Originally from KDnuggets https://ift.tt/2AmfcDz
The Data Scientist From 2018 To 2020: What Has Changed?

The data scientist from 2018 to 2020: What has changed?
For the last 3 years, we at 365 Data Science have been trying to answer one big question: “What makes a data scientist?”
Since we are talking data science, the only logical way to approach the question is to ask the data. And that’s what we’ve done for 3 consecutive years. Since 2018 we have explored 1001 data scientist LinkedIn profiles to uncover the most interesting trends in the data science field.
In this article, we will go through the most important findings from the last 3 years. We have also created a very cool and interactive PowerBI dashboard which you can use to analyze the data yourself.
If you prefer to digest our own analysis, just keep on reading.
According to the data, the average data scientist from 2018 to 2020 is a male with a second-tier degree, coming from a quantitative background, which is not necessarily data science or computer science.
Their preferred programming language is Python, but they’d often know R and SQL. Many of the new data scientist positions are being filled by people who are already data scientists. So, the field feels much more saturated. Getting into data science still looks like a great opportunity, but the ‘data scientist’ position becomes more and more exclusive.

That said, let’s dive deeper into the education, years of experience, and programming skills of a data scientist from 2018 to 2020.
What Education Makes a Data Scientist from 2018 to 2020?
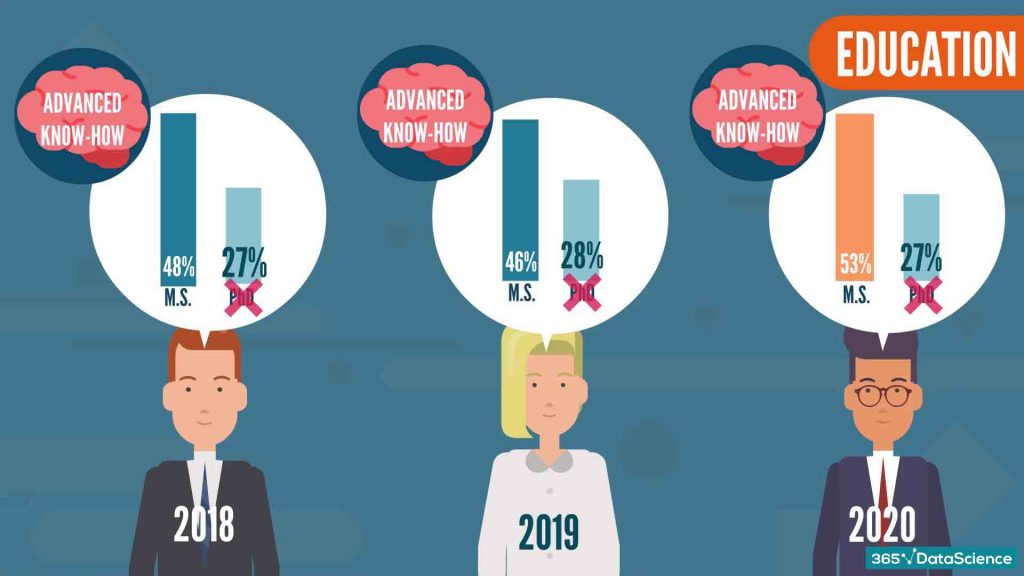
Our sample shows that at least 80% of the people held a minimum of a Master’s degree.
This isn’t as surprising, considering data science is a field that expects advanced know-how from the person — usually achieved by graduate or postgraduate types of education, or independent advanced research in other cases.
And while specialization is important, a Ph.D. is not really a requirement for breaking into data science.
Indeed, over the years, the number of Ph.D. holders has remained consistent, making up about 27% of our study.
On the contrary, starting from 2018 there was a rise of about 20% in the professionals with a Master’s degree compared to the 2019 cohort.
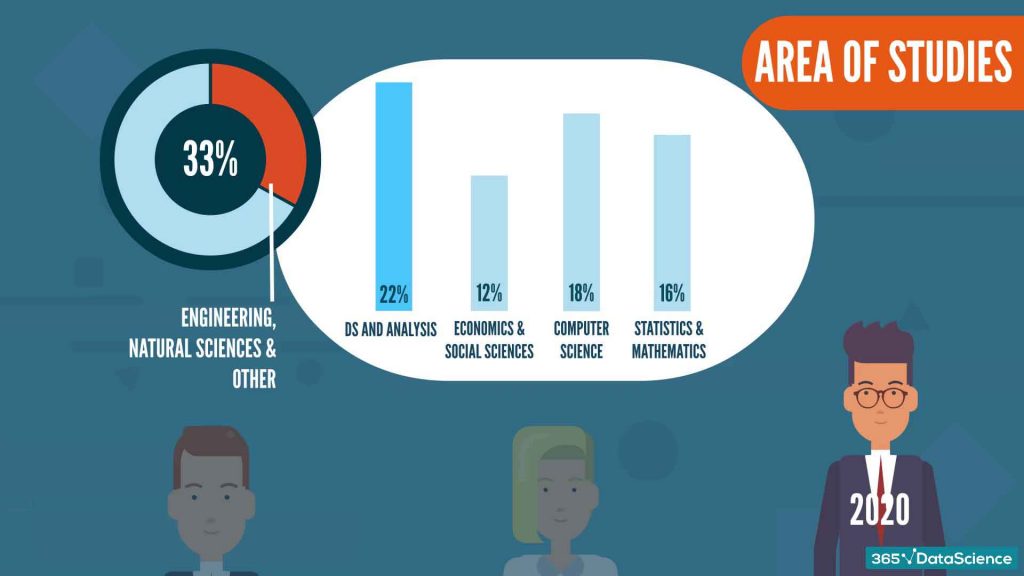
What Area of Studies Makes a Data Scientist from 2018 to 2020?
