Originally from KDnuggets https://ift.tt/3fITNXT
KDnuggets Top Authors Reward Program
Originally from KDnuggets https://ift.tt/3cTQvPH
Data Labeling Case StudyCosmetics Brand Classification and Labeling
Data Labeling Case Study — Cosmetics Brand Classification and Labeling
Lipstick Effect
There is a famous “lipstick effect” in economic theory, which refers to an interesting economic phenomenon that lipstick is sold hot due to economic depression, also known as “ small luxury items preference “. For example, in 2008, during the global financial crisis, the cosmetics industry continued to be on rising.
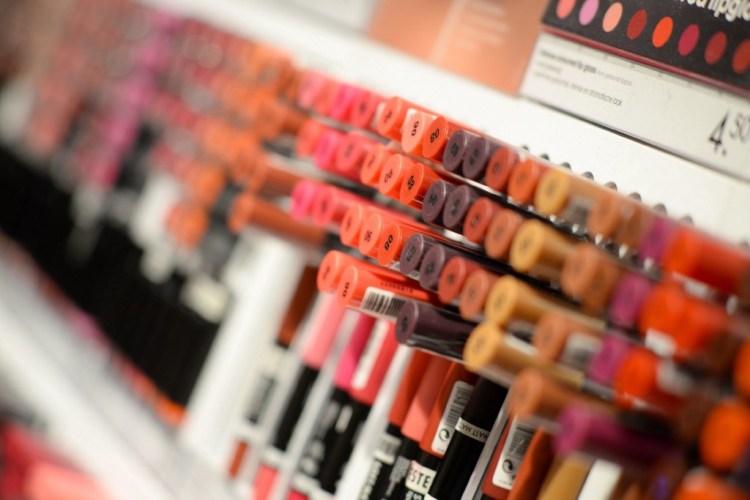

Despite that the Covid-19 epidemic in 2019 disturbs routine life, it cannot disturb the admiration for beauty. Due to the limitation of physical conditions, the cosmetics industry constantly uses artificial intelligence to develop its business online.
Image Recognition Case
Brand search accuracy is one of the main directions of AI technology in the field of cosmetics, which needs AI graphics and image recognition, and machine learning. Recently, we have a case that requires 10,000 + cosmetics brand classification and labeling.

ByteBridge has obvious advantages in image classification and labeling.
Quality Control
Firstly, we divide the work into two components: brand identification and brand labeling to further minimize human error.
Secondly, quality assurance is embedded into the labeling process as we introduce the consensus mechanism: we assign the same task to dozens of workers for quality check, and the correct answer comes from the majority output. In this way, the efficiency can be greatly improved.
ByteBridge takes advantage of the automatic operation and management platform to accomplish the mission in three days, which helps customers save time and cost.

Flexibility
ByteBridge, a human-powered data labeling tooling platform with real-time workflow management, providing flexible data training service for the machine learning industry.
On the dashboard, clients can set labeling rules, iterate data features, attributes and workflow, scale up or down, make changes based on what they are learning about the model’s performance in each step of test and validation.
Trending AI Articles:
2. How AI Will Power the Next Wave of Healthcare Innovation?
These labeling tools are available: Image Classification, 2D Boxing, Polygon, Cuboid.
For example, you can choose image classification service:
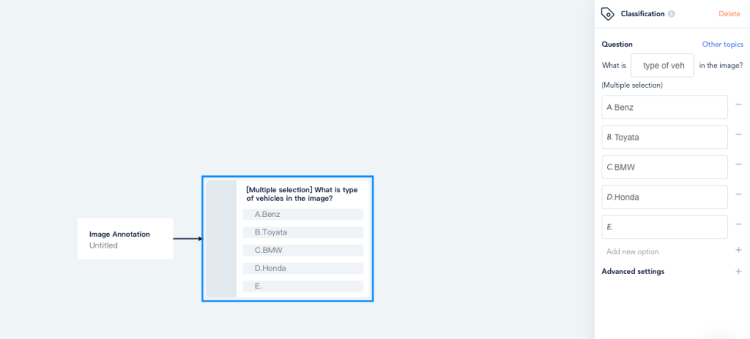
Or you can choose object counting service
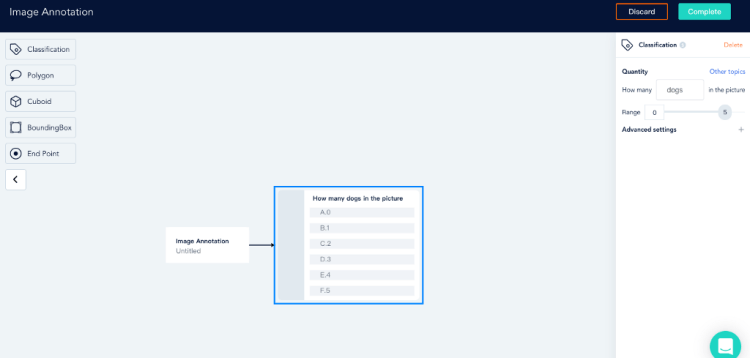
For more services deblocking, please have a look at bytebridge.io, the clear pricing is available.
Don’t forget to give us your ? !




