Originally from KDnuggets https://ift.tt/3tURvc1
source https://365datascience.weebly.com/the-best-data-science-blog-2020/rejection-sampling-with-python
365 Data Science is an online educational career website that offers the incredible opportunity to find your way into the data science world no matter your previous knowledge and experience.
Originally from KDnuggets https://ift.tt/3tURvc1
source https://365datascience.weebly.com/the-best-data-science-blog-2020/rejection-sampling-with-python
Originally from KDnuggets https://ift.tt/3d6IBBv
Originally from KDnuggets https://ift.tt/3ceyOKn
Originally from KDnuggets https://ift.tt/3d3WBvw
SEER: The start of a more powerful, flexible, and accessible era for computer vision
Continue reading on Becoming Human: Artificial Intelligence Magazine »
Maintenance represents a significant part of all Manufacturing operation’s expenses. Hence Predictive Maintenance has become important part of overall business strategy — which would help client performance monitoring, better reliability, eliminate down-time due to maintenance related failures, and extend operating life of machines. This approach promises cost savings over routine or time based Predictive maintenance.
The data provided in case study consists of temperatures of clean rooms, viz., Main-room and Pre-room. In ideal scenario, pre-room should be heated first and then the main-room. Thus, temperature of main-room should be in sync with temperature of pre-room. Sometimes, in spite of high heat in main-room, the temperature of pre-room is not as high. This implies that the pre-room is getting heated by main-room, which is an error. E.g., temperature of main-room goes high (greater than 100 degrees C) and pre-room has comparatively low temperature (less than 40 degrees C). Machine learning predictive approach will help us find out when this is going to happen and the root cause for it.


Above visualization depicts Good VS Bad condition of the machines. The X-axis shows the pre room temperature of the machine and Y-axis shows the main room temperature.
The red highlighted part shows the conditions where failure has been observed.
Machine Learning algorithms would predict using large data of machine’s state information and provide output in terms of regular A.I dashboard consisting of analytics of Prediction maintenance.
Below is current proposed architecture of System.
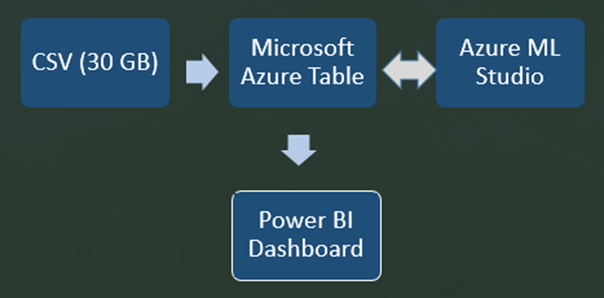
Using large pool of data of around 30 GB, CSV files will be stored in MS Azure Table for Cloud operations. Machine Learning algorithm in Azure ML studio would provide Predictive analysis which will be sent to Azure table. MS Power BI dashboard would provide real time predictive analytics charts.
● All information, data will be available on Azure cloud storage tables (Blobs). Data size is almost 20 GB which is into a single large CSV file. This consists of data (temperature, pressure, etc.) generated through the sensors which are fitted on rooms. The data is collected for each second between1st January 2017 and 31st December 2017.
● All the files which got generated during data exploration and analysis as well as Machine learning outputs are stored in the same container for easy access.
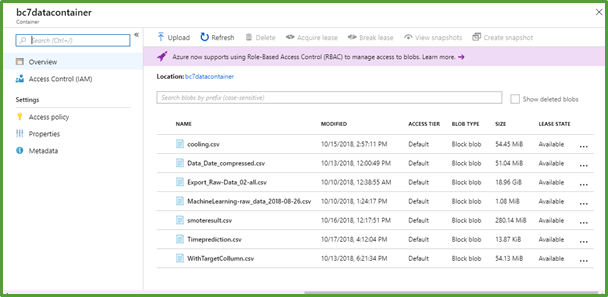
● Original Data findings
o Raw data provided to us consists of 30 million records, in single large CSV file. It was provided in Azure Blob storage account- for cloud based analysis.
o CSV file contains data for a whole year 2017, where records got generated for every second starting from Jan 2017 to Dec 2017.
o However, after initial exploration it was found that the records are getting generated after every 5 minutes. There were many duplicates due to multiple sources from which the data was getting generated. The client was informed immediately.
o All the duplicate in data points were removed to retain sanity of data for modelling & predictive dashboards.
o Now original data reduced to ~ 86K records, and records generated every 5 minutes for temperature, pressure, volume of pre-room and main room using corresponding sensors.
o We have also removed few sensors columns which has only single value throughout whole year as they will not be useful for analysis.
