
I took this problem statement from Kaggle competition. Here we have two datasets.
- True.csv
- Fake.csv
So let’s work with these datasets in collab. You can access my repository mentioned bottom of this blog.
Let’s jump directly in coding.
Primary Steps
- Import all the necessary libraries.
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import nltk,re,string,unicodedata
from nltk import pos_tag
from nltk.corpus import wordnet,stopwords
from nltk.stem.porter import PorterStemmer
from wordcloud import WordCloud,STOPWORDS
from nltk.stem import WordNetLemmatizer
from nltk.tokenize import word_tokenize,sent_tokenize
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import keras
import tensorflow as tf
from keras.preprocessing import text, sequence
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report,confusion_matrix,accuracy_score
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelBinarizer
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from string import punctuation
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import Dense,Embedding,LSTM,Dropout
from keras.callbacks import ReduceLROnPlateau
2. Load both the datasets.
true_dataset = pd.read_csv(“True.csv”)
false_dataset = pd.read_csv(“Fake.csv”)
3. Check and analyse both the datasets.
4. Creating a new column with name “category”, and assigning “0″ for false news whereas “1” for true news.
true_dataset[‘category’] = 1
false_dataset[‘category’] = 0

5. Now we need to merge both the datasets together.
dataset = pd.concat([true_dataset,false_dataset])
6. Let’s analyse the final dataset.
Data Preprocessing
In the final dataset, we don’t need few columns like “title”, “subject”, “date”. So we are going to remove them.
dataset[‘text’] = dataset[‘text’] + “ “ + dataset[‘title’]
del dataset[‘title’]
del dataset[‘subject’]
del dataset[‘date’]
Now we need to download stopwords from NLTK.
nltk.download(‘stopwords’)
stop = set(stopwords.words(‘english’))
punctuation = list(string.punctuation)
stop.update(punctuation)
Here we are going to create our own functions for doing preprocessing of our data.
def strip_html(text):
soup = BeautifulSoup(text, “html.parser”)
return soup.get_text()
#Removing the square brackets
def remove_between_square_brackets(text):
