Originally from KDnuggets https://ift.tt/3gzg07s
Top KDnuggets tweets Aug 19-25: #MachineLearning-Handling Missing Data
Originally from KDnuggets https://ift.tt/32xlDhD
Data Versioning: Does it mean what you think it means?
Originally from KDnuggets https://ift.tt/3gsyQx7
From local Jupyter Notebooks to AWS Sagemaker.
I will be covering the basics and a generic overview of what are the basic services that you’d need to know for the certification, We will not be covering deployment in detail and a tutorial of how you might be able to use these services in this guide.
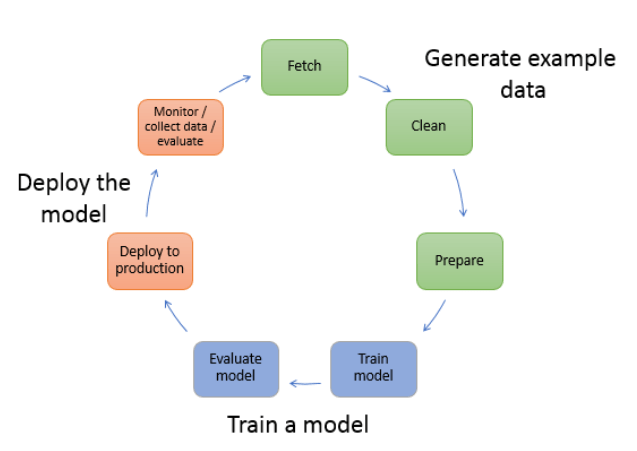
Now before you think about Machine Learning Specialty certification from AWS, if you haven’t done any certification from AWS before I will suggest you to complete AWS Cloud Practitioner.
Getting through the Cloud Practitioner is relatively easy and you will get perks. Perks like a free practice test of the next certification of your choice and 50 percent discount on you next certification exam.

There are certain key points before you embark on your journey for the Machine Learning Specialty certification:
- It is recommended that you have 1 to 2 years of experience of using AWS for ML projects and pipelines
- It is recommended for people who have relative expertise over manipulating Data sets, doing EDA, extraction, tuning etc.
- This exam is specifically built to weed out people who don’t have an analytics background and don’t have an in depth understanding of how Machine Learning pipelines work.
- It is my personal opinion that you at least understand using shell commands, Docker containers and model deployment to fully grasp the SageMaker services and pipelines.
I will be dividing the modules into few parts and my key focus will be on the SageMaker part of the certification because that alone could get you through the examination if you are very good at it.
Understanding AWS storage
For our certification we will be sticking to S3 but it’s recommended to have a minimum idea of other storage services.
Amazon Simple Storage Service or S3 stores data as objects within buckets
- You can set individual permissions(create, delete, view list of objects) for every bucket within S3
- S3 has 3 different storage classes: S3 Standard — General purpose storage for any type of data, typically used for frequently accessed data, S3 Intelligent — Tiering * — Automatic cost savings for data with unknown or changing access patterns, S3 Glacier ** — For long-term backups and archives with retrieval option from 1 minute to 12 hours. S3 standard being the most expensive.
- For our training purposes we can both provide them as separate channels using S3 buckets, we will get into more details later on while we go through the inbuilt algorithms.
- For writing and reading data using S3 you need to use boto3 framework which is preinstalled on the sagemaker note book instances.
For a better understanding of the S3 storage and availability, you can use the following link: https://aws.amazon.com/s3/storage-classes/
Jupyter notebooks: You could launch a jupyter notebook directly from an EC2 instance but you’re responsible for the following things:
- Creating the AMI(Amazon machine image, in short the OS)
- Launching those instances with this AMI.
- Configuring the autoscaling options depending on the task.
However, it’s very straight forward, you just need the ssh key pair work and add the device IP from which you are connected to the security group of the EC2 instance you are trying to connect. If you use this service you will have to take care of the Container registry, the endpoints, distribution of Training jobs and the tuning as well. The major advantage of using Sagemaker is that it manages all these things for you.