Data Labeling Case Study — Cosmetics Brand Classification and Labeling was originally published in Becoming Human: Artificial Intelligence Magazine on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
Deploy Rihanna lyric generation Model with Okteto Cloud
This is the cloud continuation of the previous article on deploying the Pytorch model with Okteto CLI and Flask API
here is the link: https://python.plainenglish.io/deploy-pytorch-model-with-okteto-cli-d494d058216
In the previous article, we learnt how to deploy a text generation model built with PyTorch using Okteto CLI and in this article, we will learn how to build a text generation model using a state of art text generation library(TEXT-GEN) and deploy the model with okteto cloud.

Text gen
Text gen is an almost state of the art library python library that allows you to build a custom text generation model with ease. Text gen is built on top of Tensorflow, so if you are familiar with tensorflow then text gen will be really easy for you.
At the end of this session we will be able to;
- Build a model for generating Rihanna kind of lyric
- Create a flask API
- Push our model to Github
- Deploy the text generation model with Okteto
- Test our model with Postman

Notebook: The Notebook for the codes can be found here.
Prerequisites:
- Okteto account
- Github
- Python 3
- Text gen
- Google colab or Jupyter lab
Before we start building the model, we need to download a dataset of Rihanna lyrics from Kaggle and also you will either have to create an account or sign in to Kaggle to download the data(click here to download the data)
After downloading the data, create the following files and folders, move the “rihanna.txt” to the data folder.
├── app
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── model.py
│ ├── api.py
├── data
├── model
├── main.py
├── Dockerfile
├── okteto.yml
└── requirements.txt
Now, let’s install the Text-gen library
$ pip install -U text-gen
After installing the package, let’s import text-gen and load our data from the data folde
from text_gen import ten_textgen as ttg
data = open('/data/rihanna.txt').read()
corpus = data.lower().split("\n")
corpus
Now, let’s plot a word cloud to see the frequent words on Rihanna lyrics.
#create the wordcloud object
corpus = str(corpus)
wordcloud = WordCloud(stopwords = STOPWORDS,
collocations=True).generate(corpus)
#plot the wordcloud object
plt.imshow(wordcloud, interpolation='bilInear')
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()

In machine learning, a model is a function with learnable parameters that maps an input to an output. The optimal parameters are obtained by training the model on data.
After plotting the word cloud, we will configure our model parameters.
A model parameter is a configuration variable that is internal to the model and whose value can be estimated from data. paramters are like car speed booster, you tune(change values) them to optimize the model and improve the accuracy and performance
pipeline = ttg.tentext(corpus)
seq_text = pipeline.sequence(padding_method = 'pre')
configg = pipeline.configmodel(seq_text, lstmlayer = 128, activation='softmax', dropout = 0.25)