1. Top 5 Open-Source Machine Learning Recommender System Projects With Resources
4. Why You Should Ditch Your In-House Training Data Tools (And Avoid Building Your Own)
o Target column has been created with this logic — if the temperature of pre-room is less than 40 degrees AND temperature of main-room is greater than 100 degrees AND difference between temperatures of both is 10 degrees AND if main-room is not in cooling condition — it terms as failure.
o Cooling condition is defined as if main-room has continuous decrease in temperature for 25 minutes.
o Total 446 records where machine shows failure according to the above definition
o There are 43 days where failure was observed.
o Total downtime in the year 2017 was 2230 minutes (37 hours).
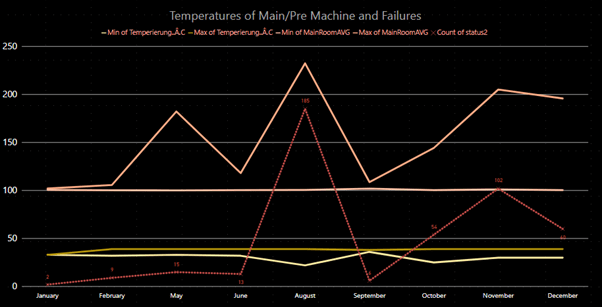
Above interactive figure shows number of failures by Month (Red line). Other lines represent Minimum and Maximum Temperatures of Pre-room and Main-room.
We observed that the highest number of failures observed in August 2017(185 failures) and minimum failures were observed in January 2017(2 failures).
We sensed that there might be seasonality or trends by time. Hence, it is suggested to use time series Machine Learning models which might help us understand failures of the machines. Hence, in later part we will apply Machine learning Model.
Also, as a target variable is binary (pass/fail), a classification algorithm will be used to understand the conditions of failures in machine.
We will use Azure Machine Learning Studio for building classification based models. We decided to build Logistic Regression and Two class Boosted decision tree approach.
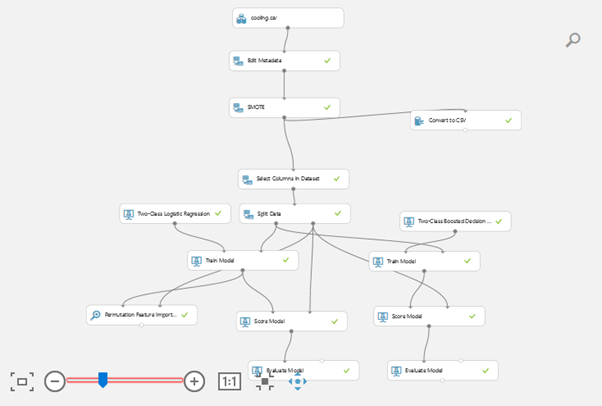
Above screenshot from Azure Machine Learning Studio shows step by step approach for building end to end solution of both Machine Learning Models.
Summary of each step:
● Cooling.csv, Edit Metadata
We import data from Azure VM Machine and select only columns required for building models. As we have used Pre-room and Main-room temperature columns for creating Target column (Status2), those won’t be considered into the set of predictor variables.
● SMOTE (Synthetic Minority Over-Sampling Technique)
In Simple terms, SMOTE function balances the skewed data. Actual Data provided has 99% of records which account to good conditions while only 1% account to bad condition. In such a huge skewed scenario, the machine gets biased towards good condition and hence fails to identify bad condition correctly. Hence, to balance the data, the number of failure records are increased artificially without impacting sanity of dataset using SMOTE function. In this case, the SMOTE helps us to reach to 77% of good and 23% of bad records. It is good ratio for Model to get trained from the data.