Let’s drive straight into AWS Sagemaker, we will cover some key concepts in depth as we try to understand the various components.
Sagemaker is a fully managed service by AWS to build, train and deploy machine Learning models at scale.
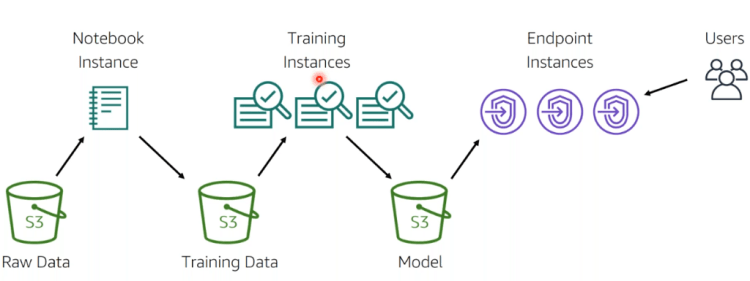
Building pipelines in Sagemaker:
You can read data from S3 in the following ways:
- Directly connect to S3
- Using AWS Glue to move data from Amazon RDS, Amazon DynamoDB, and Amazon Redshift into S3.
Training on AWS Sagemaker:
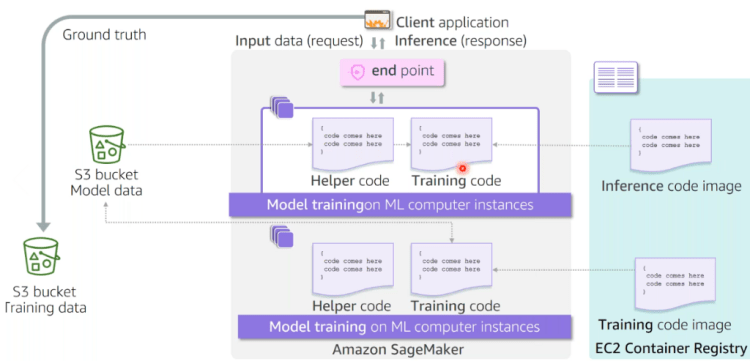
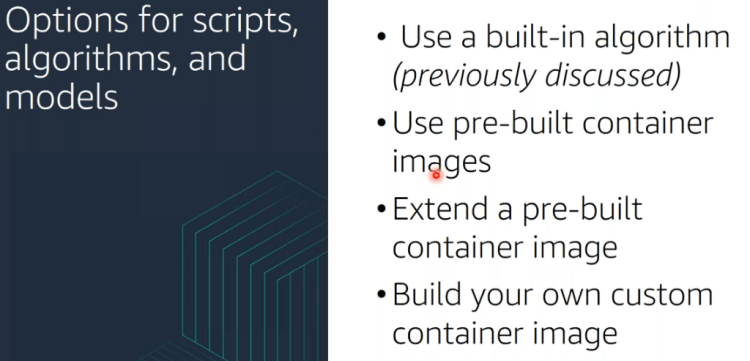
We will be covering the inbuilt algorithms in this part.
Trending AI Articles:
1. Machine Learning Concepts Every Data Scientist Should Know
3. AI Fail: To Popularize and Scale Chatbots, We Need Better Data
Just as you need the ingredients to cook a dish, A Sagemaker training job needs these key components:
- Training data S3 bucket URL(Remember, this must be globally unique!)
- What type of ML instance do you need for this job:
ml.t2.medium — ml stands for machine learning, the next section can be defined from the following table:
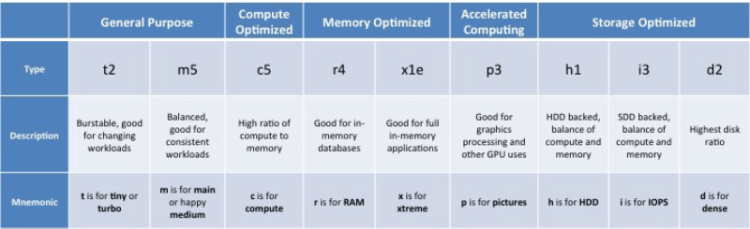
Apart from these instances you also have g4dn, inf1 instances that can be used for training
eia instances can be used for only for inference.
