Transfer learning — Working Code
How a Pre-Trained CNN Network could be used as a Feature Extractor
Objective : Learn to use Pre-Trained network to classify entirely different sets of data

The ability to use a pre-trained model as a “shortcut” to learn patterns from data it was not originally trained on.
The beauty of deep learning lies in the fact, that pre-trained models can be used to classify entirely different sets of data. This internally uses the pre-trained weights of these deep neural net architectures (trained on ImageNet dataset) to apply on our own dataset?
List of such pre-trained models in the industry are:
- Xception
- VGG16
- VGG19
- ResNet50
- InceptionV3
- InceptionResNetV2
- MobileNet
//These pre-trained models are available as part of keras.
Some popular deep learning frameworks at present are Tensorflow, Theano, Caffe, Pytorch, CNTK, MXNet, Torch, deeplearning4j, Caffe2 among many others.

Keras:
Keras is a high-level API, written in Python and capable of running on top of TensorFlow, Theano, or CNTK. Keras provides a simple and modular API to create and train Neural Networks, hiding most of the complicated details under the hood. This makes it easy to get you started on your Deep Learning journey.
Keras is a high-level API that uses deep learning libraries like Theano or TensorFlow as the backend. These libraries, in turn, talk to the hardware via lower level libraries. For example, if you run the program on a CPU, Tensorflow or Theano use BLAS libraries. On the other hand, when you run on a GPU, they use CUDA and cuDNN libraries.
If you are setting up a new system, you might want to look at this_article
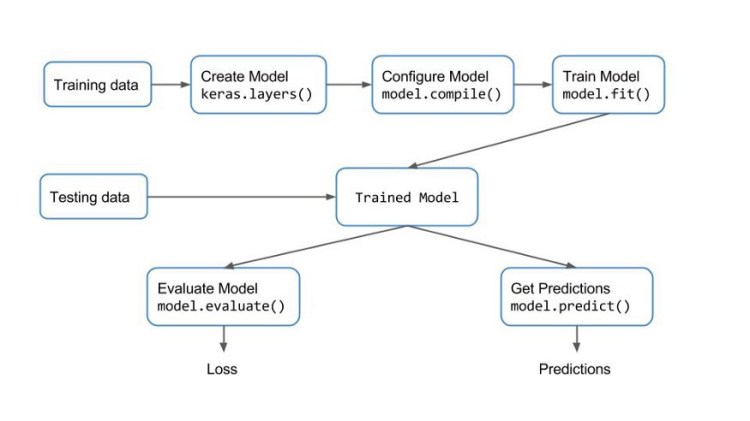
Keras provides a very simple workflow for training and evaluating the models. It is described with the following diagram.
Transfer Learning via Feature Extraction Example: flower classification:
Step 0: Arranging your Data — Train/Test and Configuration File
we are using FLOWERS17 dataset from the University of Oxford, Download the Data Set from here. You can choose to any data of your choice and perform classification using the below code. Place your labelled train data and test data in the “dataset” folder as shown in the Figure 1.3 below.
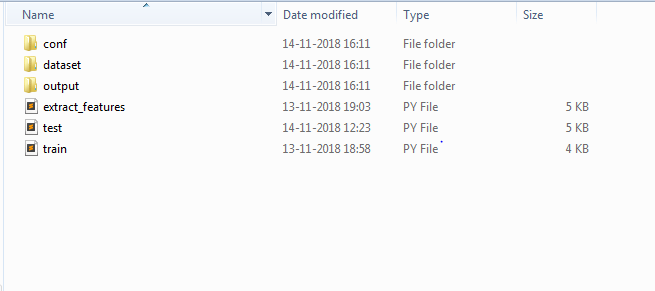
Save the below json as conf.json inside conf folder as shown in the above folder structure.
make changes to the “model”, “feature_path”, “label_path”, ”results” based on the network that you are going to choose. In the below example, i have used mobilenet pre-trained network.
“num_classes” denotes the number of classes used in your dataset. This parameter depends on the number of classes your dataset has. Example if you are classifying cats vs dogs, then there are only 2 classes. In this example of Flower Dataset we have 17 types of flowers , so the “num_classes” parameter is 17.
