You’ve built your chatbot, you’ve carefully and tirelessly trained and tested it, and you’re finally ready to launch it to go live — hoorah! But after monitoring its performance over a period of time after go-live, you notice that some user questions return incorrect intents (so give the wrong answers), despite the fact there’s training data in your model that should result in the correct intent being returned. You also spot that some user questions return the correct intent with very low confidence — so the answer isn’t presented to the user. This leaves everyone very frustrated.

As a chatbot builder, you want to understand what influence each utterance has (and even what influence each word in each utterance has) on your model’s performance. Most of the popular NLP providers use a variety of different models and algorithms that are virtually impossible for chatbot builders to fathom. And it’s also very difficult and time-consuming to do a deep dive of your training data and analyse its learning value. But you really do need to do a thorough analysis if you want to improve the performance of your bot.
Here are three techniques: two to measure your bot’s performance and one for visualising the results of its performance.

1. Cross-validation testing
This involves preparing a separate labelled dataset of utterances that your model hasn’t been trained on (this data would typically be real user questions), and then testing it agains your chatbot to assess your model performance and see if there are any gaps in your bot’s knowledge. Cross-validation testing has its advantages and disadvantages though:
Advantage:
- If you have a large file from many user interactions over many months, you are likely to have a great dataset that represents all the intents/subject areas you wish to cover.
Disadvantages:
- If you are at the early stage of your chatbot model, you may still be in the process of creating new intents, and splitting or merging some existing intents. Each time this happens, you’ll have to update your cross-validation file, and this can be time-consuming.
- Keeping this dataset out of the training data can be a challenge. Naturally, if you know the data set, you’ll check the test results and where your test fails, you may be tempted to train your model with the potential to overfit it to the cross-validation dataset
- It will only be as good as the data in it.
- Ideally, cross-validation testing will give meaningful and accurate results, but there’s no way of accurately predicting what your bot will encounter in the future, and you will constantly have to update your cross-validation dataset. You’ll also have to keep testing on your cross-validation dataset to monitor for any regression.
Trending AI Articles:
2. K-fold cross-validation testing
K-fold cross-validation testing solves some of the issues mentioned above. It’ll generate test data from your training data automatically, by removing some of the training data from where it is (the intent) and using them as test data. It’ll then evaluate your training data by dividing it into a number of sub-samples (or folds) and then using one fold at a time as a testing dataset to test on the rest of the training data. For example, you might divide your training data into 10 equal folds (you could use more or fewer folds, but 10 folds is commonly used), and then perform 10 separate tests, each time holding back one of the folds and testing your model based on the data in the “held back” fold not in your training data. This means that all training data will become test data at one point. This technique helps you to see weaknesses in your data. Again, it has its advantages and disadvantages
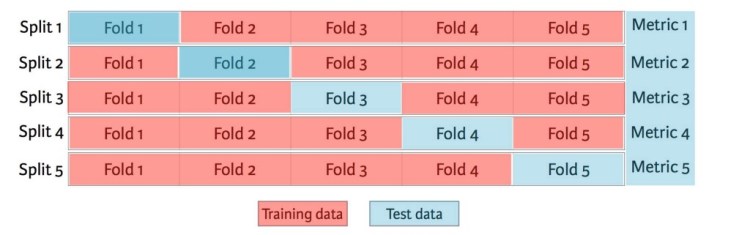
Advantages:
- If you don’t have test data, and you are in the early stage of model building, it generates the test data itself.
- K-fold is a known technique.
Disadvantages:
- It’s time-consuming
- K-fold doesn’t work well with low levels of training data (fewer than 200 samples per class or intent)
- Each change to the training data affects the fold the initial training data was in, generating variation in your test results due to the randomisation of the folding. This then makes it difficult to understand the learning value of your new changes.
Here are some Jupiter Notebooks that show examples in Python code for doing cross-validation and K-fold.
3. Visualising your test results through a confusion matrix
This technique allows you to visualize the performance of the intent predictions in the form of a table. To build a confusion matrix, you’d use a test validation dataset. Each piece of data in your dataset needs a predicted outcome (the intent that the data should return) and an actual outcome (the intent that the data actually returns in your model). From the predicted and actual outcomes, you will get a count of the number of correct and incorrect predictions.