return re.sub(‘\[[^]]*\]’, ‘’, text)
# Removing URL’s
def remove_between_square_brackets(text):
return re.sub(r’http\S+’, ‘’, text)
#Removing the stopwords from text
def remove_stopwords(text):
final_text = []
for i in text.split():
if i.strip().lower() not in stop:
final_text.append(i.strip())
return “ “.join(final_text)
#Removing the noisy text
def denoise_text(text):
text = strip_html(text)
text = remove_between_square_brackets(text)
text = remove_stopwords(text)
return text
#Apply function on review column
dataset[‘text’]=dataset[‘text’].apply(denoise_text)
Trending AI Articles:
1. Fundamentals of AI, ML and Deep Learning for Product Managers
3. Graph Neural Network for 3D Object Detection in a Point Cloud
4. Know the biggest Notable difference between AI vs. Machine Learning
Data Visualization
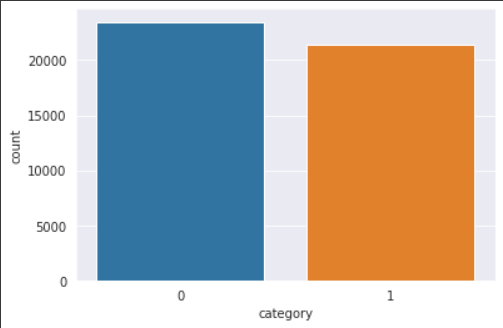
- Count Plot
sns.set_style(“darkgrid”)
sns.countplot(dataset.category)
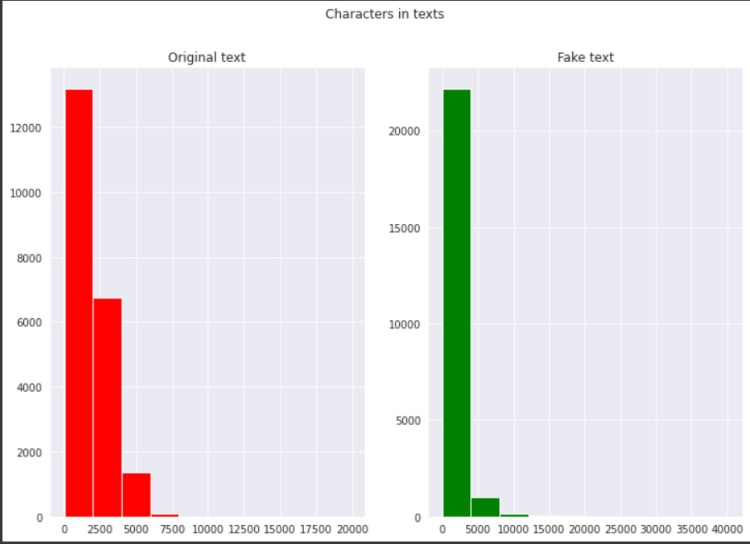
2. Sub Plot
fig,(ax1,ax2)=plt.subplots(1,2,figsize=(12,8))
text_len=dataset[dataset[‘category’]==1][‘text’].str.len()
ax1.hist(text_len,color=’red’)
ax1.set_title(‘Original text’)
text_len=dataset[dataset[‘category’]==0][‘text’].str.len()
ax2.hist(text_len,color=’green’)
ax2.set_title(‘Fake text’)
fig.suptitle(‘Characters in texts’)
plt.show()
fig,(ax1,ax2)=plt.subplots(1,2,figsize=(12,8))
text_len=dataset[dataset[‘category’]==1][‘text’].str.split().map(lambda x: len(x))
ax1.hist(text_len,color=’red’)
ax1.set_title(‘Original text’)
text_len=dataset[dataset[‘category’]==0][‘text’].str.split().map(lambda x: len(x))
ax2.hist(text_len,color=’green’)
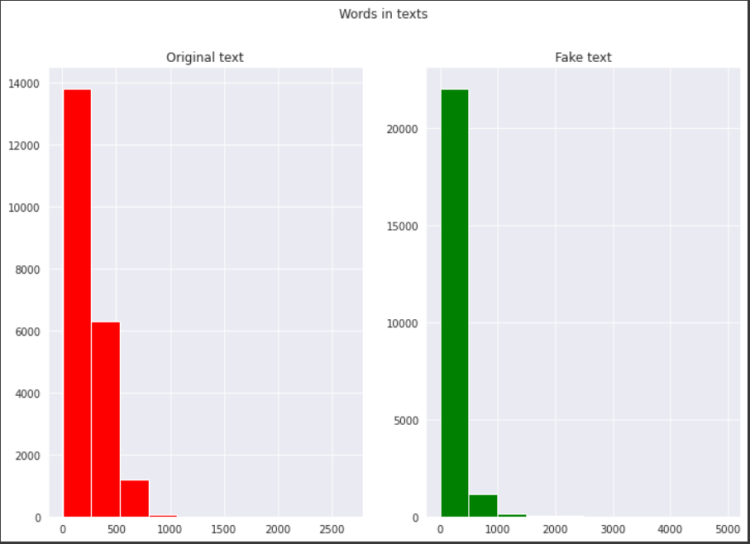
ax2.set_title(‘Fake text’)
fig.suptitle(‘Words in texts’)
plt.show()
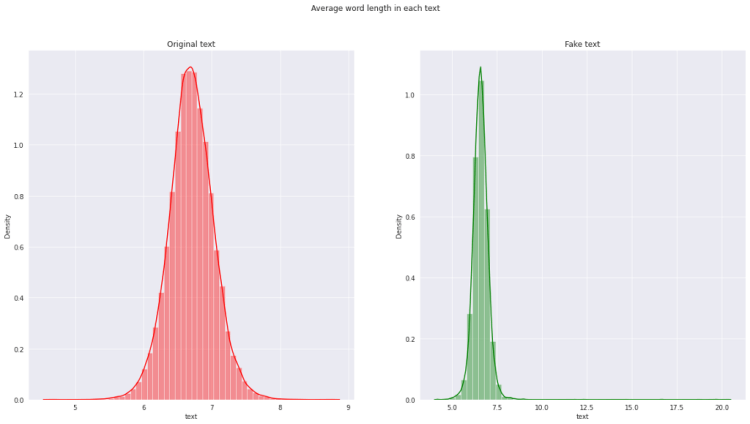
fig,(ax1,ax2)=plt.subplots(1,2,figsize=(20,10))
word=dataset[dataset[‘category’]==1][‘text’].str.split().apply(lambda x : [len(i) for i in x])
sns.distplot(word.map(lambda x: np.mean(x)),ax=ax1,color=’red’)
ax1.set_title(‘Original text’)
word=dataset[dataset[‘category’]==0][‘text’].str.split().apply(lambda x : [len(i) for i in x])
sns.distplot(word.map(lambda x: np.mean(x)),ax=ax2,color=’green’)
ax2.set_title(‘Fake text’)
fig.suptitle(‘Average word length in each text’)
Now we’ll split our dataset into training and testing.