In 2018 and 2019, “Economics and Social Sciences”, “Computer Science” and “Statistics and Mathematics” were filling up the top 3 most popular fields of study of data scientists. 2020 was the first year ever that featured “Data Science and Analysis” (22%) as the top degree. Therefore, we can assume that universities have started to catch up with the demand for data science education.
Graduates from the Engineering, Natural Sciences, and Other fields constitute approximately 11% of our data each. This indicator has remained stable throughout the years.
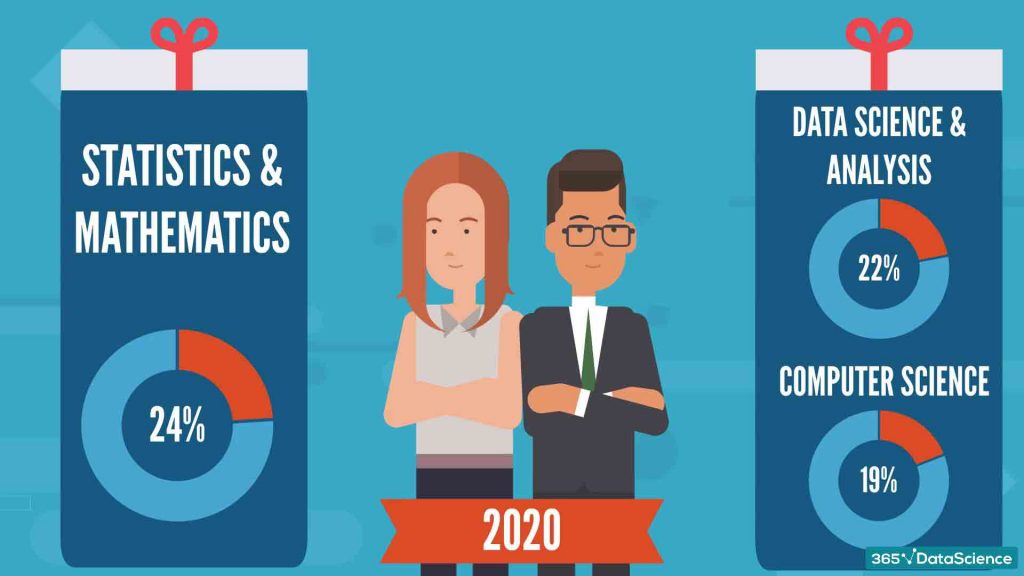
Interestingly, in 2020, most women in our sample have earned a ‘Statistics and Mathematics’ related degree (24% of the female cohort). In comparison, men most likely earned a degree in Data Science and Analysis (22%), with Computer Science (19%) being a close second.
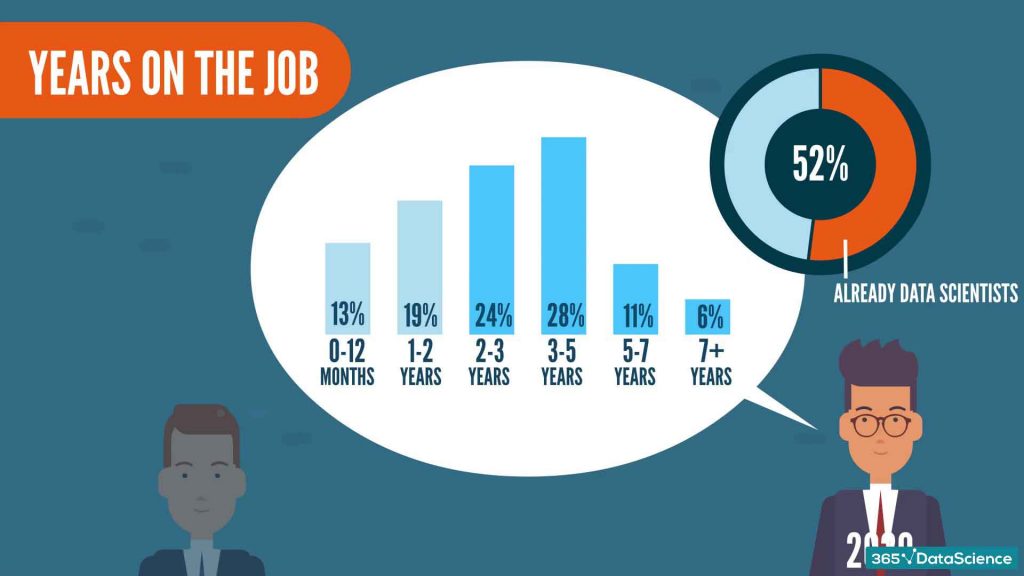
How Many Years on the Job Make a Data Scientist from 2018 to 2020?