It’s time to fit and train our data into our model. Fitting a neural network requires using a training dataset to update the model weights to create a good mapping of inputs to outputs.
model_history = pipeline.fit(loss = 'categorical_crossentropy', optimizer = 'adam', batch = 300, metrics = 'accuracy', epochs = 500, verbose = 0, patience = 10)
After training, we will save our model and generates a lyric with 100 as the word_length
pipeline.predict('yo yo', word_length = 100, segment = True)
#save the model
pipeline.saveModel('./model/model')
#check the model folder for 'modeltextgen.h5'
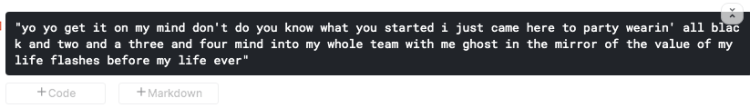
You can also load the model and use the load_model_predict function
#load the model and predict
ttg.load_model_predict(corpus = dataset, padding_method = 'pre', modelname = './model/model2textgen.h5', sample_text = text, word_length = 100)
Voila!!!!!!!! we have successfully built and save a lyric text model that generates Rihanna kind of lyric.
Trending AI Articles:
2. How AI Will Power the Next Wave of Healthcare Innovation?
Deploy with Okteto
Now it’s time to serve our model. To do this, we’re going to write a REST service using Flask. The service will have an endpoint that will take the sample text as a parameter, and generate lyrics from it.
For the “api.py” file, use the code to create a flask route.
from flask import Flask,jsonify,request,render_template, make_response
from flask_cors import CORS, cross_origin
from app.predict import prediction
app = Flask(__name__)
cors = CORS(app)
@app.route("/")
def index():
return("welcome to love letter generation pytorch model")
@app.route("/ririlyric", methods = ['GET', 'POST'])
def textgen():
text_g = request.form['content']
lyric = prediction(text_g)
return lyric
on the predict.py file, input the script below. The prediction function takes in the sample text, load the model and the training dataset.
from text_gen import ten_textgen as ttg
#load train data and the model
data = './data/data.txt'
dataset = ttg.loaddata(data)
#prediction function
def prediction(text):
lyric = ttg.load_model_predict(corpus = dataset, padding_method = 'pre', modelname = './model/model2textgen.h5', sample_text = text, word_length = 100)
return lyric
on the main.py file, input the script below so we can run the API locally.
from app.api import app
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(host= '0.0.0.0', port = 8080, debug=True)
let’s test our API locally.
$ python3 main.py
After testing the API locally, create an okteto stack manifest file okteto-stack.yml to define your application