Choosing the right Training Algorithm
Once you have decided on the instance types to use for the notebook, you have the choice of following algorithms available already from AWS or use your own algorithm, we will cover that later:
Refer these tree diagrams for an easy recall.
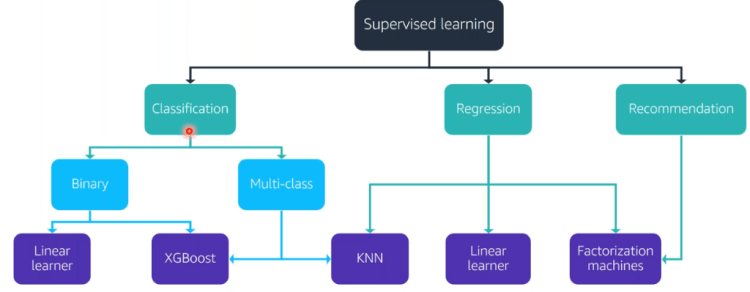
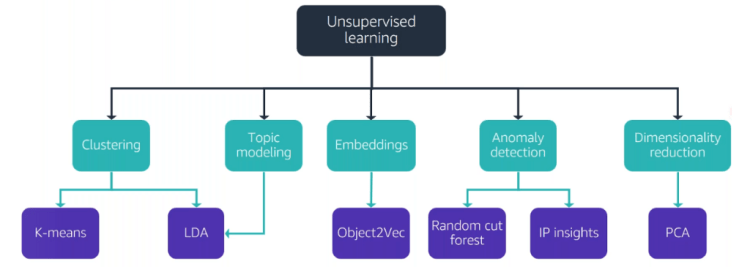


These include the parameters that are accepted for most of these algorithms(Tip! You might want to remember them)
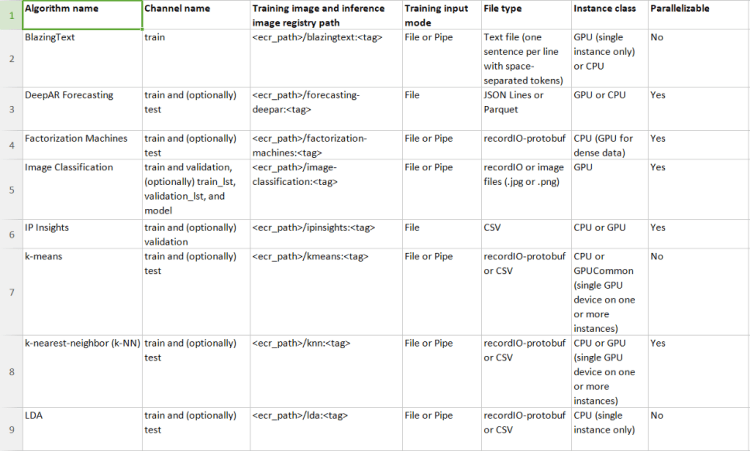
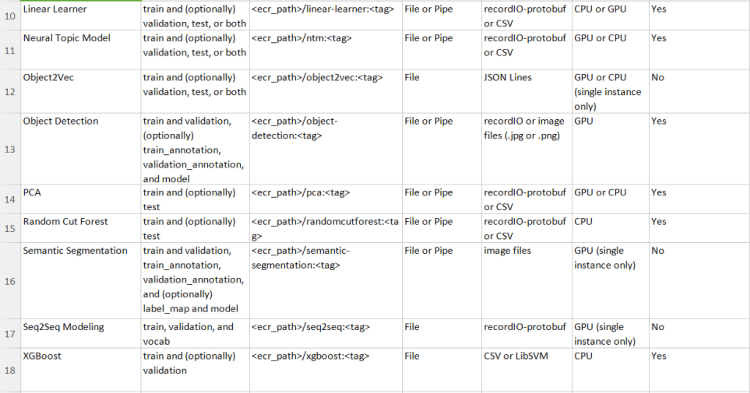
Transforming the Training Data
After you have launched a notebook, you need the following libraries to be imported, we’re taking the example of XGboost here:
import sagemaker
import boto3
from sagemaker.predictor import csv_serializer # Converts strings for HTTP POST requests on inference
import numpy as np # For performing matrix operations and numerical processing
import pandas as pd # For manipulating tabular data
from time import gmtime, strftime
import os
region = boto3.Session().region_name
smclient = boto3.Session().client('sagemaker')
from sagemaker import get_execution_role
#the IAM role that you created when you created your #notebook instance. You pass the role to the tuning job.