If you are changing jobs or working through your data analyst years, you must be wondering whether you’ve got the right experience for the position. In terms of tenure, in 2018 almost all data scientists were ‘newcomers’ to the ‘data scientist’ position. Some of this stemmed from name changes to their occupation, but mostly – the supply was so little that it was way easier to enter the field.
Currently, we are observing a much tougher playing field.
The majority of data scientists have more than 2 years on the job. And it seems like a very small proportion of the total data scientist pool is new. In fact, in 2020, 52% of the cohort, held the title ‘data scientist’ at their previous position.
What Programming Languages Make a Data Scientist from 2018 to 2020?
The programming skills a data scientist needs are arguably the most interesting area of research (at least for us). For many years, R was the preferred language a data scientist was expected to “speak”. In 2018 and 2019 Python started ‘eating away at R’. And it did so at a very fast pace. In 2020, we have reached the point where Python is by far the preferred programming language in the data science community with 74% adoption! R is not completely overthrown but becomes less and less favored among professionals.
An interesting development is the rapid year-to-year growth of SQL users. In 2020, more than 50% of data scientists actively use the language.
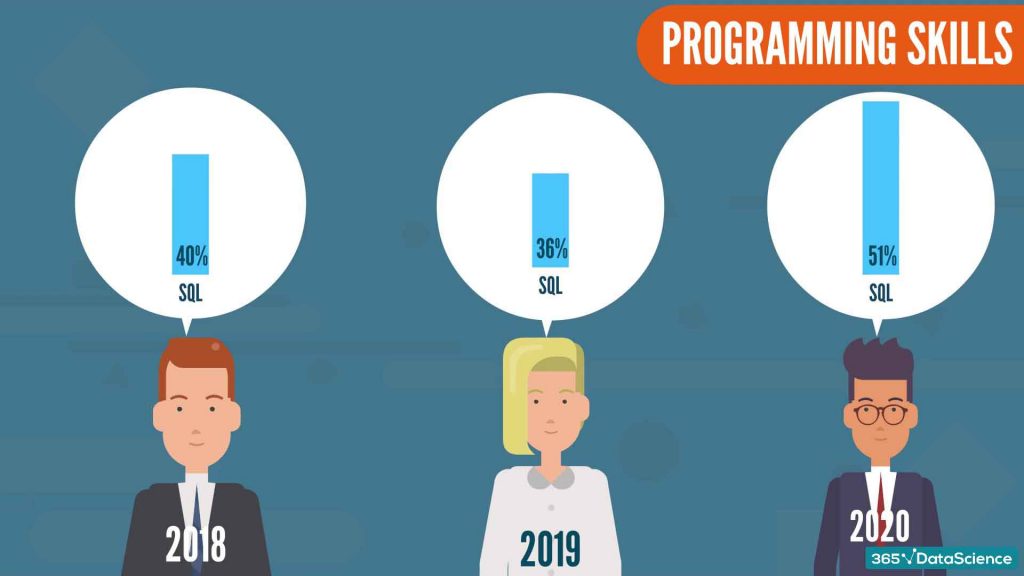
One common assumption is that companies expect from a data scientist to solve all their data-related problems; no matter if they are related to data engineering or data architecture. On another note, the adoption of BI software such as PowerBI and Tableau has also demanded a higher understanding of databases. Inevitably, data scientists had to add SQL to their toolbelt for the sake of ‘getting the job done’.

What Makes a Data Scientist from 2018 to 2020: In Conclusion
Looking at the data, the answer to “What makes a data scientist?” becomes clearer. Professionals are paving the way and universities are starting to provide a more tailored education.
From a career point of view, it seems that it is getting harder to become a data scientist. That’s mainly because data scientists tend to stay on their job for a longer period. However, different opportunities to get into the field remain, as demand still varies across countries and industries.
One thing is for sure – learn Python, if you are to become a data scientist!
And if you’d like to become an expert in all things data science, check out our career resources and hands-on tutorials.
Ready to take the next step towards a data science career?
