Synthetic Data for starters: all you need to know
Why Synthetic Data are extremely powerful for AI startups
Introduction
Imagine you want to make unrecognisable some photos from an album. The most immediate solution would be to obscure people’s faces, and make them “anonymous”. In today’s reality, this solution doesn’t work.
Suppose someone wants to re-identify the faces in these photos. It might be enough to cross-reference the available information (e.g. the clothes they are wearing), with other freely available datasets and … the re-identification game is served.
Definition of Synthetic Data … in a nutshell
Synthetic data is “any production data applicable to a given situation that is not obtained by direct measurement” (McGraw-Hill Dictionary of Scientific and Technical Terms). In practice, it is data that is artificially created rather than being collected and used. It is often generated with the help of algorithms for data anonymization.
We can distinguish between:
- Fully Synthetic Data: data is completely synthetic and doesn’t contain original data. Since the released data is completely artificially generated and doesn’t contain original data, this technique has strong privacy protection but the truthfulness of the data is lost.
- Partially Synthetic Data: generate partially synthetic data replaces only values of the selected sensitive attribute with synthetic values. Compared to Fully Synthetic Data, privacy protections are weaker and stronger accuracy rates.
In a study from 2017, MIT researchers splitted data scientists into two groups: one using synthetic data and another using real data. 70% of the time group using synthetic data was able to produce results on par with the group using real data.

History of Synthetic Data
In 1993, the idea of original fully synthetic data was created by Rubin. He originally designed this to “anonymize” the Decennial Census long-form responses for the short form households. Later that year, the idea of original partially synthetic data was created by Little. Little used this idea to synthesize the sensitive values on the public use file.
In recent years, has gained major traction as the benefits and risks of data science have become widely known.
Why using Synthetic Data
Synthetic data are extremely useful because of the following advantages:
- Meet very specific needs or conditions that are not available in real data: This can be useful when either privacy needs to limit the availability or usage of the data or when the data needed for a test environment simply does not exist.
- Protect the privacy and confidentiality of a set of data: Real data could contain personal information that you may not want to be disclosed. Synthetic data holds no personal information and cannot be traced back to any individual. Therefore, the use of synthetic data reduces confidentiality and privacy issues.
Trending AI Articles:
1. Top 5 Open-Source Machine Learning Recommender System Projects With Resources
4. Why You Should Ditch Your In-House Training Data Tools (And Avoid Building Your Own)
Some of the business functions that can benefit from synthetic data include:
- Self-driving car simulations pioneered the use of synthetic data
- Software testing and quality assurance
- Clinical and scientific trials for future studies that involve data which don’t exist yet
- Fraud protection in financial services
Applications in AI and Machine Learning
The role of synthetic data in AI and Machine Learning applications is increasing rapidly. This is because these algorithms are trained with an incredible amount of data which, without synthetic data, could be extremely difficult to obtain or generate. It can also play an important role in the creation of algorithms for image recognition and similar tasks that are becoming the baseline for AI.
Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN)
These networks introduced by Ian Goodfellow et al. in 2014. — also called GAN or Generative Adversarial Networks — are a recent breakthrough in image recognition.
They are composed of one discriminator and one generator network. While the generator network generates synthetic images that are as close to reality as possible, the discriminator network aims to identify real images from synthetic ones. Both networks build new nodes and layers to learn to become better at their tasks.
While this method is popular in neural networks used in image recognition, it has uses beyond neural networks. It can be applied to other machine learning approaches as well.

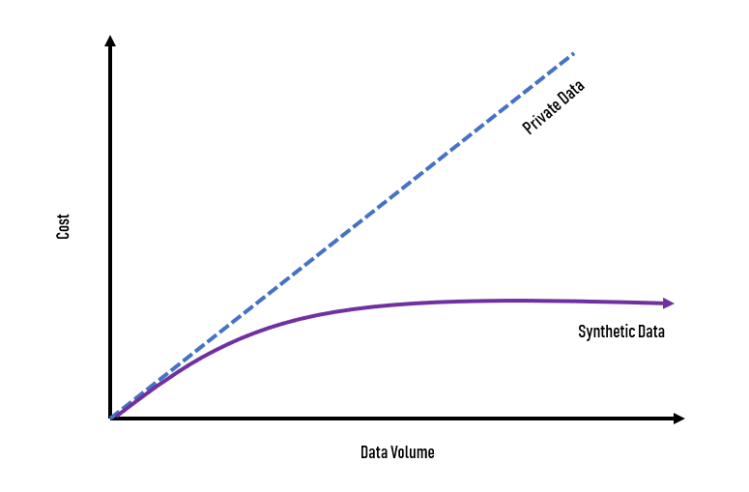
Startups vs. Tech Giants
As I mentioned above, AI and Machine Learning algorithms require immense amounts of data for proper training. The world’s most valuable technology companies, such as Google, Facebook, Amazon and Baidu harvest immense data sets of images, videos and other from their consumers, having a huge competitive advantage for allowing computers and algorithms to learn faster.
Thanks to synthetic data, this advantage is being disrupted by the ability for anyone to create and leverage synthetic data to train computers across many use cases, including retail, robotics, autonomous vehicles, commerce and much more.
“…Synthetic data will democratize the tech industry” — Evan Nisselson, TechCrunch
Some examples
- Spil.ly: Berlin-based startup that developed an augmented-reality app akin to a full-body version of Snapchat’s selfie filters. Roughly a year later since they started using synthetic data, the company had roughly 10 million images made by pasting digital humans it calls simulants into photos of real-world scenes. It looked weird, but it worked.
- Neuromation: Startup based in Tallinn that is churning out images containing simulated images for clients that want to use cameras to track the growth of livestock.
- DensePose: open-source machine learning software disclosed by FacebookAI that can apply special effects to humans in the video, trained with 50,000 images of people hand-annotated with 5 million points.
- AiFi: computer vision and artificial intelligence startup that delivers a more efficient checkout-free solution to both mom-and-pop convenience stores and major retailers.
Conclusion
Synthetic data generation is one of the important techniques for privacy-preserving data publishing. As the published data doesn’t represent any real entity, the disclosure of sensitive private data is eliminated.
Furthermore, it is a powerful solution for an AI startup who doesn’t have the resources to collect, label and process huge amounts of data typically needed to train complex algorithms. The synthetic data will make the artificial intelligence challenge between corporate and startups on equal terms.
If you liked this article, let’s connect on Linkedin!
Don’t forget to give us your ? !




Synthetic Data: a primer for a non-technical audience was originally published in Becoming Human: Artificial Intelligence Magazine on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