● Select Columns in Dataset
This module is used for selecting required columns, i.e. Pass/Fail is considered as target column & all other columns are used as predictor variables for model input.
Please note that we already removed Pre-room and Main-room temperature variables as they are used to build the target variable and hence not required in Model building activity.
● Split Data
We used 70% of total records to train model and rest 30% of data for testing. We later use Test data for understanding how model performs on Test data — measuring its accuracy and other performance parameters in later sections.
● Two Class Logistic Regression, Two Class Boosted decision trees
These two are difference algorithms applied simultaneously to compare which one provides best output.
● Train Model, Score Model & Evaluate Model.
Train Model initiates model training activity, thereby building a function inside which will explain at what parameters failure conditions are occurring. Score model provides it’s output so that we can compare actual Pass/Fail condition & model interpreted Pass/Fail conditions.
Evaluate model will simply evaluate how many times model is giving correct output — means when Machine is in Good condition, model is saying it’s in good condition & when Machine is in Bad condition model is also saying it’s in Bad conditions. These are called True Positive and True Negative conditions.
When Model is interpreting actual Good condition as Bad condition — it’s called as False Positive. When Model is interpreting actual Bad condition as Good condition — it’s called as False Negative. Both of these conditions are an error of model & Data Scientist team should focus on making these two errors as small as possible.
It is also important to note that we will never have both of these errors as 100% correct ideally — simple reason of which we cannot always provide model all data that is required. For example — we are not providing any data about other conditions of computer cooling, weather conditions, size/capacity of pressure pumps, maintenance times and all millions of other things which we will never know!
Machine Learning Models Output & Accuracy
We have used 3 models for Machine Learning. We will state reasons of using them & their benefits & their performance parameters.
This algorithm is used when we have target column as binary or some classes. For example — Pass/Fail, True/Fail, Good/Better/Best etc. Algorithm use logarithmic theory for identifying various conditions when machine is in Good condition & Bad condition. Then it reduces those large conditions to optimum number of columns to make unique conditions of various sensors that explains Pass & Fail output.
The Yellow highlighted part is Evaluate Model which find out performance this Logistic regression model.
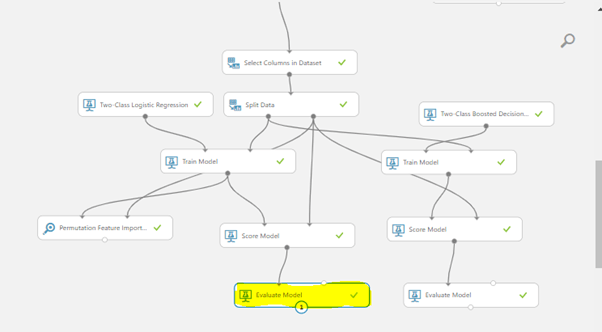
Below in Fig no are also provided its accuracy numbers.
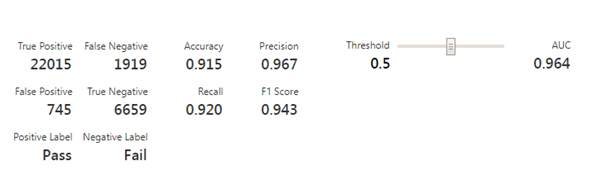
Accuracy of Model is 0.915 or 91.5%
Cases where model is giving correct output = True Positive + True Negative =22015+6659= 28674
Cases where model is giving wrong output = False Positive + False Negative =1919+745=2664
True Positive means machine is saying that condition is Good & model also predicts as Good. While True Negative means machine is saying that it’s condition is Bad & model also predicts as Bad.
False Negative means machine is saying that it’s condition is Good and model is giving output as Fail. This means we are getting false alerts from Model that Machine requires maintenance while actually it’s not required. Note that 1919 is a large number, that means we should find ways to decrease this number as it will waste lot of resources time at the end just to understand it’s a fake alert.