{
"model" : "mobilenet",
"weights" : "imagenet",
"include_top" : false,
"train_path" : "dataset/train",
"test_path" : "dataset/test",
"features_path" : "output/flowers_17/mobilenet/features.h5",
"labels_path" : "output/flowers_17/mobilenet/labels.h5",
"results" : "output/flowers_17/mobilenet/results.txt",
"classifier_path" :"output/flowers_17/mobilenet/classifier.pickle",
"model_path" : "output/flowers_17/mobilenet/model",
"test_size" : 0.10,
"seed" : 9,
"num_classes" : 17
}
Trending AI Articles:
1. Machine Learning Concepts Every Data Scientist Should Know
3. AI Fail: To Popularize and Scale Chatbots, We Need Better Data
Similarly if you are to use, inceptionV3 with only 4 classes instead of mobilenet, Use the below json.
{
“model” : “inceptionv3”,
“weights” : “imagenet”,
“include_top” : false,
“train_path” : “dataset/train”,
“test_path” : “dataset/test”,
“features_path” : “output/flowers_17/inceptionv3/features.h5”,
“labels_path” : “output/flowers_17/inceptionv3/labels.h5”,
“results” : “output/flowers_17/inceptionv3/results.txt”, “classifier_path”:“output/flowers_17/inceptionv3/classifier.pickle”,
“model_path” : “output/flowers_17/inceptionv3/model”,
“test_size” : 0.10,
“seed” : 9,
“num_classes” : 4
}
Step 1: Feature Extract
Copy the below code in a file and save it as extract_features.py file as shown in the folder structure Figure 1.3 above
# filter warnings
import warnings
warnings.simplefilter(action="ignore", category=FutureWarning)
# keras imports
from keras.applications.vgg16 import VGG16, preprocess_input
from keras.applications.vgg19 import VGG19, preprocess_input
from keras.applications.xception import Xception, preprocess_input
from keras.applications.resnet50 import ResNet50, preprocess_input
from keras.applications.inception_resnet_v2 import InceptionResNetV2, preprocess_input
from keras.applications.mobilenet import MobileNet, preprocess_input
from keras.applications.inception_v3 import InceptionV3, preprocess_input
from keras.preprocessing import image
from keras.models import Model
from keras.models import model_from_json
from keras.layers import Input
# other imports
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
import numpy as np
import glob
import cv2
import h5py
import os
import json
import datetime
import time
# load the user configs
with open('conf/conf.json') as f:
config = json.load(f)
# config variables
model_name = config["model"]
weights = config["weights"]
include_top = config["include_top"]
train_path = config["train_path"]
features_path = config["features_path"]
labels_path = config["labels_path"]
test_size = config["test_size"]
results = config["results"]
model_path = config["model_path"]
# start time
print ("[STATUS] start time - {}".format(datetime.datetime.now().strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M")))
start = time.time()
# create the pretrained models
# check for pretrained weight usage or not
# check for top layers to be included or not
if model_name == "vgg16":
base_model = VGG16(weights=weights)
model = Model(input=base_model.input, output=base_model.get_layer('fc1').output)
image_size = (224, 224)
elif model_name == "vgg19":
base_model = VGG19(weights=weights)
model = Model(input=base_model.input, output=base_model.get_layer('fc1').output)
image_size = (224, 224)
elif model_name == "resnet50":
base_model = ResNet50(weights=weights)
model = Model(input=base_model.input, output=base_model.get_layer('flatten').output)
image_size = (224, 224)
elif model_name == "inceptionv3":
base_model = InceptionV3(include_top=include_top, weights=weights, input_tensor=Input(shape=(299,299,3)))
model = Model(input=base_model.input, output=base_model.get_layer('custom').output)
image_size = (299, 299)
elif model_name == "inceptionresnetv2":
base_model = InceptionResNetV2(include_top=include_top, weights=weights, input_tensor=Input(shape=(299,299,3)))
model = Model(input=base_model.input, output=base_model.get_layer('custom').output)
image_size = (299, 299)
elif model_name == "mobilenet":
base_model = MobileNet(include_top=include_top, weights=weights, input_tensor=Input(shape=(224,224,3)), input_shape=(224,224,3))
model = Model(input=base_model.input, output=base_model.get_layer('custom').output)
image_size = (224, 224)
elif model_name == "xception":
base_model = Xception(weights=weights)
model = Model(input=base_model.input, output=base_model.get_layer('avg_pool').output)
image_size = (299, 299)
else:
base_model = Noneprint ("[INFO] successfully loaded base model and model...")