Check out the complete Data Science Program today. Start with the fundamentals with our Statistics, Maths, and Excel courses. Build up a step-by-step experience with SQL, Python, R, Power BI, and Tableau. And upgrade your skillset with Machine Learning, Deep Learning, Credit Risk Modeling, Time Series Analysis, and Customer Analytics in Python. Still not sure you want to turn your interest in data science into a career? You can explore the curriculum or sign up 12 hours of beginner to advanced video content for free by clicking on the button below.
The post The Data Scientist From 2018 To 2020: What Has Changed? appeared first on 365 Data Science.
from 365 Data Science https://ift.tt/2xVUysZ
What Is an ARMA Model?

In time series, we often rely on past data to make estimates about current and future values. However, sometimes that’s not enough. When unexpected events like natural disasters, financial crises, or even wars happen, there can be a sudden shift in values. That’s why we need models that simultaneously use past data as a foundation for estimates, but can also quickly adjust to unpredictable shocks.
In this tutorial, we’re going to talk about one such model, called “ARMA”, which takes into account past values, as well as past errors when constructing future estimates.
What does ARMA stand for?
The name ARMA is short for Autoregressive Moving Average. It comes from merging two simpler models – the Autoregressive, or AR, and the Moving Average, or MA. In analysis, we tend to put the residuals at the end of the model equation, so that’s why the “MA” part comes second. Of course, this will become apparent once we examine the equation.
What does a simple ARMA model look like?
Let’s suppose that “Y” is some random time-series variable. Then, a simple Autoregressive Moving Average model would look something like this:
yt = c + ϕ1 yt-1 + θ1 ϵ t-1 + ϵ t
If you’ve checked our previous articles on the AR and MA models, you’ve already seen ALL parts of this equation, so we’ll quickly go over all of them.
What do yt and yt-1 stand for?
For starters, yt and yt-1 represent the values in the current period and 1 period ago respectively. As was the case with the AR model, we’re using the past values as a benchmark for future estimates.
What do ϵ t and ϵ t-1 stand for?
Similarly, ϵ t and ϵ t-1 are the error terms for the same two periods. The error term from the last period is used to help us correct our predictions. By knowing how far off we were in our last estimate, we can make a more accurate estimation this time.
What does c stand for?
As always, “c” is just a baseline constant factor. In simply means we can plug in any constant factor here. If the equation doesn’t have such a baseline, we just assume c=0.
What do ϕ1 and θ1 stand for?
The two remaining parameters are ϕ1 and θ1. The former, ϕ1, expresses on average what part of the value last period (yt-1) is relevant in explaining the current one. Similarly, the latter, θ1, represents the same for the past error term (ϵ t-1). Just like in previous models, these coefficients must range between -1 and 1 to prevent the coefficients from blowing up.
Of course, in more complex models, ϕi, and θiexpress the importance of the values and error terms for the “i-th” lag. For example, ϕ4, expresses what part of the value 4 periods ago is still relevant, while θ3describes what portion of the residual from 3 periods ago is important today.
How do we define a more complex ARMA model?
Before we move forward, we need to specify some aspects of defining ARMA models. For instance, each model of the kind is defined by two “orders”. One is known as the “AR” order, while the other one as the “MA” order. The former is associated with the autoregressive components, while the latter represents the moving-average parts. Hence, an ARMA (P, Q) model, takes the previous values up to P periods ago, but also takes the residuals of up to Q lags.
Then, the equation for an ARMA (2,3) would look like this:
yt = ϕ1 yt-1 + ϕ2 yt-2 + θ1 ϵ t-1 + + θ2 ϵ t-2 + θ3 ϵ t-3 + ϵ t
It’s crucial to understand that the two orders, P and Q, can be, but mustn’t necessarily be equal in value. This is vital because usually either the error term (ϵ t-i) or the past value (y t-i) loses significance faster. Hence, many realistic predictive models have different Autoregressive and Moving Average orders.
How to apply the ARMA Model?
Understanding the theory behind a model is only half of the task at hand. To use ARMA models, we need to run regressions where we compare how the actual values compare against the estimates from the model. Doing so requires computing the constant coefficients, as well as all the + ϕi and θi values.
Lucky for us, Python is well-suited for the job. With convenient libraries like Pandas and Statsmodels, we can determine the best-fitting autoregressive model for any given data set.
If you want to learn more about implementing autoregressive models in Python, or how the model selection process works, make sure to check out our step-by-step Python tutorials.
If you’re new to Python, and you’re enthusiastic to learn more, this comprehensive resource on learning Python programming will guide you all the way from the installation, through Python IDEs, Libraries, and frameworks, to the best Python career paths and job outlook.
Ready to take the next step towards a career in data science?
Check out the complete Data Science Program today. Start with the fundamentals with our Statistics, Maths, and Excel courses. Build up a step-by-step experience with SQL, Python, R, Power BI, and Tableau. And upgrade your skillset with Machine Learning, Deep Learning, Credit Risk Modeling, Time Series Analysis, and Customer Analytics in Python. Still not sure you want to turn your interest in data science into a career? You can explore the curriculum or sign up 12 hours of beginner to advanced video content for free by clicking on the button below.