False Positive means machine is saying it’s condition is Bad however model is predicting as normal condition. Please note that 745 is large number of times it is providing False Positive alter.
This algorithm is used when you need output in human readable form. It also gives better accuracy in some cases than Logistic Regression. Team has decided to build both models & compare its accuracy so that we can choose which fits best.
In below image Yellow highlighted part is evaluation module for Decision tree algorithm built.
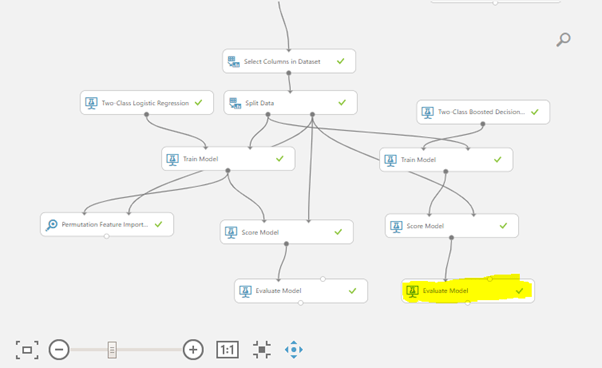
Right click on Evaluate Model, go to Evaluation Results and then Visualize.
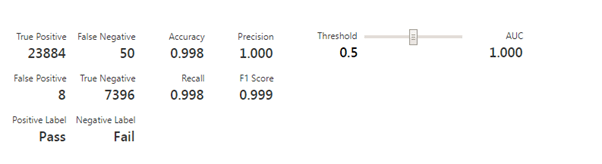
As you can see accuracy of Decision tree model is 0.998 or 99.8%.
You can compare number of False positives and False negatives ( 50 & 8 ) than Logistic Model ( 1919 & 754 ) . Hence this model is performing much better than earlier model & in long run we will stick with this Decision Tree algorithm for better accuracy.
Another benefit of Decision Tree model is that it gives us RULES when machine fails. This is most important for Business as we can identify where fault is occurring and take measures to reduce such failures.
BELOW ARE FAILURES CONDITIONS FOUND BY MACHINE LEARNING ALGORITHM:
There are 3 types of conditions of failures & below are conditions where these failures occur.
∙ Fail condition 1
1. Heiztemperatur.Wand.oben.rechts..ï…C >= 120.
2. Temp..RGA.1.HV.Schieber.PK..ï…C < 129.7
3. Temp..Reduzierung.Bypass..ï…C >= 60
4. Schwingungssensor..mm.s < 0.1099
5. Druck.Barion.XHV..mbar >= 0.0002389
∙ Fail Condition 2
1. Heiztemperatur.Wand.oben.rechts..ï…C >=120.
2. Temp..RGA.1.HV.Schieber.PK..ï…C >=129.7
3. Druck.RGA.1..mbar < 0 4.
4. Heiztemperatur.Tï…r.links..ï…C >=459.8
5. Schwingungssensor..mm.s >=0.08006
∙ Fail Condition 3
1. Heiztemperatur.Wand.oben.rechts..ï…C >=120.
2. Temp..RGA.1.HV.Schieber.PK..ï…C < 129.7
3. Temp..Reduzierung.Bypass..ï…C >=60
4. Schwingungssensor..mm.s < 0.1099
5. Druck.Barion.XHV..mbar < 0.0002389
6. Druck.Barion.XHV..mbar < 0
We use another model to understand if there is natural factors involved in machine failures. This means weather, temperature, seasons (as we have complete full year data, Spring, Summer, Autumn and Winter) are impacting to machine or not. We also can see if machine is failing at regular intervals irrespective of other sensors state.
Based on understanding of data, model is predicted DOWNTIME intervals by month & date.
It helps Businesses to budgets their efforts, resource for machine maintenance and thereby reducing total cost of maintenance.




Predictive Maintenance: This Is How Machine Learning /AI can transform Manufacturing Industry —… was originally published in Becoming Human: Artificial Intelligence Magazine on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.