role = get_execution_role()
print(role)
bucket = 'sagemaker-MyBucket'
#replace with the name of your S3 bucket
prefix = 'sagemaker/DEMO-automatic-model-tuning-xgboost-dm'
Next Download the data and do EDA.
Hyperparameter Tuning
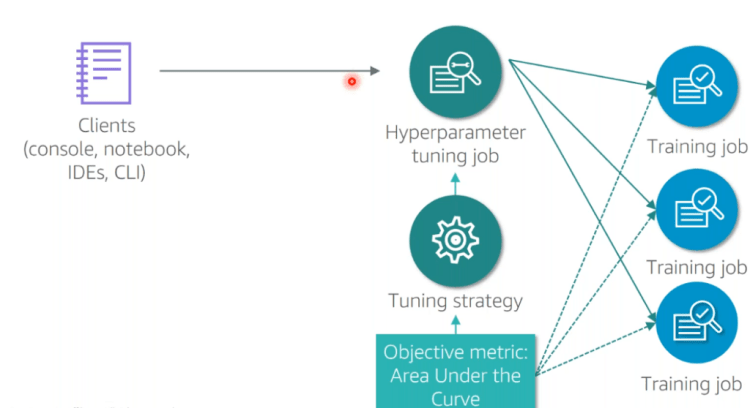
Hyperparameter tuning job specifications can be found here
from sagemaker.amazon.amazon_estimator import get_image_uri
training_image = get_image_uri(boto3.Session().region_name, 'xgboost')
s3_input_train = 's3://{}/{}/train'.format(bucket, prefix)
s3_input_validation ='s3://{}/{}/validation/'.format(bucket, prefix)
tuning_job_config = {
"ParameterRanges": {
"CategoricalParameterRanges": [],
"ContinuousParameterRanges": [
{
"MaxValue": "1",
"MinValue": "0",
"Name": "eta"
},
{
"MaxValue": "2",
"MinValue": "0",
"Name": "alpha"
},
{
"MaxValue": "10",
"MinValue": "1",
"Name": "min_child_weight"
}
],
"IntegerParameterRanges": [
{
"MaxValue": "10",
"MinValue": "1",
"Name": "max_depth"
}
]
},
"ResourceLimits": {
"MaxNumberOfTrainingJobs": 20,
"MaxParallelTrainingJobs": 3
},
"Strategy": "Bayesian",
"HyperParameterTuningJobObjective": {
"MetricName": "validation:auc",
"Type": "Maximize"
}
}
training_job_definition = {
"AlgorithmSpecification": {
"TrainingImage": training_image,
"TrainingInputMode": "File"
},
"InputDataConfig": [
{
"ChannelName": "train",
"CompressionType": "None",
"ContentType": "csv",
"DataSource": {
"S3DataSource": {
"S3DataDistributionType": "FullyReplicated",
"S3DataType": "S3Prefix",
"S3Uri": s3_input_train
}
}
},
{
"ChannelName": "validation",
"CompressionType": "None",
"ContentType": "csv",
"DataSource": {
"S3DataSource": {
"S3DataDistributionType": "FullyReplicated",
"S3DataType": "S3Prefix",
"S3Uri": s3_input_validation
}
}
}
],
"OutputDataConfig": {
"S3OutputPath": "s3://{}/{}/output".format(bucket,prefix)
},
"ResourceConfig": {
"InstanceCount": 2,
"InstanceType": "ml.c4.2xlarge",
"VolumeSizeInGB": 10
},
"RoleArn": role,
"StaticHyperParameters": {
"eval_metric": "auc",
"num_round": "100",
"objective": "binary:logistic",
"rate_drop": "0.3",
"tweedie_variance_power": "1.4"
},
"StoppingCondition": {
"MaxRuntimeInSeconds": 43200
}
}
tuning_job_name = "MyTuningJob"
smclient.create_hyper_parameter_tuning_job(HyperParameterTuningJobName = tuning_job_name,
HyperParameterTuningJobConfig = tuning_job_config,
TrainingJobDefinition = training_job_definition)
