How to Deploy AI models ? Part 5- Deploying Web-application on Heroku-CLI
This Part is the continuation of the Deploying AI models Part-3 , where we deployed Iris classification model using Decision Tree Classifier. You can skip the training part if you have read the Part-3 of this series. In this article, we will have a glimpse of Flask which will be used as the front end to our web application to deploy the trained model for classification on Heroku platform.
1.Iris Model Web application using Flask.
1.1. Packages
The following packages were used to create the application.
1.1.1. Numpy
1.1 .2. Flask, Request, render_template from flask
- 1.3. Dataset, Ensemble, Model Selection from sklearn

1.2. Dataset
The dataset is used to train the model is of iris dataset composed of 4 predictors and 3 target variable i.e. Classes
Predictors: Sepal Length, Sepal Width, Petal Length, Petal Width
Target : Setosa [0], Versicolor[1], Verginica[2]
Dataset Shape: 150 * 5

1.3. Model
For training the model we followed the following procedure:
Data Split up: 8:2 ie. 80% training set and 20% for the test set
Model: Ensemble- RandomForestClassifier with n_estimators=500)
Saving Model: Saved in the pickle file
Below is the code for the training the model.
import sklearnimport
sklearn.datasetsimport sklearn.ensemble
import sklearn.model_selection
import pickle
import os
#load data
data = sklearn.datasets.load_iris() #Split the data into test and
traintrain_data, test_data, train_labels, test_labels = sklearn.model_selection.train_test_split(data.data, data.target, train_size=0.80)
print(train_data,train_labels)
#Train a model using random forestmodel = sklearn.ensemble.RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=500)model.fit(train_data, train_labels)
#test the model
result = model.score(test_data, test_labels)
print(result)
#save the model
filename = ‘iris_model.pkl’
pickle.dump(model, open(filename, ‘wb’))
1.4. Frontend using Flask
For feeding the value in the trained model we need some User Interface to accept the data from the user and feed into the trained neural network for classification. As we have seen in the sectioin 1.2 Dataset where we have 4 predictors and 3 classes to classify.
File name: index.html should be placed inside templatre folder.
<h1>Sample IRIS Classifier Model Application</h1>
<form action=””method=”post”>
<input type=”text” name=”sepal_length” placeholder=”Sepal Length” required=”required” />
<input type=”text” name=”sepal_width” placeholder=”Sepal Width” required=”required” />
<br>
<br>
<input type=”text” name=”petal_length” placeholder=”Petal Length” required=”required” />
<input type=”text” name=”petal_width” placeholder=”Petal Width” required=”required” />
<br>
<br>
<br>
<button type=”submit” class=”btn btn-primary btn-block btn-large”>Submit Data</button> </form>
<br>
<br>
The above shown code is for taking the input from the user and display it in the same page. For this we have used action=”” this will call the prediction fubtion when we will submit the data with the help of this form and to render the predicted output in the same page after prediction.
Trending AI Articles:
1. Top 5 Open-Source Machine Learning Recommender System Projects With Resources
4. Why You Should Ditch Your In-House Training Data Tools (And Avoid Building Your Own)
File name: app.py
import numpy as np
from flask import Flask, request, jsonify, render_template
import pickle
import os
#app name
app = Flask(__name__)
#load the saved model
def load_model():
return pickle.load(open(‘iris_model.pkl’, ‘rb’)) #home
page@app.route(‘/’)
def home():
return render_template(‘index.html’)
@app.route(‘/predict’,methods=[‘POST’])
def predict():
‘’’ For rendering results on HTML GUI ‘’’
labels = [‘setosa’, ‘versicolor’, ‘virginica’]
features = [float(x) for x in request.form.values()]
values = [np.array(features)] model = load_model()
prediction = model.predict(values)
result = labels[prediction[0]]
return render_template(‘index.html’, output=’The Flower is
{}’.format(result))
if __name__ == “__main__”:
port=int(os.environ.get(‘PORT’,5000))
app.run(port=port,debug=True,use_reloader=False)
In the python script, we called the index.html page in the home() and loaded the pickle file in load_model () function.
As mention above we will be using the same index.html for user input and for rendering the result. when we will submit the form via post method the data will be send to the predict() via action=”” and predict function from the app.py file and it will be processed and the trained model which we have loaded via load_model () function will predict and it will be mapped the respective class name accordingly.
To display the data we will render the same template i.e. index.html. If you would have remember we used keyword in the index.html page we will be sending the value in this field after prediction by rendering in the index.html page by the following Flask function.
render_template(‘index.html’, output=’The Flower is
{}’.format(result))
where index.html is the template name and output=’The Flower is
{}’.format(result) is the value to be rendered after prediction.
1.5. Extracting Packages and their respective versions
We need to create the require.txt file which contains the name of package we used in our application along with their respective version. The process of extracting the requirement.txt file is explained in the Article: Deep Learning/Machine Learning Libraries — An overview.
For this application below is the requirement.txt file content.
Flask==1.1.2
joblib==1.0.0
numpy==1.19.3
scikit-learn==0.23.2
scipy==1.5.4
sklearn==0.0
Along with requirement.txt, you need the Proctfile which calls the main python script i.e. script which will run first. For this Webapplication the Proctfile content is below.
web: gunicorn -b :$PORT app:app
app -->is the name of the python scripy i.e. app.py
2. Heroku
It is a PaaS platform which supports many programming languages. Initially in 2007 it was supporting only Ruby programming language but not it supports many programming language such as Java, Node.js, Scala, Clojure, Python, PHP, and Go. It is also known as polyglot platform as it features for a developer to build, run and scale applications in a simillar manner across most of the language it was acquired by Salesforce.com in 2010.
Applications that are run on Heroku typically have a unique domain used to route HTTP requests to the correct application container or dyno. Each of the dynos are spread across a “dyno grid” which consists of several servers. Heroku’s Git server handles application repository pushes from permitted users. All Heroku services are hosted on Amazon’s EC2 cloud-computing platform.
You can register on this link and can host upto 5 application with student account.
3. Deploying Web application
In above, section we have constructed our web application successfully and now it’s time to deploy it. For deploying we have two option Deploying via Github and Deploying via Local System. In this article we will see how we can deploy any ML/DL model using Heroku CLI.
3.1. Deploying via Heroku CLI
The local repository should look like the below image:

As mentioned in the section 2, after login in the heroku platform follow the below step:
Step1: Create new app and name the application and click on create app. You will land on the below page.
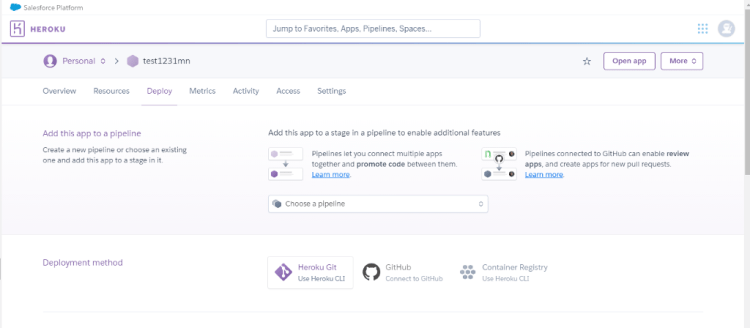
In Fig.2 you can see, we have 3 option by which we can deploy, in this article we will use the option which allows us to deploy the application directly with ourGithub repository.
Note: for Installation visit this Link.
Step2: Select heroku CLI from the available option to deploy the application to heroku.
Step3: Navigate to the directory where the project file is kept.
Command: cd “Path of the directory”
Step4: Initialise the directory with git.
Command: git init
Command: heroku git: remote -a “Name of the Application created”
The above commands will create the git reposisoty in your local system. For deployement follow tye below process:
Step5: We need to add all our filled so that it can be tracked for any changes we will do in later stages of our project.
Command: git add .
Step 6: Commit the repository.
Command: git commit -am “version 1”
Step 7: Push the repository into Heroku.
Command: git push heroku master
Congratulation!! you have sucessfully deployed an web application via Heroku CLI.
4. Deployed Web Application
The overview of the deployed web application with Iris Application: Link is shown below.
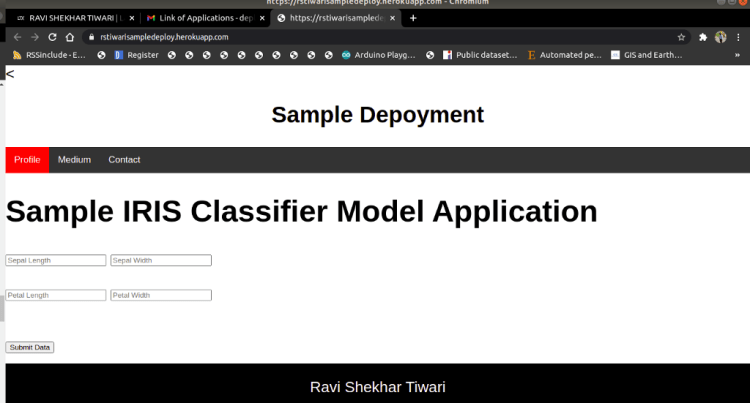
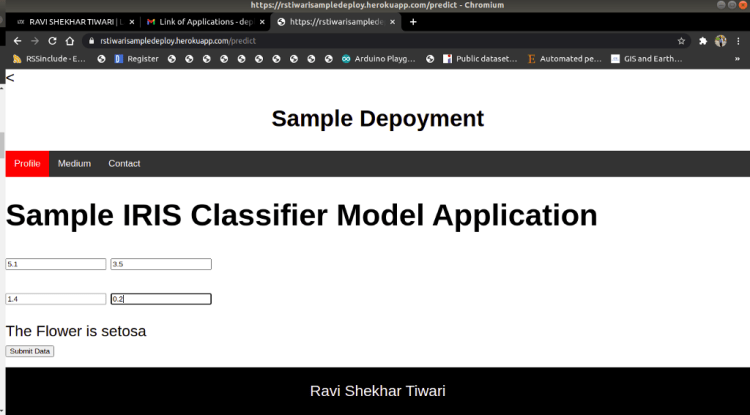
Special Thanks:
As we say “Car is useless if it doesn’t have a good engine” similarly student is useless without proper guidance and motivation. I will like to thank my Guru as well as my Idol “Dr. P. Supraja”- guided me throughout the journey, from the bottom of my heart. As a Guru, she has lighted the best available path for me, motivated me whenever I encountered failure or roadblock- without her support and motivation this was an impossible task for me.
Reference:
Extract installed packages and version : Article Link.
Notebook Link Extract installed packages and version : Notebook Link
How to Deploy AI Models? — Part 1 : Link
How to Deploy AI Models? — Part 2 Setting up the Github For Herolu and Streamlit : Link
YouTube : Link
Deployed Application: Link
Iris Application: Link
If you have any query feel free to contact me with any of the -below mentioned options:
Website: www.rstiwari.com
Medium: https://tiwari11-rst.medium.com
Google Form: https://forms.gle/mhDYQKQJKtAKP78V7
Don’t forget to give us your ? !




How to Deploy AI models ? Part 5- Deploying Web-application on Heroku-CLI was originally published in Becoming Human: Artificial Intelligence Magazine on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