The post What Is an ARMA Model? appeared first on 365 Data Science.
from 365 Data Science https://ift.tt/2xSZsa7
The Elements of Statistical Learning: The Free eBook
Originally from KDnuggets https://ift.tt/3fAuCnX
AI ML IoT cybersecuritythe future of business and careers
AI, ML, IoT, cybersecurity — the future of business and careers
Advice for emerging start-up entrepreneurs

By Igor Sill, Geneva Venture Partners
Billionaire investor Mark Cuban is not bashful about discussing his thoughts on artificial intelligence (AI), predicting that the next richest founders will be AI entrepreneurs.
Cuban says if you want to stay ahead of the curve as future entrepreneur: “I am telling you…the world’s first Trillionaires (that’s with a “T”) are going to come from somebody who masters AI and all its derivatives, and applies it in ways we never thought of.” “We are going through the process where software will automate software, automation will automate automation.”

This movement exploded following Google’s acquisition of UK-based Deepmind. This AI startup’s mission was to “solve intelligence” and was backed by visionary investors Elon Musk and Peter Thiel. Since its integration into Google, Deepmind has transformed Google in oh so many ways. All Google searches are now piped through Deepmind’s artificial neural network given its efficiency over human intervention in finding relevant and accurate search results.
For the past two decades, growth rates and unicorn valuations have defined venture investment funding success for most technology companies. Every venture capital firm likes to insist that they are strategically unique and “different” even though they usually all operate from this very same playbook.
I contend that angel (seed) investors contribute far more value to a start-up than a committee-oriented venture firm partnership. An angel investor with prior high growth IPO experience with sufficient “success pattern matching” intuition combined with an extensive industry network offers a higher probability of startup success, while committee-driven VC firm decisions are just that.
Common VC firm mistakes are: misevaluating the founding team’s abilities; playing the Shark Tank valuation trap; misunderstanding the target market; Committeethinkology; assuming that a market is too small; presumes that a market already has an entrenched leader; and most importantly, lack of interest or time in mentoring, coaching, contributing and opening critical partnership doors. After all, they’re investing someone else’s money, not their own.
When coupled with seed entrepreneurs pounding VC doors, the overwhelming selection challenge becomes all too consuming and is frequently relegated to the firm’s low level Associates. Thus, the majority of mega million venture firms have moved to the Series A and later stages where quantifiable metrics exist. Both Siebel Systems and Salesforce avoided traditional VC firms until much later financing rounds, instead relying on supportive angels for their seed and Series A financing. To address this widening gap in startup funding, founders are seeking experienced angel investors as their clear first choice.
In backing start-ups, I became acutely in tune to the founders’ mindset and would rally behind those that focused on building with an attitude of unselfish responsibility and social conscientiousness. My relationships and my network became theirs.

Harvard’s Clayton Christiansen proclaimed that disruptive innovation is a process in which a new offering initially takes root in simple applications at the bottom of a market, typically by being less expensive, better and more accessible — and then relentlessly moves upmarket, eventually displacing established market leaders. Salesforce’s upstart dominance over Siebel Systems is a well recognized Silicon Valley disruption example. Zoom video over Webex and Skype is yet another, etc., etc.
New Age Disruptive Market Opportunities — AI, IoT, ML, Cybersecurity
The IoT (Internet of Things) is a system of interrelated computing devices, sensors, mechanical and digital machines with the ability to transfer information over a network without requiring human interaction, so this would includesecurity systems, thermostats, cars, electronic appliances, lights in household and commercial environments, alarm clocks, speaker systems, vending machines and most things imaginable, plus some. And, that is just the tip of the iceberg.
The acceleration in the scope, scale and economic impact of IoT when coupled with Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Language (ML) and cybersecurity technology have the potential to be an incredibly positive force in the world. New implementations in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are incorporating algorithms to prevent cybersecurity attacks while securing software vulnerabilities, allowing security experts to conduct more higher-level examinations of threats.
Essentially, every appliance and device we use today, and even those we have yet to imagine will be affected. In fact, IoT and more importantly, The Industrial Internet of Thing revolution (IIoT), is already well on its way. According to a new market research report Digital Transformation Market (IoT, Cloud, Big Data, AI, Cybersecurity, IT, Telecom) published by Meticulous Research®, the digital transformation market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 22.7% to reach $3,294 Billion by 2025. The cybersecurity market size is projected to reach $258.99 Billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 11.9%.
The digitization of machines, vehicles, systems, sensors and other elements of the physical world is an innovative idea providing powerful solutions. We are already experiencing a real impact by changing how goods are produced and distributed, how products are serviced and refined, and how doctors and patients manage health and wellness. Business-to-business enterprise applications will probably capture more value — nearly 70% over consumer uses.
Another significant disruptive force is the degree to which the world is much more connected through global trade and movements in capital, people, and information (data and communication), what politicians call “flows.”
