Originally from KDnuggets https://ift.tt/38XJUjm
Auto Rotate Images Using Deep Learning
Originally from KDnuggets https://ift.tt/3fsFYK7
How I Solved Sudoku With a Business Rules Engine
Originally from KDnuggets https://ift.tt/3fruaI6
Top Stories Jul 6-12: A Laymans Guide to Data Science Workflow; Free MIT Courses on Calculus: The Key to Understanding Deep Learning
Originally from KDnuggets https://ift.tt/2OkUpnt
Foundations of Data Science: The Free eBook
Originally from KDnuggets https://ift.tt/2OkJiLh
How to Use Data Augmentation to 10x Your Image Datasets

It’s a known fact that machine learning models need data to be trained. Without training data, even complex algorithms are essentially useless. So what do you do when you don’t have the necessary amount of data?
Over the years, researchers have developed a variety of ingenious solutions. Data Augmentation is one of these solutions. Instead of trying to find and label more data points, we construct new ones based on what we have.
Wait? Can we do that? Sure we can. Though it is not always easy and it might not produce the best results, it’s still a viable alternative.
Expanding a dataset with Data Augmentation methods is not only helpful for the challenge of limited data. It can also reduce overfitting and improve the generalization of our models because it increases the diversity of our training set.
So let’s cut to the chase: How can we perform Data Augmentation?
I think the image below says it all. In this article, we will focus on image augmentation as it is currently the most active field of research, but most of these techniques can be applied to all sorts of data.
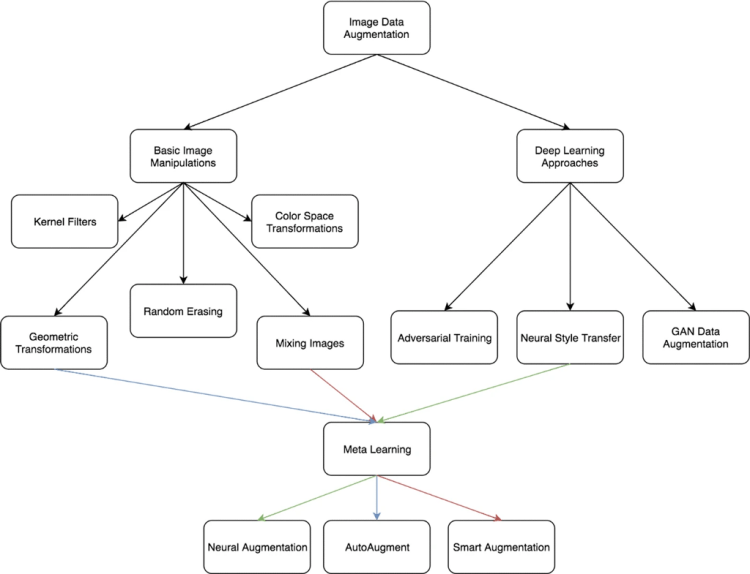
Basic Image Manipulations
The first simple thing to do is to perform geometric transformations to the image. You might assume that machine learning can easily distinguish two identical images with different rotations, but it can’t.
Image flipping, cropping, rotations, and translations are some obvious first steps. We can also change the color space of the image using contrast, sharpening, white balancing, color jittering, random color manipulation and many other techniques (called photometric transformations). If you’ve ever used Instagram filters or Snapseed, then you’ll get what I’m saying. You can get as creative as you want.

Moreover, you can mix images together, randomly erase segments of an image, and of course, combine all the above in all sorts of various ways.
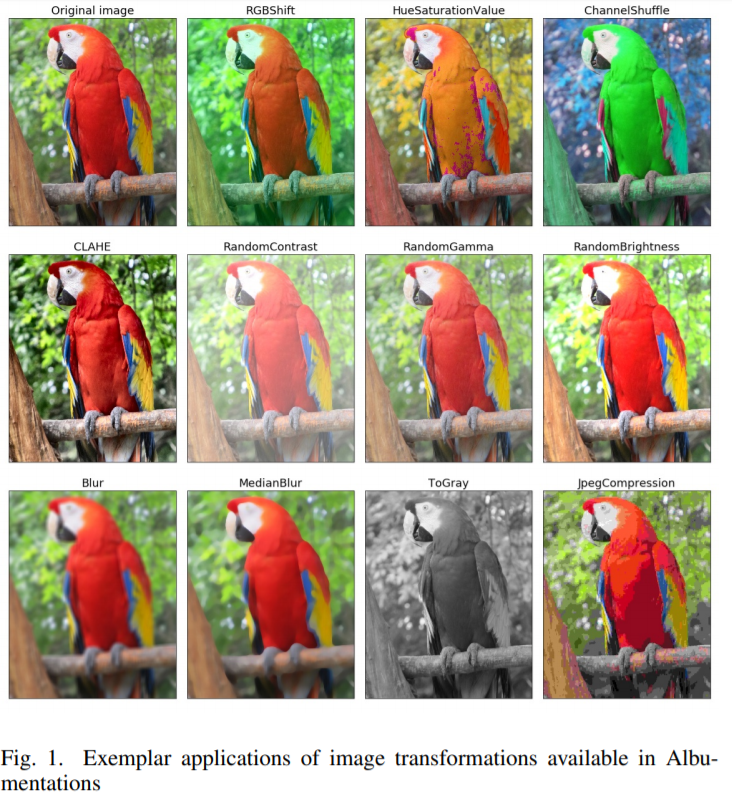