name: riry
services:
api:
public: true
image: okteto/riri-service
build: .
ports:
- 8080
resources:
cpu: 1
memory: 516Mi
and a Dockerfile
FROM python:3.8
WORKDIR /app
EXPOSE 8080
ADD data/data.txt /app/data/data.txt
ADD model/modeltextgen.h5 /app/model/modeltextgen.h5
ADD requirements.txt requirements.txt
RUN pip install -r requirements.txt
ADD . /app/
CMD ["python", "main.py"]
Create a GitHub repo and push the code to GitHub
$ git add .
$ git commit -m "textgenpush"
$ git remote add origin <github repo url>
$ git push origin master
Okteto cloud
Now, it’s time to deploy our application. For this, we’ll be using Okteto Cloud. Okteto Cloud is a free developer platform powered by Kubernetes that lets you code, build and run cloud-native applications entirely in the cloud. With Okteto cloud, you can deploy your Machine Learning model with just a click of a button
After pushing our files to GitHub, it’s time to deploy our model.
okteto empower developers to innovate and deliver cloud-native applications faster than ever.
Create an account on Okteto, click on the deploy icon and a pop up will appear asking you to input your GitHub repo link with the branch you want to deploy.
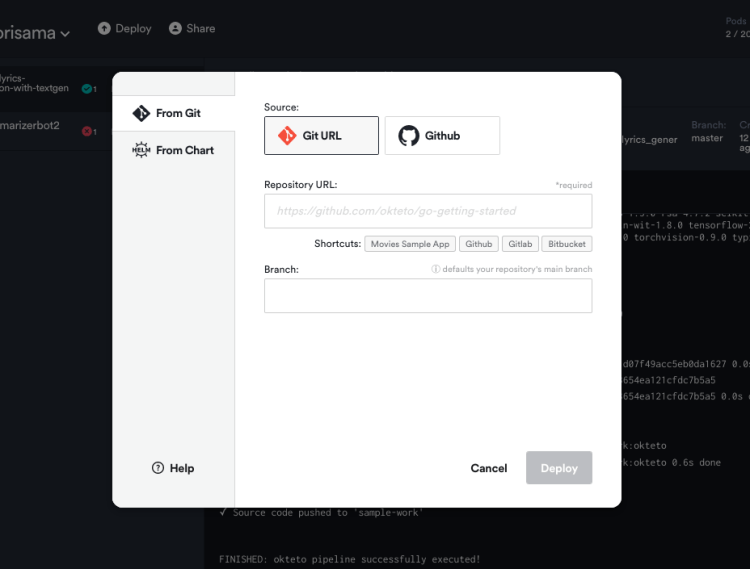
Now click on deploy.
Volia!!!!!! deployed successfully.
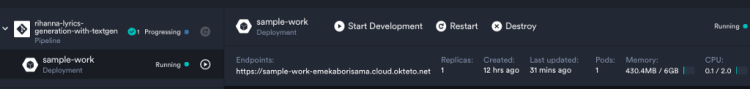
Test our API
Now we have deployed our Rihanna lyric generation model, the deployment command starts an application on your dashboard. Let’s test our API with Postman. Copy the URL from okteto and use the “GET” method with /ririlyric endpoint on Postman
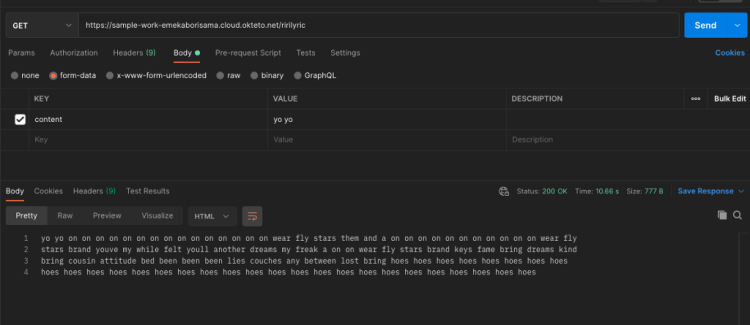
Further work:
- Hyperparameter tuning using the “hyper-param” function on text-gen
- Get more data
- Segment text (Incoming feature on text-gen)
- Increase the word_length to get more words or text
- Add Okteto GitHub action to automate deployment
Here is the Github repo for this project
Conclusion:
In all, we have been able to build a Rihanna lyric generator using text-gen and also learnt how easy it is to deploy a machine learning model with okteto
Resources
- https://github.com/Emekaborisama/Rihanna_lyrics_generation_with_textgen
- https://python.plainenglish.io/deploy-pytorch-model-with-okteto-cli-d494d058216
- https://okteto.com/blog/building-a-machine-learning-application-with-spago/
- https://okteto.com/blog/building-and-deploying-a-fastapi-app-in-okteto-cloud/
- https://github.com/Emekaborisama/textgen
Don’t forget to give us your ? !