What the COVID-19 pandemic and the subsequent lockdowns have shown is how ill-prepared the higher education system was for the challenge. Although 97% of universities and colleges have eventually switched to online or blended learning, their journeys weren’t smooth — 63% of students say the quality of instructions has worsened. Now schools across the globe are rushing their digital transformation initiatives adopting educational technology to make learning, and remote learning in particular, more efficient and personalized, possibly without spending a fortune on digitizing their operations. But how do higher education institutions navigate educational innovations? And how can artificial intelligence, cloud computing, intelligent automation, and teleconferencing help schools achieve higher academic performance and drive revenue? Let’s dive in.
Technology can transform every aspect of how students, professors, and alumni interact and how campuses are running, easing the shift toward cheaper, more accessible, and more engaging education.

With student lifecycle management software, universities and colleges can develop a data-driven approach to education, automate routine processes, and let students access educational resources anywhere, anytime. One of the biggest trends in educational technology, SLM software optimizes the entire student lifecycle, from prospecting and enrollment through creating a nurturing learning environment to graduation and alumni support.
1. Top 5 Open-Source Machine Learning Recommender System Projects With Resources
4. Why You Should Ditch Your In-House Training Data Tools (And Avoid Building Your Own)
Prospecting and enrollment
Doing their research about a university, applicants usually visit its website, go through the schools’ social media, weigh out alumni’s impressions, and only then submit an application. SLM solutions optimize the interaction between the potential students and the school at each of these touch points.
Data analytics and AI bring in robust insights to universities’ recruitment campaigns. The techs allow monitoring how effective a school’s marketing efforts are in real time to attract the best students.
Leveraging artificial intelligence and machine learning in education allows processing myriads of social media data to uncover what students, alumni, and parents really think about your school. And competitive intelligence helps to compare a school’s academic performance and its attractiveness for potential applicants against other higher education institutions.
To speed up or even automate student enrollment, universities are widely adopting CRM software. CRMs foster application management at every stage — from application receipt and confirmation through analyzing if it meets the set requirements to routing the application for approval and claiming the final verdict.
Information and communication technologies in education also ignite the transition to more affordable subscription-based online learning (think: Netflix-style smart education platforms). Students would soon be able to browse through a school’s available programs, subscribe to the one they like, and connect a credit card for automatic monthly payments. A pioneer in subscription-based learning, Boise State University enrolls 3,500 fully online students a year, and almost every learner fully completes their credit commitment. Online students also pay 30% less in tuition fees.
Billing and accounting operations
Tech savvy students of today expect their tuition and other payments to be handled smoothly and quickly, which calls for colleges to adopt billing and accounting technology for education. Such solutions usually feature an accounting portal for the administration and a mobile app for students. The students can use the app to conveniently pay tuition fees or make on-campus purchases, while the accounting portal allows centralized and swift payments processing. The University of Wyoming, for example, used to send out their bills via the postal service with the help of a contractor who manually processed, printed, and mailed out the bills. It took approximately a week before the bills reached the students, which was slow and also rather costly. Today, however, the university uses e-billing software to automatically process thousands of bills, saving about $45,000 a year.

Curriculum personalization
With AI solutions for education, universities can tailor the learning process to a student’s academic achievements, background, interests, and inclinations. To empower academic success, AI analyzes tests, assignments, classroom participation notes, and other data to build a unique student profile and identify what makes the student engage and what causes struggles. Based on the profile, AI provides tips on how educational materials can be tweaked. For example, AI can tell whether a particular student prefers listening, reading, or watching a video to take in information. As a result, students start benefiting from a personalized learning environment; instructors use reports on students’ academic achievements to further improve the way they teach; curriculum and content designers get useful insight into content usage; and college administrations tap in useful statistics on the school’s overall performance and the bottlenecks that may halt it.