# path to training dataset
train_labels = os.listdir(train_path)
# encode the labels
print ("[INFO] encoding labels...")
le = LabelEncoder()
le.fit([tl for tl in train_labels])
# variables to hold features and labels
features = []
labels = []
# loop over all the labels in the folder
count = 1
for i, label in enumerate(train_labels):
cur_path = train_path + "/" + label
count = 1
for image_path in glob.glob(cur_path + "/*.jpg"):
img = image.load_img(image_path, target_size=image_size)
x = image.img_to_array(img)
x = np.expand_dims(x, axis=0)
x = preprocess_input(x)
feature = model.predict(x)
flat = feature.flatten()
features.append(flat)
labels.append(label)
print ("[INFO] processed - " + str(count))
count += 1
print ("[INFO] completed label - " + label)
# encode the labels using LabelEncoder
le = LabelEncoder()
le_labels = le.fit_transform(labels)
# get the shape of training labels
print ("[STATUS] training labels: {}".format(le_labels))
print ("[STATUS] training labels shape: {}".format(le_labels.shape))
# save features and labels
h5f_data = h5py.File(features_path, 'w')
h5f_data.create_dataset('dataset_1', data=np.array(features))h5f_label = h5py.File(labels_path, 'w')
h5f_label.create_dataset('dataset_1', data=np.array(le_labels))h5f_data.close()
h5f_label.close()
# save model and weights
model_json = model.to_json()
with open(model_path + str(test_size) + ".json", "w") as json_file:
json_file.write(model_json)
# save weights
model.save_weights(model_path + str(test_size) + ".h5")
print("[STATUS] saved model and weights to disk..")print ("[STATUS] features and labels saved..")
# end time
end = time.time()
print ("[STATUS] end time - {}".format(datetime.datetime.now().strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M")))
Step 2: Train
Copy the below code in a file and save it as train.py file as shown in the folder structure Figure 1.3 above
# organize imports
from __future__ import print_functionfrom sklearn.metrics import classification_report
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
import numpy as np
import h5py
import os
import json
import pickle
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# load the user configs
with open('conf/conf.json') as f:
config = json.load(f)
# config variables
test_size = config["test_size"]
seed = config["seed"]
features_path = config["features_path"]
labels_path = config["labels_path"]
results = config["results"]
classifier_path = config["classifier_path"]
train_path = config["train_path"]
num_classes = config["num_classes"]
classifier_path = config["classifier_path"]
# import features and labels
h5f_data = h5py.File(features_path, 'r')
h5f_label = h5py.File(labels_path, 'r')
features_string = h5f_data['dataset_1']
labels_string = h5f_label['dataset_1']
features = np.array(features_string)
labels = np.array(labels_string)
h5f_data.close()
h5f_label.close()
# verify the shape of features and labels
print ("[INFO] features shape: {}".format(features.shape))
print ("[INFO] labels shape: {}".format(labels.shape))print ("[INFO] training started...")
# split the training and testing data
(trainData, testData, trainLabels, testLabels) = train_test_split(np.array(features),
np.array(labels),
test_size=test_size,
random_state=seed)print ("[INFO] splitted train and test data...")
print ("[INFO] train data : {}".format(trainData.shape))
print ("[INFO] test data : {}".format(testData.shape))
print ("[INFO] train labels: {}".format(trainLabels.shape))
print ("[INFO] test labels : {}".format(testLabels.shape))
# use logistic regression as the model
print ("[INFO] creating model...")
model = LogisticRegression(random_state=seed)
model.fit(trainData, trainLabels)
# use rank-1 and rank-5 predictions
print ("[INFO] evaluating model...")