These numbers are then organised into a table, or matrix where
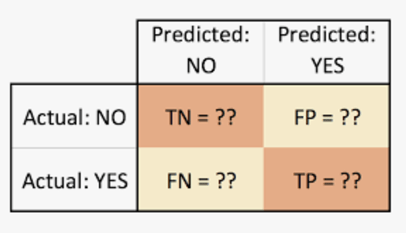
- True positive (TP) for correctly predicted event values
- False positive (FP) for incorrectly predicted event values
- True negative (TN) for correctly predicted no-event values
- False negative (FN) for incorrectly predicted no-event values
IMPORTANT: You’ll want to think how you categorise the right and wrong predictions that are below your chatbot confidence threshold.
These values can then be used to calculate more classification metrics like precision and recall, and F1 scores. Precision highlights any false-positive problems you may have in your model and recall highlights any false-negative problems. The F1 score is an overall measure of a model’s accuracy. The confusion matrix technique has its own advantages and disadvantages.
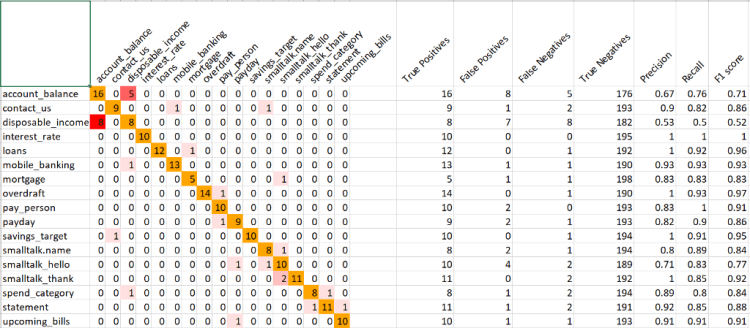
Advantages:
- It provides a good visual of your bot’s performance (see diagram above as an example)
Disadvantages:
- It is a very time-consuming task
- Calculations for these additional metrics are quite complex
- It can be quite challenging to interpret unless you’re familiar with the statistics involved
- It won’t necessarily help you see why an utterance isn’t working
Here’s a link to some further information on the confusion matrix approach
In summary, the cross-validation, K-fold and confusion matrix methods for diagnosing and improving a chatbot are very time-consuming, and difficult to understand if you’re not a statistician. Also, you’re likely to find a lot of issues that need fixing, and you’ll probably want to fix them all at once — but this in turn will generate challenges as you try to understand which changes worked/helped your model and which didn’t. You also need to think about the possible further regression (the ripple effect of changing data in one part of the model modifying the performance of the rest of the model) of your chatbot, and it’s very difficult to identify and unpick these newly created problems.
Modern tools are arriving on the market
Some companies choose to rely on the help of a tool such as QBox. QBox is another way of testing your chatbot to help improve your its accuracy and performance — in a matter of minutes. It analyses and benchmarks your chatbot training data and gives insight by visualising and understanding where your chatbot does and doesn’t perform, and why. You can see your chatbot’s performance at model level, intent level and utterance level, even word-by-word analysis, in clear and easy-to-understand visuals.