On-campus communication
Key innovative technologies that make it easier for students to engage in campus experiences are chatbots and videoconferencing. Chatbots provide immediate responses to student queries and solve many extra tasks, from helping navigate the campus to reminding about upcoming exams to sending out grades reports, and more. Georgia State University, for instance, has implemented a chatbot to help newly admitted students prepare for the enrollment. Namely, the chatbot gives answers to the questions about the financial aid and housing and helps freshmen register for classes. During the first month after the implementation, the chatbot exchanged about 50,000 texts, and less than 1% of students had to be routed to the university staff for further clarifications. Videoconferencing has become the key enabler of distant and blended learning, but the value this technology drives in education will endure after the pandemic as well. Conferencing apps may help professors make the learning process more engaging, enjoyable, and convenient. They could, for instance, invite subject-matter experts to hold video lectures or consult students via online office hours. Yale University, for example, uses videoconferencing to teach rare languages like Yoruba and Zulu with the students and the instructor being miles away from each other.

Putting educational innovations to use, universities can create next-gen campus infrastructures that meet the demand of today’s tech savvy students. Smart campuses embrace technology applications that make up a connected infrastructure and create intuitive experiences for students, professors, prospects, and college administration.
Campus safety and security
Higher education institutions may leverage AI-powered CCTV cameras, biometric technology, and facial recognition to keep unauthorized people off campus, so that a student can get in a dorm only if they allow their fingerprints or facial features to be scanned by AI. The same technology can be used to automatically track classes attendance, identify absentees, or get real-time feedback about which parts of a class make students engage and which fail to arouse interest. But as good as improved safety and automated tracking may sound, AI-powered surveillance and facial recognition cause fierce resistance among students and evoke debate about the moral implications of modern tech. One way of alleviating the ethical concerns while improving security is recognizing violent behaviors and potential threats rather than facial features. Several startups like ZeroEyes and Athena claim to rely on such an approach in their safety and security solutions.
Smart dorm and recreation
To provide better services and drive cost savings, housing, dining, and recreation facilities can be digitized, too. For instance, relying on the data fetched from motion tracking sensors, smart lighting systems and connected thermostats can automatically turn off the lights and lower room temperature when no one is around. The University of Arizona has already adopted smart college and campus technologies, but they have gone beyond standard use cases and also deployed a network of plumbing sensors to monitor water lines usage and prevent leaks. When it comes to dining, techs drive student experience here as well. With technology integrated into dining services, students can conveniently look through the available menu options via a self-service kiosk or a mobile app, view nutrition information, and place an order. Many higher education institutions also set up technology to provide for quality recreation. ASU has, too, implemented connected sensors to monitor weather, humidity, temperature, and noise levels inside the university’s sports arena.

To liven up the learning process, enhance student engagement, and maintain the sense of community despite the lockdown, colleges and universities have started leveraging smart learning environments, virtual tutors, and gamification.
Smart learning environments
Bringing whiteboards, 360-degree video tools, and augmented and virtual reality in education, colleges can create immersive learning experiences. Interactive whiteboards, for instance, allow more flexibility in content delivery, support file sharing, and provide simple access to the internet, engaging learners via multiple models of interaction. AR and VR simulations help students grasp complex concepts, reconstruct historical events, engage in practical training, and more. San Diego State University, for instance, has already turned the power of VR in education to their benefit. The smart school uses VR headsets to teach astronomy and make students experience ideas that cannot be explained verbally via visual means. And here’s an interesting use case of augmented reality in education. Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute has built an immersion lab with a 360-degree projection system that “transports” the school’s Mandarin learners to Chinese city streetscapes. Conversing with AI-powered avatars that recognize learners’ speech, gestures, and facial expressions, the students master Mandarin twice as fast as their fellows taught in conventional classrooms.
Virtual tutors
Virtual tutors are intelligent, AI-powered avatars one can converse with just like with a human. The behavior of a virtual tutor can be tailored to any task, from enhancing medical students training to facilitating foreign language practice. The avatars can even be trained to mimic a person with a trauma to, say, act as a patient for psychology students. Among the universities that have already adopted virtual teachers and tutors is the University of Buffalo’s Graduate School of Education. The school uses an avatar named Kevin to enhance learning experience for students majoring in teaching. Now the students perfect their tutoring and instructing skills talking to a virtual counterpart and already notice an increase in their professional confidence.