Deploy Rihanna lyric generation Model with Okteto Cloud was originally published in Becoming Human: Artificial Intelligence Magazine on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
How to Deploy AI models? Part 7- Deploying Web-application on Heroku via Docker
How to Deploy AI models? Part 7- Deploying Web-application on Heroku via Docker
This Part is the continuation of the Deploying AI models Part-3 , where we deployed Iris classification model using Decision Tree Classifier. You can skip the training part if you have read the Part-3 of this series. In this article, we will use Flask as the front end to our web application to deploy the trained model for classification on Heroku platform with the help of docker.
Note: If you have followed my Model Deployement series from starting you can skip the section 1.
Article: Deploying AI models Part-3
1.Iris Model Web application using Flask.
1.1. Packages
The following packages were used to create the application.
1.1.1. Numpy
1.1.2. Flask, Request, render_template from flask
- 1.3. Dataset, Ensemble, Model Selection from sklearn
1.2. Dataset
The dataset is used to train the model is of iris dataset composed of 4 predictors and 3 target variable i.e. Classes
Predictors: Sepal Length, Sepal Width, Petal Length, Petal Width
Target : Setosa [0], Versicolor[1], Verginica[2]
Dataset Shape: 150 * 5

1.3. Model
For training the model we followed the following procedure:
Data Split up: 8:2 ie. 80% training set and 20% for the test set
Model: Ensemble- RandomForestClassifier with n_estimators=500)
Saving Model: Saved in the pickle file
Below is the code for the training the model.
import sklearnimport
sklearn.datasetsimport sklearn.ensemble
import sklearn.model_selection
import pickle
import os
#load data
data = sklearn.datasets.load_iris()
#Split the data into test andtrain
train_data, test_data, train_labels, test_labels = sklearn.model_selection.train_test_split(data.data, data.target, train_size=0.80)
print(train_data,train_labels)
#Train a model using random forest
model=sklearn.ensemble.RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=500)model.fit(train_data, train_labels)
#test the model
result = model.score(test_data, test_labels)
print(result)
#save the model
filename = ‘iris_model.pkl’
pickle.dump(model, open(filename, ‘wb’))
1.4. Frontend using Flask
For feeding the value in the trained model we need some User Interface to accept the data from the user and feed into the trained neural network for classification. As we have seen in the sectioin 1.2 Dataset where we have 4 predictors and 3 classes to classify.
File name: index.html should be placed inside template folder.
<h1>Sample IRIS Classifier Model Application</h1>
<form action=””method=”post”>
<input type=”text” name=”sepal_length” placeholder=”Sepal Length” required=”required” />
<input type=”text” name=”sepal_width” placeholder=”Sepal Width” required=”required” />
<br>
<br>
<input type=”text” name=”petal_length” placeholder=”Petal Length” required=”required” />
<input type=”text” name=”petal_width” placeholder=”Petal Width” required=”required” />
<br>
<br>
<br>
<button type=”submit” class=”btn btn-primary btn-block btn-large”>Submit Data</button> </form>
<br>
<br>
The above shown code is for taking the input from the user and display it in the same page. For this we have used action=”” this will call the prediction fubtion when we will submit the data with the help of this form and to render the predicted output in the same page after prediction.