f = open(results, "w")
rank_1 = 0
rank_5 = 0
# loop over test data
for (label, features) in zip(testLabels, testData):
# predict the probability of each class label and
# take the top-5 class labels
predictions = model.predict_proba(np.atleast_2d(features))[0]
predictions = np.argsort(predictions)[::-1][:5]
# rank-1 prediction increment
if label == predictions[0]:
rank_1 += 1
# rank-5 prediction increment
if label in predictions:
rank_5 += 1
# convert accuracies to percentages
rank_1 = (rank_1 / float(len(testLabels))) * 100
rank_5 = (rank_5 / float(len(testLabels))) * 100
# write the accuracies to file
f.write("Rank-1: {:.2f}%\n".format(rank_1))
f.write("Rank-5: {:.2f}%\n\n".format(rank_5))
# evaluate the model of test data
preds = model.predict(testData)
# write the classification report to file
f.write("{}\n".format(classification_report(testLabels, preds)))
f.close()
# dump classifier to file
print ("[INFO] saving model...")
pickle.dump(model, open(classifier_path, 'wb'))
# display the confusion matrix
print ("[INFO] confusion matrix")
# get the list of training lables
labels = sorted(list(os.listdir(train_path)))
# plot the confusion matrix
cm = confusion_matrix(testLabels, preds)
sns.heatmap(cm,
annot=True,
cmap="Set2")
plt.show()
Step 3: Test
Copy the below code in a file and save it as test.py file as shown in the folder structure Figure 1.3 above
# test script to preform prediction on test images inside
# dataset/test/ -- image_1.jpg -- image_2.jpg
# ...
# organize imports
from __future__ import print_function
# keras imports
from keras.applications.vgg16 import VGG16, preprocess_input
from keras.applications.vgg19 import VGG19, preprocess_input
from keras.applications.xception import Xception, preprocess_input
from keras.applications.resnet50 import ResNet50, preprocess_input
from keras.applications.inception_resnet_v2 import InceptionResNetV2, preprocess_input
from keras.applications.mobilenet import MobileNet, preprocess_input
from keras.applications.inception_v3 import InceptionV3, preprocess_input
from keras.preprocessing import image
from keras.models import Model
from keras.models import model_from_json
from keras.layers import Input
# other imports
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
import numpy as np
import os
import json
import pickle
import cv2
# load the user configs
with open('conf/conf.json') as f:
config = json.load(f)
# config variables
model_name = config["model"]
weights = config["weights"]
include_top = config["include_top"]
train_path = config["train_path"]
test_path = config["test_path"]
features_path = config["features_path"]
labels_path = config["labels_path"]
test_size = config["test_size"]
results = config["results"]
model_path = config["model_path"]
seed = config["seed"]
classifier_path = config["classifier_path"]
# load the trained logistic regression classifier
print ("[INFO] loading the classifier...")
classifier = pickle.load(open(classifier_path, 'rb'))
# pretrained models needed to perform feature extraction on test data too!
if model_name == "vgg16":