Monitoring can be done directly on the AWS console itself
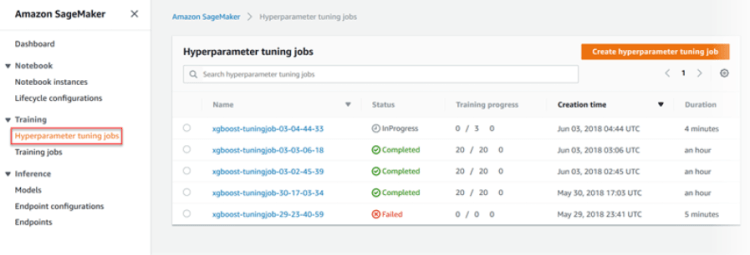
Evaluating is very straight forward,You use a Jupyter notebook in your Amazon SageMaker notebook instance to train and evaluate your model.
- You either use AWS SDK for Python (Boto) or the high-level Python library that Amazon SageMaker provides to send requests to the model for inferences.
How to Debug?
Say hello to the Amazon SageMaker Debugger!
It provides full visibility into model training by monitoring, recording, analyzing, and visualizing training process tensors. Using Amazon SageMaker Debugger Python SDK we can interact with objects that will help us debug the jobs. If you are more interested in the api, you can check it out here.
You can check the list of rules here.
Deploying the model
- After I created a model using createmodel api. Speicify S3 path where the model artifacts are stored and the Docker registry path for the image that contains the inference code.
- Create an HTTPS endpoint configuration i.e: Configure the endpoint to elastically scale the deployed ML compute instances for each production variant job, for further details about the API, check CreateEndpointConfig api.
- Next launch it using the CreateEndpoint api
I will discuss more about the details of deployment in the next part.
Don’t forget to give us your ? !




From local Jupyter Notebooks to AWS Sagemaker. was originally published in Becoming Human: Artificial Intelligence Magazine on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
NLP Tutorial for Machine Learning
Natural Language Processing (NLP) consists of developing applications and services capable of understanding human languages. Some…
Continue reading on Becoming Human: Artificial Intelligence Magazine »
Via https://becominghuman.ai/nlp-tutorial-for-machine-learning-7fdac1f815b5?source=rss—-5e5bef33608a—4
source https://365datascience.weebly.com/the-best-data-science-blog-2020/nlp-tutorial-for-machine-learning
ResNet: Convolution Neural Network
ResNet : Convolution Neural Network
ResNet, also known as residual neural network, refers to the idea of adding residual learning to the traditional convolutional neural network, which solves the problem of gradient dispersion and accuracy degradation (training set) in deep networks, so that the network can get more and more The deeper, both the accuracy and the speed are controlled.