File name: app.py
import numpy as np
from flask import Flask, request, jsonify, render_template
import pickle
import os
#app name
app = Flask(__name__)
#load the saved model
def load_model():
return pickle.load(open(‘iris_model.pkl’, ‘rb’)) #home
page@app.route(‘/’)
def home():
return render_template(‘index.html’)
app.route(‘/predict’,methods=[‘POST’])
def predict():
‘’’ For rendering results on HTML GUI ‘’’
labels = [‘setosa’, ‘versicolor’, ‘virginica’]
features = [float(x) for x in request.form.values()]
values = [np.array(features)] model = load_model()
prediction = model.predict(values)
result = labels[prediction[0]]
return render_template(‘index.html’, output=’The Flower is
{}’.format(result))
if __name__ == “__main__”:
port=int(os.environ.get(‘PORT’,5000))
app.run(port=port,debug=True,use_reloader=False)
In the python script, we called the index.html page in the home() and loaded the pickle file in load_model () function.
As mention above we will be using the same index.html for user input and for rendering the result. when we will submit the form via post method the data will be send to the predict() via action=”” and predict function from the app.py file and it will be processed and the trained model which we have loaded via load_model () function will predict and it will be mapped the respective class name accordingly.
To display the data we will render the same template i.e. index.html. If you would have remember we used keyword in the index.html page we will be sending the value in this field after prediction by rendering in the index.html page by the following Flask function.
render_template(‘index.html’, output=’The Flower is
{}’.format(result))
where index.html is the template name and output=’The Flower is
{}’.format(result) is the value to be rendered after prediction.
1.5. Extracting Packages and their respective versions
We need to create the require.txt file which contains the name of package we used in our application along with their respective version. The process of extracting the requirement.txt file is explained in the Article: Deep Learning/Machine Learning Libraries — An overview.
For this application below is the requirement.txt file content.
Flask==1.1.2
joblib==1.0.0
numpy==1.19.3
scikit-learn==0.23.2
scipy==1.5.4
sklearn==0.0
Trending AI Articles:
2. How AI Will Power the Next Wave of Healthcare Innovation?
2. Docker
Docker is an apparatus intended to make it simpler to make, convey, and show applications to utilizing holders. Holders permit a designer to bundle up an application with the entirety of the parts it needs, like libraries and different conditions, and convey it as one bundle. Thusly, on account of the compartment, the engineer can have confidence that the application will run on some other Linux machine paying little mind to any modified settings that machine may have that could vary from the machine utilized for composing and testing the code.
Docker is a cycle like a virtual machine. However, in contrast to a virtual machine, instead of making an entire virtual working framework, Docker permits applications to utilize a similar Linux bit as the framework that they’re running on and just requires applications be transported with things not previously running on the host PC. This gives a huge presentation help and decreases the size of the application. Also, significantly, Docker is open source. This implies that anybody can add to Docker and extend it to address their own issues on the off chance that they need extra highlights that aren’t accessible out of the crate.
Here, we will write the docker file the Dockerfile which will build the docker image and we can ship it anywhere irrespective of the unser enviroment. Here we will create the Docker file and I will explain the file line by line below.
FROM ubuntu:latest #line 1
RUN apt-get update -y #line 2
RUN apt-get install -y python-pip python-dev build-essential #line 3
COPY . /app #line 4
WORKDIR /app #line 5
RUN pip install -r requirements.txt #line 6
ENTRYPOINT [“python”] #line 7
CMD [“streamlit run app.py”] #line 8
Now, above is the code for the Dockerfile where,
Line 1: States we will use latest version of the ubuntu as our base image. Since docker was initially built on linux OS so i have used Linux as base image thought this is optional you can directly install python and build the container, but it is recommended to have base image.
Line 2: This line will update the Linux OS system.
Line 3: We are installing python
Line 4: We are copying the folder where we have kept our script and supporting materials for the application inside docker enviroment.
Line 5: Setting our working directory as app, where all the scripts are present inside docker.
Line 6: We are installing all the python packages required for the web application. Check the below article to find how we can extract the installed packages in python.
Article: Deep Learning/Machine Learning Libraries — An overview
Line 7 and Line 8: States that we will be using the Python applicarion to run the script with the command to run the script.
Building Docker image:
command: docker build -t streamlit-heroku:latest
The above line will create the image of the contained as mentioned in the Dockerfile.
Running Container:
The below command will execute the container but docker has its own Ip address and as well as the port just like any other OS, so we need to map the docker container port with our OS system so we can access the web application, which can be done by adding -p 8501:8501 or you can add Expose 8501 in Dockerfile it will automatically expose the mentioned port.
command: docker run -d -p 8501:8501 streamlit-heroku:latest
3. Heroku
It is a PaaS platform which supports many programming languages. Initially in 2007 it was supporting only Ruby programming language but not it supports many programming language such as Java, Node.js, Scala, Clojure, Python, PHP, and Go. It is also known as polyglot platform as it features for a developer to build, run and scale applications in a simillar manner across most of the language it was acquired by Salesforce.com in 2010.
pplications that are run on Heroku typically have a unique domain used to route HTTP requests to the correct application container or dyno. Each of the dynos are spread across a “dyno grid” which consists of several servers. Heroku’s Git server handles application repository pushes from permitted users. All Heroku services are hosted on Amazon’s EC2 cloud-computing platform.
You can register on this link and can host upto 5 application with student account.
If you have gone throught the Part 5 of Model Deployement series then it will be easy for you, but it is always recommended to checkout the below link.
Commands to deploy the container on heroku using CLI:
heroku container:login
heroku create dockerapp
heroku container:push web — app streamlit-heroku:latest
You will get the below messages as response which says that the Docker image has been built, tagged and successfully pushed. We are almost there with completing our deployment. The container is pushed but not released yet. I’m not exactly sure what could be the reason to have it in pushed stage before releasing. Anyways, the below command would release the container.
heroku container:release web — app streamlit-heroku:latest
Once it is released, you would get the message as done. Now it is time to check out our awesome app running on Heroku.
Congratulation!!! we have completed our series of Model deployement.
Special Thanks:
As we say “Car is useless if it doesn’t have a good engine” similarly student is useless without proper guidance and motivation. I will like to thank my Guru as well as my Idol “Dr. P. Supraja”- guided me throughout the journey, from the bottom of my heart. As a Guru, she has lighted the best available path for me, motivated me whenever I encountered failure or roadblock- without her support and motivation this was an impossible task for me.
Reference:
Extract installed packages and version : Article Link.
Deployed Application: Link
Github Documentation: Link
Notebook Link Extract installed packages and version : Notebook Link
YouTube : Link
If you have any query feel free to contact me on any of the below-mentioned options:
Website: www.rstiwari.com
Github page: Link
Medium: https://tiwari11-rst.medium.com
Google Form: https://forms.gle/mhDYQKQJKtAKP78V7
Don’t forget to give us your ? !