Data Augmentation using Machine Learning
Besides basic image manipulations, more and more engineers are starting to use machine and deep learning techniques to augment their data. Think about it this way: We can use machine learning models to produce more data to train more machine learning models. Some of the most promising works are below:
Feature Space Augmentation and Autoencoders
In the above examples, we transformed images on the input space. We can also apply transformations in feature space.
With Neural Networks we can very efficiently map high dimensional inputs (such as images) in lower-dimensional representation (known as feature or latent space). Think of it as encoding a 3D tensor into a 1D vector without losing too much information. Having an image encoding in a few dimensions makes it much easier to perform augmentations.
Many interesting papers suggest different ways to do so such as joining k nearest neighbors together, adding noise, interpolation, and more.
Trending AI Articles:
1. Natural Language Generation:
The Commercial State of the Art in 2020
4. Becoming a Data Scientist, Data Analyst, Financial Analyst and Research Analyst
Autoencoders have proven the best choice to extract feature space representations. Autoencoders are a special type of neural networks, which try to reconstruct the input. They consist of two networks, an encoder and a decoder. The encoder takes the input and encodes it into a vector in lower dimensions (feature space). The decoder takes that vector and tries to reconstruct the original input.
By doing this, the latent vector in the middle contains all the information about the dataset and can be extracted to do all sorts of things, including data augmentation.
GAN-based Data Augmentation
Generative Modeling is one of the most exciting techniques at the moment because it can produce completely new images. Generative models can generate new patterns in data because they learn the distribution of the data and not the boundary between them (as is common in most machine learning models).
In that direction, Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN) have become the industry and research standard. GANs consist of two networks, the generator, and the discriminator. The generator’s job is to produce fake data with nothing but noise as input. The second model, the discriminator, receives as input both the real images and the fake images (produced by the generator) and learns to identify the image as fake or real.
As these networks compete against each other, and by training them simultaneously (in a process called adversarial training), the magic begins:
The generator becomes better and better at image generation because its ultimate goal is to fool the discriminator. The discriminator, in turn, becomes better and better at distinguishing fake from real images, because its goal is to not be fooled. The result is incredibly realistic fake data from the generator.
GANs have produced some of the most realistic images and videos we’ve ever seen. Remember deep fakes? That was all the work of GANs. So why not use them for data augmentation instead of replacing Jack Nickolson with Jim Carrey in the Shining?
Meta-Learning
Last but not least, we have Meta-Learning. Meta-Learning is a relatively new area, in which we use neural networks to optimize other neural networks by tuning their hyperparameters, improving their layout, and more. In terms of data augmentation, things get a little more complicated.
In simple terms, we use a classification network to tune an augmentation network into generating better images.
Take a look at the image below: By feeding random images to the Augmentation Network (most likely a GAN), it will generate augmented images. Both the augmented image and the original are passed into a second network, which compares them and tells us how good the augmented image is. After repeating the process the augmentation network becomes better and better at producing new images.
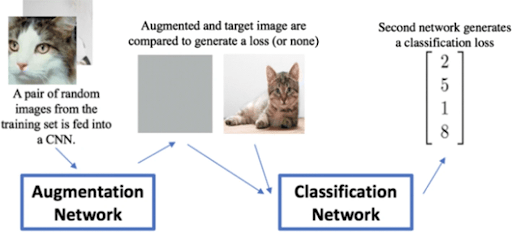
Of course, this procedure is not the only one available, but it’s a very good starting point for the different research papers in the area.
Conclusion
Data Augmentation is by no means an easy task. There have been quite a few interesting works (here is a collection of them) but there is still much room for improvement. For example, we can still improve the quality of GANs samples, find new ways to use Meta-Learning, and perhaps establish a taxonomy of different augmentation techniques.
And of course, we can still discover new ways to use these techniques in other forms of data, such as text, tabular data, graph data, and more. Why not also expand beyond that? How about Reinforcement Learning? Or search algorithms? The stage is yours.
Original article by Sergios Karagiannakos, reposted with permission.
Don’t forget to give us your ? !