Gamified virtual campus solutions
Having switched to videoconferencing to enable distance learning, universities and colleges are now embracing gamification features and augmented reality apps for education to create virtual campuses. Virtual campuses are interactive environments where students can meet, study, and chat. Just like in video games, a student uses their laptops’ keyboard and a microphone to walk around the campus and talk with other students or professors presented by digital avatars. Stanford’s Graduate School of Business is one of the pioneers in adopting virtual campus technology. The environment they’ve built allows students to navigate the digital copy of the school’s campus, “teleport” from one room to the next and attend online classes with an instructor’s avatar on the virtual stage. In turn, the instructors can put students into private groups, hand out lecture notes, and more.

In the US, every classroom includes students with special needs, and assistive learning innovations in education can make a difference to how they learn.
Writing assistance
Students struggling with literacy or those who want to boost their writing skills, for instance, can benefit from AI-powered spelling and grammar check, word prediction, and automated text formatting. Apart from that, modern writing assistance tools, like Hemingway Editor, Ghotit, or Ginger, can evaluate the clarity and readability of texts and even provide tailored practice sessions based on the mistakes a student made in the past. At the University of Michigan, for example, professors and students already use an AI-powered tool that analyzes students’ papers to let students take their writing skills a step further and help professors streamline grading.
Speech-to-text solutions
Speech-to-text software can assist students with special needs in communicating with their teachers and peers. Office 365 applications, for instance, feature an AI-based add-in that converts speech into text as a student speaks into a microphone. Another helpful tool is Microsoft’s Immersive Reader. The tool was designed specifically for students with dyslexia and dysgraphia and allows them to have any text read out loud, and even broken into syllables.
Tech for students with hearing and vision disabilities
Many apps and browsers today come with built-in screen magnifiers, high contrast mode, dictation, and audiovisual assistants that can read the contents of a web page out loud. For the students who need Braille support, colleges and universities can leverage Braille keyboards to improve the learning experience even further. And students with hearing difficulties can benefit from videoconferencing tools with built-in captioning, sound-field systems, as well as FM systems — wireless devices that transmit sounds directly to a hearing aid and help students communicate even in a noisy environment.
In the US, one in three college students reports having some kind of mental health disorder. In addition to offering individual and group therapy, universities can promote the use of tech like mobile apps and chatbots to expand their mental health care to the students who are reluctant to turn to in-person services. Mental health apps relying on cognitive behavioral therapy, for instance, have proven effective in alleviating anxiety, depression, and stress levels. Such apps can also analyze data from a mobile phone’s built-in sensors or wearables to reveal changes in students’ behavior patterns and provide tips on how to prevent worsening of the revealed mental health conditions. Mobile apps and chatbots help freshmen adjust to college, too. Offering personalized exercises and daily activities, the chatbots help build up resilience and increase well-being. The University of Michigan, for example, uses a similar bot that allows students to take a survey and get tailored resources to boost their mental health.

Innovative in every possible field but paradoxically conservative when it comes to redesigning their own structures, higher education institutions have to battle many challenges on their way to digital transformation. The ones that need special attention are:
Technologies are shaping the future of higher education, and many higher education institutions have already tapped in digital transformation — whether to make education more accessible and fun, improve daily operations, or drive cost savings. But no matter the goals, colleges and universities should not underestimate the importance of thorough planning. It is with a thought-out digital transformation strategy and the support of an experienced tech partner that higher education institutions get the most from investing in tech.
If you’re thinking to dive in digital transformation yourself and seek consultancy from a partner with proven EdTech competencies to realize your boldest ideas, you are welcome to drop ITRex a line.




Educational innovations: 5 ways technology is transforming universities and colleges was originally published in Becoming Human: Artificial Intelligence Magazine on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
Originally from KDnuggets https://ift.tt/3rbRoqM
Originally from KDnuggets https://ift.tt/3lTdMnT
Originally from KDnuggets https://ift.tt/3tDAJhg