If businesses execute digital transformation properly, integrating the physical and digital worlds could generate up to $11.1 trillion a year in economic value by 2025. That’s a huge disruptable market opportunity. An angel investor’s financial heaven.
Top 4 Most Popular Ai Articles:
1. Cheat Sheets for AI, Neural Networks, Machine Learning, Deep Learning & Big Data
3. Getting Started with Building Realtime API Infrastructure
4. How I used machine learning as inspiration for physical paintings
Real time AI application development infrastructure is a deep, complicated space that’s going through a massive transformation. Palantir, has successfully exploited this segment with great execution skills, building a culture of working for the common good and building a future where data can be leveraged to serve people, create value and improve the quality of life. Palantir was founded back in 2003 and they, along with many others (Microsoft, Lucid, IBM, Amazon, Facebook, Apple, Nvidia, etc), developed legacy tools, and legacy enterprise software applications and outdated platforms. There are tremendous numbers of old generation, outdated and vulnerable software applications operating out there. As an early stage seed investor, I seek out disruptive technology application solutions suitable for large, addressable global markets, and driven by brilliant, passionate, tried-and-proven entrepreneurs. Once the right technology is beta-tested, then proven, it’s all about customer traction and team execution. Closing customers early in a startup’s life is essential to avoid building “yet another” similar solution. So, I suggest, entrepreneurs build applications that businesses love. Ask, what is it this industry really crying out for, what does it really need? What stands in the way of achieving this need? One major reason for a technology company’s breakthrough success is its dynamic, constantly evolving business plan, tuning into the market’s needs, seizing new opportunities and always striving for much bigger customer successes. Of course an entrepreneur’s survival instincts are an important and powerful characteristic. Somehow, the survival instinct is closely related to luck. I’ve found that the harder one works, the luckier they become. And, of course being at the right place at the right time helps, so, one needs to survive long enough in order for that to happen.
Seek out Investors Who Understand and Appreciate your Business
Most VCs focus solely on early traction analytics, assessing evidence of strong traction as sufficient to validate product acceptance. Ask other founders who have worked with the VCs you’re considering to tell you about their biggest contributions, their biggest value, their corporate connections. I contend that connecting with good investors, qualifying them and asking them about their enterprise, AI, ML, Cybersecurity, SaaS experience may be a very important element that a “partner” provides. A value-added investor should be part financier, business development advocate, strategic alliances door opener, executive search consultant, deal-maker connector, fundraiser and sound business advisor.
It takes a very special skillset to bridge that gap, and to fund, support and build a community around a next generation transformative go-forward vision.
One such start-up which I believe has all the elements for success: an experienced leadership team, next-generation AI disruptive technology in a huge and growing market and the ability and skill to execute, while demonstrating social benefits of its technology capabilities when it comes to corporate values, is Walnut Creek-based VantIQ.
A successful startup is often driven by the vision of its founders and its core leadership team and that is what the founding team of VantIQ has achieved. VantIQ has created and developed a technology stack for the rapid design, development, deployment and operation of next-generation, real-time AI & IoT applications that transforms business processes.
With AI, privacy, and behavior-manipulation concerns, modern tech companies today face significant and complex problems. Thus, it is important to demonstrate clearly the social as well as economic benefits when it comes to corporate values. I found that VantIQ shares a deep commitment and intense sense of purpose in the role they play in society and how they create value for their customers. I believe the best technology businesses are intrinsically aligned with the long-term interests of society.
Leadership team
I have tremendous confidence in VantIQ’s co-founder & CEO, Marty Sprinzen, the former founder of Forte Software and former COO of Ingres Corporation. Sprinzen along with co-founder & CTO, Paul Butterworth and his team built one of the most successful scalable enterprise-class distributed applications software companies in history. Sun Microsystems acquired public-traded Forte Software for $540 Million in mid 1999 causing ORACLE’s Larry Ellison to acquire the combined Forte/Sun Microsystems so as to offer ORACLE’s customers and prospects a sustained technology growth path.
Market & Competition
Founded in late 2015, and now with over four years in development, revisions and successful deployments, I believe that VantIQ is several years ahead of its competitors. The company has made incredible market inroads here in the US, as well as UK, Europe, Japan, China, LATAM and more than quadrupled its growth last year with even greater growth prospects this year, despite the pandemic. VantIQ is seeing dramatic growth globally across all industry sectors driven by digital transformation mandates that encompass big data, AI, machine learning security and IoT.
Summary
My pattern-matching intuitive approach has been formed by a set of experiences about how businesses function during a time of fast-paced innovation and competition. Winning the customer confidence of Fortune 500 companies is not easy, but VantIQ has demonstrated it can do so even though it’s still a growing startup with no traditional VC firm funding. I believe VantIQ can and will be the category leader in AI, IIoT platform solutions and applications globally. That is why I made a substantial investment and commitment in VantIQ’s leadership team: Marty, Paul and Miguel.