How to Use Data Augmentation to 10x Your Image Datasets was originally published in Becoming Human: Artificial Intelligence Magazine on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
Part 1: Image Processing

Sudoku Solver AI with OpenCV
We will be creating a Sudoku Solver AI using python and Open CV to read a Sudoku puzzle from an image and solving it. There a lot of methods to achieve this goal. Thus in this series, I have compiled the best methods I could find/research along with some hacks/tricks I learned along the way.
This article is a part of the series Sudoku Solver AI with OpenCV.
Part 1: Image Processing
Part 2: Sudoku and Cell Extraction
Part 3: Solving the Sudoku
What is Sudoku?
Sudoku is a logic-based, combinatorial number-placement puzzle with a 9×9 grid with digits so that each column, each row, and each of the nine 3×3 subgrids that compose the grid contain all of the digits from 1 to 9. (Wikipedia).
To learn more about how to solve the same, check out Peter Norvig’s Solving Every Sudoku Puzzle.
Let us get started…
Steps
I am trying to be as detailed as possible in listing the steps along with there descriptions.
- Import the image
- Pre Processing the Image
2.1 Gaussian blur: We need to gaussian blur the image to reduce noise in thresholding algorithm
2.2 Thresholding: Segmenting the regions of the image
2.3 Dilating the image: In cases like noise removal, erosion is followed by dilation.

1. Import the image
Firstly, we need to imposrt the image of the Sudoku. We will be using openCV for this.
# a function to read the
def read_img():
# I wanted the user to have the liberty to choose the image
print("Enter image name: ")
image_url = input()
#image url also conatins the image extension eg. .jpg or .png
#reading in greayscale
img = cv2.imread(image_url, img = cv2.imread(image_url, cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE))
2. Pre Processing the Image
2.1 Gaussian blur:
We need to Blur the image using gaussian blur to reduce noise obtained in thresholding algorithm (adaptive thresholding). To know more about what exactly is Gaussian blur, https://datacarpentry.org/image-processing/06-blurring/.
Syntax: GaussianBlur(src, dst, ksize, sigmaX)
- src − input image
- dst − output image
- ksize − A Size object representing the size of the kernel.
- sigmaX − A variable of the type double representing the Gaussian kernel standard deviation in X direction.
# Note that kernel sizes must be positive and odd and the kernel must be square.
proc = cv2.GaussianBlur(img.copy(), (9, 9), 0)
Trending AI Articles:
1. Natural Language Generation:
The Commercial State of the Art in 2020
4. Becoming a Data Scientist, Data Analyst, Financial Analyst and Research Analyst
2.2 Thresholding Algorithms
Why is thresholding used in image processing? We need to separate an image into some regions (or their contours), the process is called segmentation. So, one of the ways to segment such regions is called thresholding.
# cv2.adaptiveThreshold(src, maxValue, adaptiveMethod, thresholdType, blockSize, constant(c))
# blockSize – Size of a pixel neighborhood that is used to calculate a threshold value for the pixel: 3, 5, 7, and so on.
# C – Constant subtracted from the mean or weighted mean (see the details below). Normally, it is positive but may be zero or negative as well.
process = cv2.adaptiveThreshold(process, 255, cv2.ADAPTIVE_THRESH_GAUSSIAN_C, cv2.THRESH_BINARY, 11, 2)

2.3 Invert colors and Dilation
In order to successfully extract the grid, we need to invert the colors
process = cv2.bitwise_not(process, process)
We need to use dilation as while using Gaussian Thresholding we reduced noise which in turn lead shrinking of our object. So we need to dilate it.
# np.uint8 will wrap.
# For example, 235+30 = 9.
kernel = np.array([[0., 1., 0.], [1., 1., 1.], [0., 1., 0.]], np.uint8)
process = cv2.dilate(process, kernel)
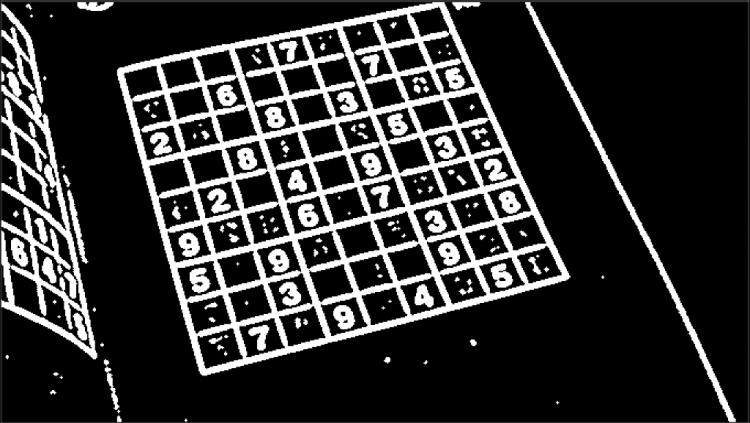
Next Steps:
Check out Part 2: Sudoku and Cell Extraction to complete your Sudoku Solver AI. Feel free to reach out to me if you have any questions.