How to Deploy AI models ? Part 7- Deploying Web-application on Heroku via Docker was originally published in Becoming Human: Artificial Intelligence Magazine on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
How to Dockerize Any Machine Learning Application
Originally from KDnuggets https://ift.tt/39P6zQR
Automated Text Classification with EvalML
Originally from KDnuggets https://ift.tt/3cQMBXN
Top Stories Mar 29 Apr 4: Top 10 Python Libraries Data Scientists should know in 2021; Shapash: Making Machine Learning Models Understandable
Originally from KDnuggets https://ift.tt/3rTRaEO
The Best Machine Learning Frameworks & Extensions for TensorFlow
Originally from KDnuggets https://ift.tt/3cQ68HO
Online Education Trends: Top 4 AI Applications for Distance and Blended Learning

Online learning has been there for years. Yet today, eLearning technology poses a real challenge to the traditional education models with more and more schools and universities turning to artificial intelligence solutions for education. Still, many educational institutions feel skeptical about adopting online learning tools. “A lack of in-person interaction sucks all the joy out of education” and “innovations in online education are too complex to handle” are the most commonly cited barriers halting the future of online and blended learning.
The good news is that artificial intelligence can help overcome these barriers and transform eLearning as we know it. To prove that, we’ve summarized key online education trends giving a look over the applications of AI for eLearning and offering a blueprint for a successful AI adoption. So, let’s waste no time and dive right in.

AI and eLearning: Top 4 trends in online education
1. Personalized learning
With artificial intelligence in eLearning systems, educators can create personalized learning pathways and provide students with tailored content following their academic performance and learning goals. An AI engine may be integrated into a school’s LMS system, turning a simple data repository into a real-life version of the Hogwarts’ sorting hat.
The only difference is that it puts students into learning buckets, like visual and aural learners or loners and team players. So, students who don’t easily succeed in a standard one-size-fits-all paradigm can, for example, take a survey that would identify their learning styles, preferred educational resources, and other performance-influencing factors. And the AI engine powering the survey would draft recommendations on how to adjust the curriculum and the instructions to make the student engage.
Take, for example, the i-Learn program that is currently implemented across schools in Flanders, Belgium. Flemish educators leverage AI and online education to embrace personalized learning. They’ve partnered with a tech vendor to create a portal for deploying various EdTech apps for different domains, topics, proficiency levels, and learning profiles. The portal is to be rolled out in at least 10% of the Flemish schools by September 2022.

2. Skills-oriented learning
Educators often think that online education lacks practice. But tapping in eLearning trends, schools can implement interactive online learning with a focus on building up vital skills. AI-powered chatbots, interactive mobile apps, and virtual assistants can help students master hard and soft skills, like speaking a foreign language, diagnosing a patient, or leveling up their communication and problem-solving skills.
Students who are embarrassed to speak a foreign language, for example, can tame their anxiety conversing with AI-powered chatbots. The chatbots — now accessible through popular language learning apps like Duolingo — allow learners to go through life-like communicative scenarios and prepare for offline conversations. In turn, online assistants like custom-made SAMI (Social Agent Mediated Interaction) can help address a lack of social contact and emotional engagement for online students, informing them about interests and backgrounds they share with classmates.
Trending AI Articles:
2. How AI Will Power the Next Wave of Healthcare Innovation?
One of the hottest online learning trends, Coursera-like online educational platforms are often used to enable skills-based learning. Colleges and universities, too, are increasingly adopting tech and switching to fully online degrees based on similar eLearning platforms. In such cases, AI steps in to improve student retention and keep online learners engaged. AI technology in online education can monitor how consistently a student attends online lectures and submits assignments. And if the algorithms predict a possible drop-out, they give the student a push to go forward with learning. The experience of edX, for example, proves that a timely nudge accounts for a 30% higher student retention.