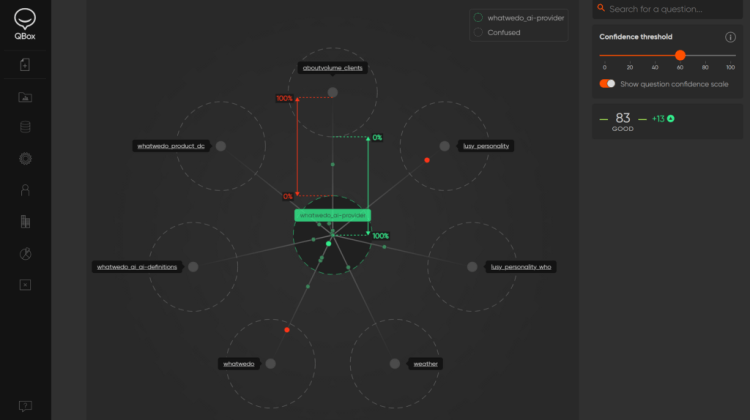
For example, we built a very simple banking bot based on common customer-banking questions. But I noticed that some user questions requesting a contact telephone number didn’t always return the correct intent with good confidence — despite having training data to that effect. I was able to diagnose the problem quickly by doing a deep dive into the actual training data and getting word-by-word analysis, using the visuals that QBox provides:
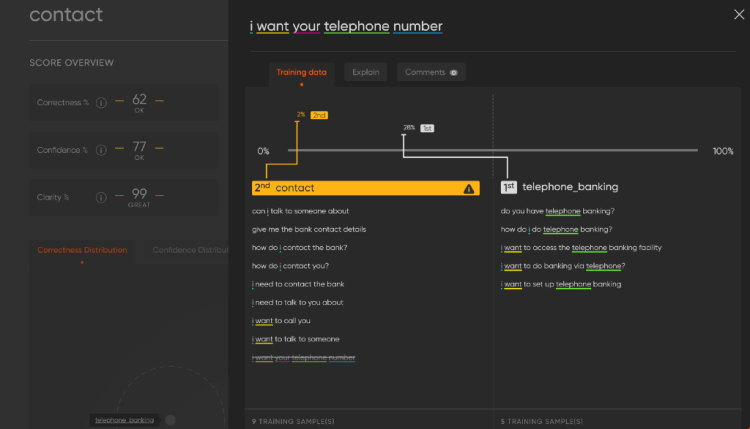
This helped me to diagnose why the training data wasn’t working as expected.
From the colour-coded words (on the left), I had a good understanding of the word density, and could see I had several instances of “telephone” in a different intent, and a lack of variations on asking for a telephone number in my contact_us intent.
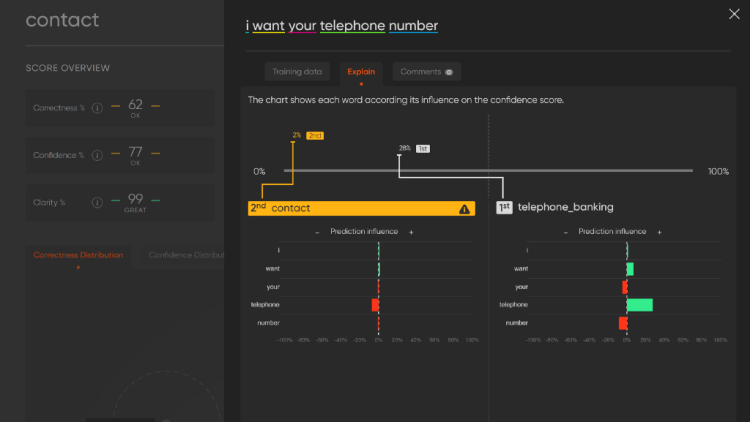
You can get an even deeper word-by-word analysis by using the QBox Explain feature (bottom illustration). This chart shows each word according to its influence on the prediction. In this illustration, you can easily see the biggest influencer to return an incorrect intent is “telephone”, and the lack of influence this word has on my Contact intent. This information clearly showed what the problem was and what I needed to do to fix it: add a little more training data to my Contact intent to strengthen the concept of asking for a telephone number.
Once you make changes to your chatbot, you can test your model again through QBox to validate those changes and see what effect they’ve had on your model overall — whether good or bad.
To find out more, visit QBox.ai.
Conclusion
Nobody would dispute the importance of ensuring your chatbot performs well to secure customer satisfaction. More recently, we’re seeing that it’s becoming a business requirement to understand the NLP model performance, analysing regression, ensuring clear KPIs are set and building your model development as part of a DevOps (MLOps) strategy. Whichever technique you use, it should help you on the path to improving performance, and ultimately your confidence in your model.

Don’t forget to give us your ? !




How to stop your chatbot giving the wrong answers was originally published in Becoming Human: Artificial Intelligence Magazine on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