base_model = VGG16(weights=weights)
model = Model(input=base_model.input, output=base_model.get_layer('fc1').output)
image_size = (224, 224)
elif model_name == "vgg19":
base_model = VGG19(weights=weights)
model = Model(input=base_model.input, output=base_model.get_layer('fc1').output)
image_size = (224, 224)
elif model_name == "resnet50":
base_model = ResNet50(weights=weights)
model = Model(input=base_model.input, output=base_model.get_layer('flatten').output)
image_size = (224, 224)
elif model_name == "inceptionv3":
base_model = InceptionV3(include_top=include_top, weights=weights, input_tensor=Input(shape=(299,299,3)))
model = Model(input=base_model.input, output=base_model.get_layer('custom').output)
image_size = (299, 299)
elif model_name == "inceptionresnetv2":
base_model = InceptionResNetV2(include_top=include_top, weights=weights, input_tensor=Input(shape=(299,299,3)))
model = Model(input=base_model.input, output=base_model.get_layer('custom').output)
image_size = (299, 299)
elif model_name == "mobilenet":
base_model = MobileNet(include_top=include_top, weights=weights, input_tensor=Input(shape=(224,224,3)), input_shape=(224,224,3))
model = Model(input=base_model.input, output=base_model.get_layer('custom').output)
image_size = (224, 224)
elif model_name == "xception":
base_model = Xception(weights=weights)
model = Model(input=base_model.input, output=base_model.get_layer('avg_pool').output)
image_size = (299, 299)
else:
base_model = None
# get all the train labels
train_labels = os.listdir(train_path)
# get all the test images paths
test_images = os.listdir(test_path)
# loop through each image in the test data
for image_path in test_images:
path = test_path + "/" + image_path
img = image.load_img(path, target_size=image_size)
x = image.img_to_array(img)
x = np.expand_dims(x, axis=0)
x = preprocess_input(x)
feature = model.predict(x)
flat = feature.flatten()
flat = np.expand_dims(flat, axis=0)
preds = classifier.predict(flat)
prediction = train_labels[preds[0]]
# perform prediction on test image
print ("I think it is a " + train_labels[preds[0]])
img_color = cv2.imread(path, 1)
cv2.putText(img_color, "I think it is a " + prediction, (140,445), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1, (0,0,255), 2)
cv2.imshow("test", img_color)
# key tracker
key = cv2.waitKey(0) & 0xFF
if (key == ord('q')):
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
OUTPUT:
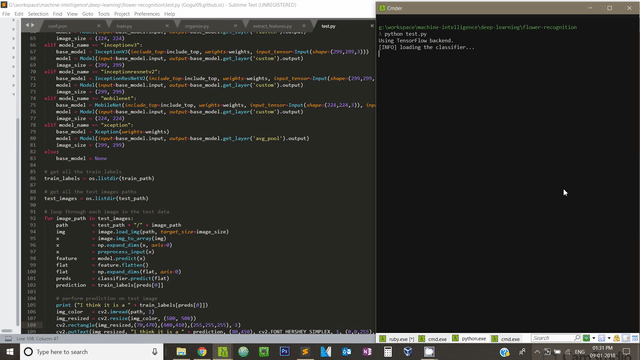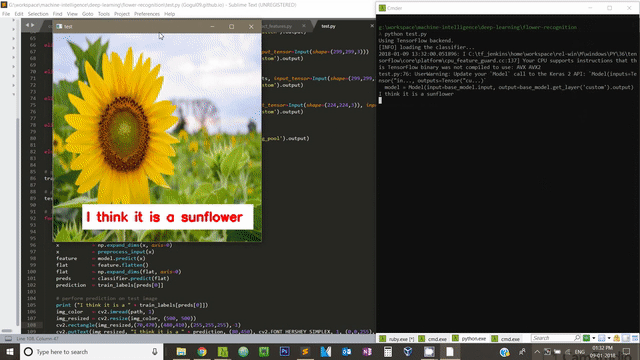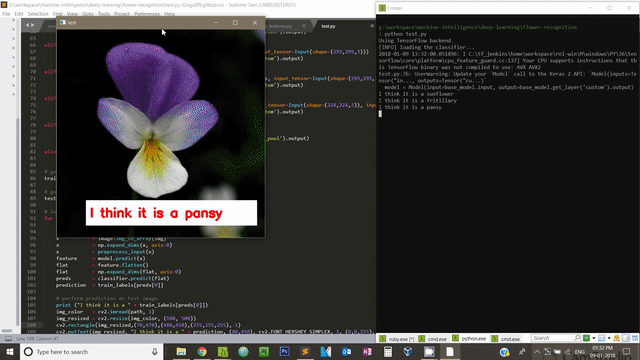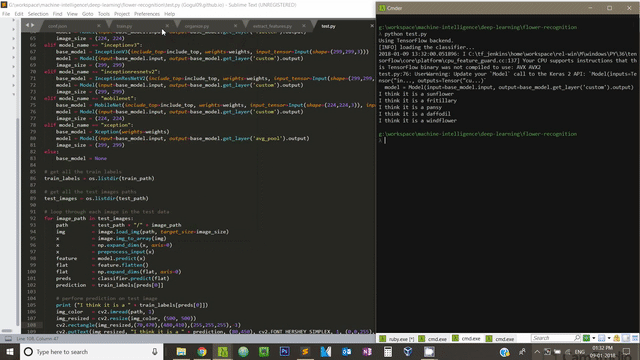
If you enable GPU in your computer, you can speed up feature extraction as well as training process.
Don’t forget to give us your ? !




Transfer Learning | Treating networks as arbitrary feature extractors | Computer Vision | CNN | was originally published in Becoming Human: Artificial Intelligence Magazine on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
Via https://becominghuman.ai/transfer-learning-working-code-f2fe63dde981?source=rss—-5e5bef33608a—4