Don’t forget to give us your ? !




AI, ML, IoT, cybersecurity — the future of business and careers was originally published in Becoming Human: Artificial Intelligence Magazine on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
A comprehensive Guide For All Your Blockchain App Development Needs
An authoritative guide to Blockchain app development

Blockchain technology based application from scratch can be a tedious task for a developer. So, this is a complete guide highlighting all the blockchain app development needs.
Everybody knows that Blockchain technology is the future. It has shaped each and every industry vertical from fintech industry to healthcare & education. In fact, it is the most effective technology to automate business processes today.
That’s why I have created this blockchain guide which would answer all your programming as well as web app development needs.

You are going to learn various things in this blog.
-> Best Blockchain development platforms
-> Types of blockchain programming
-> Top blockchain development languages
-> Use cases of each mentioned blockchain frameworks
-> Lastly, videos on blockchain development
Two Types Of Blockchain Programming
1. DApp development or building smart contracts
If you develop a centralized application, you have to run the backend code on the centralized servers. On the other hand, decentralized applications run their backended code on a decentralized peer-to-peer network. Similar to other web app development, DApps can have its frontend code be written in any of the frontend languages & user-interfaces so that it can make call to the backend servers.
2. Architecture programming of blockchain
When bitcoin blockchain was released in 2009, the coding of its rules and regulations governing that situation was done using C++ programming. Similarly, before a blockchain can be released, all its main features consisting of its architecture & protocols should be settled down. This type of coding can be done using web app development programming languages like C, java that actually works closer to the machine.
Blockchain programming languages
A.Solidity
It is object-oriented, JS domain-specific and high-level programming language given by Ethereum team. It was inspired by other programming languages including Python, C++, JS for developing decentralized applications on the Ethereum platform i.e. EVM(Ethereum virtual machine). Using EVM, smart contracts are written on the Ethereum platform. Till now, it is the most adapted programming language in the blockchain industry and Ethereum community.
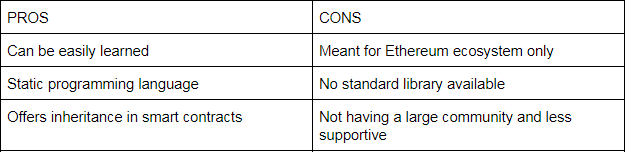
Use case: Smart contract development
Here I can show you how it is developed. A smart contract is written in Solidity language. Before this, you need to set up machine for local development:
1)For node environment, use
Install using Brew: brew install node@8
2) Smart contracts are usually compiled by Solc compiler. You can use npm to install:
npm install -g solc
3) Now is the time to run Go Ethereum which is referred as geth
4) Now, install truffle using npm
npm install -g truffle
5) Lastly, create a virtual Ethereum blockchain for fake accounts used during the development.
npm install -g ganache-cli
Hence, the local machine is setup for blockchain development
How to write smart contract?
- First add truffle coding file:
module.exports = {
networks: {
development: {
host: “127.0.0.1”,
port: 8545,
network_id: “*” // Match any network id
}
}
};
2) Now, you have to create a contract “counter.sol” file
pragma solidity ^0.4.23;contract Counter {
event CounterIncrementedEvent(int count);
event CounterDecrementedEvent(int count); int private count = 0; function incrementCounter() public {
count += 1;
emit CounterIncrementedEvent(count);
} function decrementCounter() public {
count -= 1;
emit CounterDecrementedEvent(count);
} function getCount() public constant returns (int) {
return count;
}
}
3) Add the deployment script “2_initial_migration.js” for counter.sol
var Counter = artifacts.require(“./Counter.sol”);module.exports = function(deployer) {
deployer.deploy(Counter);
};
4) Now, write the truffle test cases:
const Counter = artifacts.require(“Counter”);contract(‘Counter test’, async (accounts) => {
let instance; before(async () => {
instance = await Counter.deployed();//deploy contract
}); it(“Initial value of counter should be zero”, async () => {
let count = await instance.getCount.call({from: accounts[0]});
assert.equal(count, 0);
});});
5) Finally, you can now run the test cases
To run ganache-cli, use code:
Ganache-cli
To run truffle tests: use code
truffle test
So, you have deployed and tested your first smart contract app.
However, the full code is available here (https://github.com/sarveshgs/firstBlockchainApp)
B. Go
The language was developed by Google in 2007 and bring out among public in 2012. It is a popular domain-general programming language. It has a similar syntax as of C programming language and is statically typed. It comes with various features viz. User-friendly, robust, performing, highly secure and multi-purpose language. Since, it contains a rich standard library, it provides maximum flexibility when blockchain developers use GO for their blockchain projects. You can take free consultation from expert Golang app developer team if you wish to have a high performing and advance application offering features like fast data compilation in less time, collecting clutter for boosting up speed and performance and many more.