Resources:
Solving Every Sudoku Puzzle
Thresholding
Dilation
Other:
1.https://hackernoon.com/sudoku-solver-w-golang-opencv-3-2-3972ed3baae2
2. https://medium.com/@aakashjhawar/sudoku-solver-using-opencv-and-dl-part-1-490f08701179
Don’t forget to give us your ? !




Part 1: Image Processing was originally published in Becoming Human: Artificial Intelligence Magazine on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
Via https://becominghuman.ai/image-processing-sudokuai-opencv-45380715a629?source=rss—-5e5bef33608a—4
source https://365datascience.weebly.com/the-best-data-science-blog-2020/part-1-image-processing
10 Machine Learning Projects to boost your Portfolio

Getting a good job in the field of Machine Learning is getting very competitive. The best way to showcase your Machine Learning skills is in the form of Portfolio of Data Science and Machine Learning Projects.
A good Portfolio of Projects will show that you can apply those Machine Learning skills in your work.
Here are 10 Machine Learning Projects which will boost your Portfolio and will help you to get a job as a Data Scientist.
1. Human Activity Recognition with Machine Learning
Human activity recognition is the problem of classifying sequences of data recorded by specialized harnesses or smartphones into known well-defined Human activities.
It involves predicting the movement of a body, based on the sensor data, and involves deep knowledge of the domain from signal processing to correctly measure the features from the data to fit into a machine learning model. See Complete Project.
2. Predict Customer Churn with Machine Learning
Prediction of Customer Churn means our beloved customers intending to leave us in the future. We do this by implementing a predictive model with the help of machine learning and python.
With this model, you can expect a good understanding of customer churn in your own company. See Complete Project.

3. Movie Reviews Sentiment Analysis with Machine Learning
Sentiment relates to the meaning of a word and is associated with an opinion or an emotion, and analysis if you are a Data Scientist.
This is the process of looking at data and creating a binary classification using Machine Learning to learn and predict whether the movie reviews are positive or negative. See Full Project.
4. Bitcoin Price Prediction with Machine Learning
Bitcoin is the very first decentralized digital currency. This means this is not being governed by the government or by any central bank or any other authority.
In this project, you will learn to build your Python program with the Machine Learning algorithm, Support Vector Machines, so you can start trading and making money. See Full Project.
5. Student Performance Analysis with Machine Learning
Performance evaluation of students is essential to check the feasibility of improvement. Regular evaluation not only improves the performance but also helps in understanding where the students are lacking.
This Project is an automated solution for the performance evaluation of a student using machine learning. See full project.
6. Movie Recommendation System with Machine Learning
Recommendation systems are becoming increasingly important in today’s busy world. People are always short with their time and try to accomplish the work in their limited 24 hours.
The purpose of a recommendation system is basically to search for content that would be interesting to an individual. In this project, you will learn to create a Movie Recommendation system with Machine Learning. See full Project.
7. Email spam Detection with Machine Learning
Email spam is also called junk emails, are unsolicited messages sent in bulk by email (spamming).
In this project, you will learn how to detect email spam using a Machine Learning technique called Natural Language Processing and Python. See full Project.
Trending AI Articles:
1. Natural Language Generation:
The Commercial State of the Art in 2020
4. Becoming a Data Scientist, Data Analyst, Financial Analyst and Research Analyst
8. Amazon Product Reviews Sentiment Analysis with Machine Learning
Sentiment relates to the meaning of a word and is associated with an opinion or an emotion, and analysis if you are a Data Scientist.
This is the process of looking at data and creating a binary classification using Machine Learning to learn and predict whether the product reviews are positive or negative. See full Project.
9. Algorithmic Trading Strategy with Machine Learning and Python
Trading strategies are usually verified by backtesting: you reconstruct, with historical data, trades that would have occurred in the past using the rules that are defined with the strategy that you have developed. See full Project.
10. Weather Forecasting with Machine Learning
In this article, I will show how we can do Weather Forecasting with Machine Learning algorithm and compare some frameworks for further classification. See full Project.
Don’t forget to give us your ? !




10 Machine Learning Projects to boost your Portfolio was originally published in Becoming Human: Artificial Intelligence Magazine on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
7 Signs you are data literate
Originally from KDnuggets https://ift.tt/3iZDYLl
PyTorch LSTM: Text Generation Tutorial
Originally from KDnuggets https://ift.tt/3eqgPOG
