in Becoming Human: Artificial Intelligence Magazine on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
Via https://becominghuman.ai/deep-learning-an-overview-5f40feb15d1e?source=rss—-5e5bef33608a—4
source https://365datascience.weebly.com/the-best-data-science-blog-2020/deep-learning-an-overview