The problem caused by increasing depth :
- The first problem brought by increasing depth is the problem of gradient explosion / dissipation . This is because as the number of layers increases, the gradient of backpropagation in the network will become unstable with continuous multiplication, and become particularly large or special. small. Among them , the problem of gradient dissipation often occurs. i.e effect of the weight decreases.
- Another problem of increasing depth is the problem of network degradation, that is, as the depth increases, the performance of the network will become worse and worse, which is directly reflected in the decrease in accuracy on the training set. The residual network article solves this problem. And after this problem is solved, the depth of the network has increased by several orders of magnitude.
Trending AI Articles:
1. Machine Learning Concepts Every Data Scientist Should Know
3. AI Fail: To Popularize and Scale Chatbots, We Need Better Data
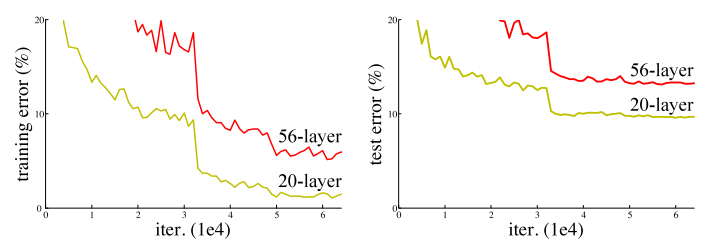
From above figure we can conclude that till 20th layer its ok. But if we increase the number of layers , instead of increase in accuracy it starts decreasing.Based on this problem the ResNet comes into picture.

ResNet :
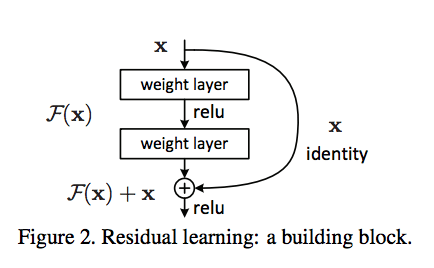
The block contains two branches (i) Indentity branch that refers to own itself i.e x . (ii) F(x) referes to the network part called residual mapping .
Assume x as input .If weights over which we are training are negative just skip the input. We are passing those weights into relu activation function which not allow to pass it for further calculation.
Why we use identity blog if there is relu which chop off all negative weights ?
The main architecture contains image → convolution → relu . For negative weights if I will able to stop is to pass in convolution layer and make unnecessary calculations and then is send to the relu , then is can be say I will able to reduce the parameters as well as calculations.
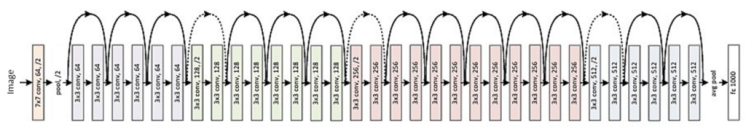
This is equivalent to reducing the amount of parameters for the same number of layers , so it can be extended to deeper models. So the author proposed ResNet with 50, 101 , and 152 layers , and not only did not have degradation problems, the error rate was greatly reduced, and the computational complexity was also kept at a very low level .
Don’t forget to give us your ? !




ResNet : Convolution Neural Network was originally published in Becoming Human: Artificial Intelligence Magazine on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
Via https://becominghuman.ai/resnet-convolution-neural-network-e10921245d3d?source=rss—-5e5bef33608a—4
source https://365datascience.weebly.com/the-best-data-science-blog-2020/resnet-convolution-neural-network
How to Optimize Your CV for a Data Scientist Career
Originally from KDnuggets https://ift.tt/3lkPt1j
Breaking Privacy in Federated Learning
Originally from KDnuggets https://ift.tt/2CZtb3M
KDnuggets News 20:n33 Aug 26: If I had to start learning Data Science again how would I do it? Must-read NLP and Deep Learning articles for Data Scientists
Originally from KDnuggets https://ift.tt/3aZ4Zva
Unifying Data Pipelines and Machine Learning with Apache Spark and Amazon SageMaker
Originally from KDnuggets https://ift.tt/32qfm73