3. Automated administrative tasks
AI technology used in online education spares tutors and instructors the trouble of manually reviewing and grading assignments and monitoring students during online tests so instructors can have more time to develop quality eLearning content and interact with students. AI-powered reviewing and grading software can independently “read” and grade assignments building on the grades given by human instructors.
After training, such software can bulk-check student papers with the precision of a human. Grading software has already proved its effectiveness in science, technology, engineering, and math classes, unbiasedly grading two times more assignments than a human professor during the same time. However, grading systems are more challenging to apply in social sciences and humanities. At least 21 states in the US use technology to evaluate essays, from middle school to college level, yet AI algorithms powering the adopted software remain biased. For example, using advanced words tricks algorithms into thinking an essay is well-written when in fact, it doesn’t have any substance. The algorithms have also turned out to be biased against students from different nationalities and cultures, deeming their essays as poorly written. When it comes to preventing cheating at online exams, AI-powered remote proctoring software can help.
Educators may rely on proctoring solutions to automatically detect suspicious behaviors by recording students during tests via their computer’s camera or preventing students from switching browser tabs. An Educause poll suggests that 54% of institutions are already using eLearning tech for proctoring, and another 23% are considering using it. However, some educational organizations failed to weigh out the ethics of remote proctoring, which caused severe resistance from students and parents. Still, there are institutions whose approach to remote proctoring can be named a best practice. Florida State University, for example, encrypts all of the data collected by proctoring software, and it is professors, not the AI algorithms, that make the final decision on whether a student cheated or not.

4. Eliminating barriers
International students or students with special needs benefit from artificial intelligence eLearning tools as well. Translation tools, for instance, can accurately translate a lecture into a student’s native language. Voice recognition and speech-to-text software can transcribe lectures. And referencing tools can help students grasp complex content, say, breaking down a lengthy reading assignment into a set of simple, easily digestible, and structured pieces.
Many education institutions worldwide have already adopted assistive learning technology, including the University of Massachusetts and Sheffield University. Both schools use similar speech-to-text software that transcribes live speech and makes it easier for online students to digest educational content.

Incorporating AI into eLearning systems: 4 steps towards success
If you’re planning to enrich your eLearning software with AI capabilities, but don’t know where to start, here’s our high-level AI adoption plan you may rely on.
- Conduct an inventory of your eLearning technology tools and systems. Study what technology tools and software you already have to estimate the scope of work you’ll have to carry out when adopting AI for online education. Some eLearning solutions, for example, have built-in AI capabilities, which only need to be configured, and some require relatively simple customization. Other software solutions, in turn, can be enhanced via third-party or custom plugins. But occasionally, you might have to go for custom eLearning software development, giving your IT infrastructure a complete overhaul.
- Collect your data. The key to AI’s successful performance is thorough training of AI algorithms on the large volumes of quality data. So, you’ll have to put effort into aggregating your educational data, including the information from your eLearning systems, a corporate website, social media, student surveys, and other sources. However, mind that additional data restoration and cleaning may be required to eliminate bias in many cases.
- Elaborate on an AI use case. Identify how you can leverage AI to improve your online education process without causing critical disruption to your current operations while guaranteeing economic efficiency. Then, put down a specific use case, like task automation or curriculum personalization, mapping it to your objectives and thinking out general compliance and security factors. And if you think you lack the experience to do so, it might be better to turn to a consultant.
- Design an AI adoption strategy. Create a high-level AI implementation strategy, putting down desired outcomes and KPIs, amending current operations to include AI, and choosing tools that will help you monitor both adoption progress and AI performance.
Final thoughts
Artificial intelligence will continue to transform online learning, making it more enjoyable and results-driven. It could also help educators transition to new, more effective educational models with an emphasis on competencies, not grades. But to maximize the benefits of AI, both educators and EdTech providers will need to balance the AI’s impact and ethics, eliminating bias and constantly improving algorithm accuracy.
Feeling inspired yet? If you think about tapping into the future of online learning and expanding your eLearning software with AI capabilities, contact ITRex!
Don’t forget to give us your ? !




Online Education Trends: Top 4 AI Applications for Distance and Blended Learning was originally published in Becoming Human: Artificial Intelligence Magazine on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