x_train,x_test,y_train,y_test = train_test_split(dataset.text,dataset.category,random_state = 0)
Creating Model
Tokenizing
max_features = 10000
maxlen = 300
tokenizer = text.Tokenizer(num_words=max_features)
tokenizer.fit_on_texts(x_train)
tokenized_train = tokenizer.texts_to_sequences(x_train)
x_train = sequence.pad_sequences(tokenized_train, maxlen=maxlen)
tokenized_test = tokenizer.texts_to_sequences(x_test)
X_test = sequence.pad_sequences(tokenized_test, maxlen=maxlen)
Embedding
EMBEDDING_FILE = ‘glove.twitter.27B.100d.txt’
Model
#LSTM
model = Sequential()
model.add(Embedding(max_features, output_dim=embed_size, weights=[embedding_matrix], input_length=maxlen, trainable=False))
model.add(LSTM(units=128 , return_sequences = True , recurrent_dropout = 0.25 , dropout = 0.25))
model.add(LSTM(units=64 , recurrent_dropout = 0.1 , dropout = 0.1))
model.add(Dense(units = 32 , activation = ‘relu’))
model.add(Dense(1, activation=’sigmoid’))
model.compile(optimizer=keras.optimizers.Adam(lr = 0.01), loss=’binary_crossentropy’, metrics=[‘accuracy’])
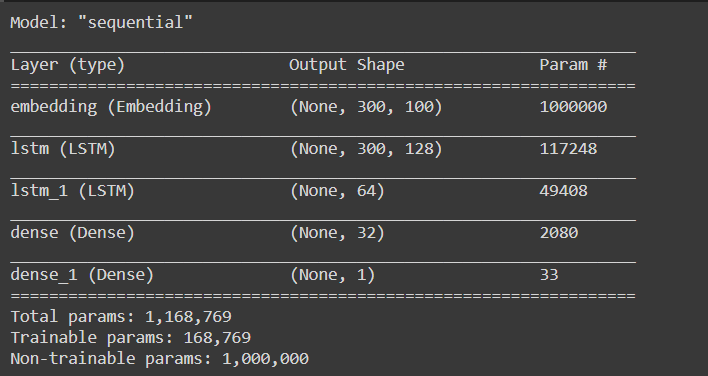
Summary of our model
model.summary()
Fitting the model
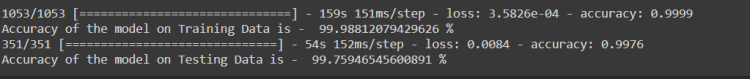
history = model.fit(x_train, y_train, batch_size = batch_size , validation_data = (X_test,y_test) , epochs = epochs , callbacks = [learning_rate_reduction])
Accuracy of the model
You can clone my repository from here. And can also work with this dataset and can come with another approach.
Don’t forget to give us your ? !




Machine Learning Model for Detecting Fake News. was originally published in Becoming Human: Artificial Intelligence Magazine on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