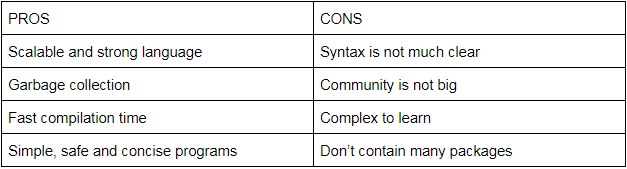
Use cases: Go-Ethereum apps , Hyperledger Fabric, Loom Network

How to create Ethereum apps using Go?
You can build native Ethereum applications using eth-go. Infact, Ethereum comes with a global config found in the “ethutil package”.
First you need to set base path for global config.
func main() {
// Read config
ethutil.ReadConfig(“.test”, ethutil.LogStd, nil, “MyEthApp”)
}
Now, you can set up & create your Ethereum node:
func main() {
// Read config
ethutil.ReadConfig(“.test”, ethutil.LogStd, nil, “MyEthApp”)
// Create a new ethereum node
ethereum, err := eth.New(eth.CapDefault, false)
if err != nil {
panic(fmt.Sprintf(“Could not start node: %s\n”, err))
}
// Set the port (default 30303)
ethereum.Port = “10101”
// Once we reach max, bounce them off.
ethereum.MaxPeers = 10
}
Once the base Ethereum stack get set up. Now, connect it to the main network:
package main
import (
“github.com/ethereum/eth-go”
“github.com/ethereum/eth-go/ethutil”
)
func main() {
// Read config
ethutil.ReadConfig(“.test”, ethutil.LogStd, nil, “MyEthApp”)
// Create a new ethereum node
ethereum, err := eth.New(eth.CapDefault, false)
if err != nil {
panic(fmt.Sprintf(“Could not start node: %s\n”, err))
}
// Set the port (default 30303)
ethereum.Port = “10101”
// Once we reach max, bounce them off.
ethereum.MaxPeers = 10
keyRing := ethutil.GetKeyRing()
// Create a new key if non exist
if keyRing.Len() == 0 {
// Create a new keypair
keyPair, err := ethutil.GenerateNewKeyPair()
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
// Add the keypair to the key ring
keyRing.Add(keyPair)
}
ethereum.Start(true)
ethereum.WaitForShutdown()
}
Hence, you node should be catching up with the blockchain now.
For full source code, please click here.(https://github.com/ethereum/go-ethereum/wiki/Creating-your-own-Ethereum-apps-using-Eth-go)
Top 4 Most Popular Ai Articles:
1. Cheat Sheets for AI, Neural Networks, Machine Learning, Deep Learning & Big Data
3. Getting Started with Building Realtime API Infrastructure
4. How I used machine learning as inspiration for physical paintings
C. Python
It is the most demanding programming language among new coders as it has a simple syntax like English language. It is one of the popular and modern programming languages used to create web apps on a server. It can also connect to database systems, perform complex mathematics and handle big data. In fact, each blockchain ecosystem contains one or more public tools written using Python language.
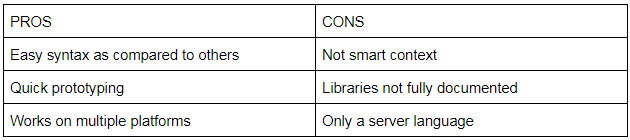
Use cases: Smart contracts on Hyperledger, Ethereum(pyethereum), Contracts for NEO
D. JavaScript
It is the most preferred language among software developers today and widely used for rapid web application development. It has various wonderful frameworks viz. Angular, React, Node and jQuery for website application development. The best thing about this language is that it perfectly suits blockchain operations as it can handle asynchronous actions involved in it. Moreover, it can easily handle the communications between all the different types of blockchain nodes.

Use cases:- Hyperledger Fabric SDK, Smart contracts development
E. C++
It is one of the oldest and most admired languages for web app development. As we all know that it is an extension of the C language

Use cases:– Cryptocurrency development, Bitcoin, Ripple, Bitcoin cash, Litecoin, Stellar, Monero
Blockchain platforms
1. Ethereum:
It is one of the popular blockchain development platforms which comes open-source for developing DApps running on blockchain technology. It not only track transactions but also program them. It facilitates scripting or smart contracts which are running via nodes in the respective network. Blockchain developers use Go, Python, C++, Java languages to build apps. However, smart contracts are built using high level programming language known as Solidity.
Use cases: ICO’s, Digital Identity Management, Smart contracts development, Fintech apps
2. Hyperledger:
It is considered as the king of open source blockchains and act as a leader by providing related training, tools and events for the development of blockchain-based distributed ledgers. The aim behind using Hyperledger for blockchain applications is to provide modular blockchain tech which is consisting of easy-to-use and rich APIs. Hyperledger platform comes with a lot of features viz. data privacy, immutability, information sharing, reduces security risks and increase authenticity.
Use cases: B2B contracts, Supply chain management, Manage depository assets
3. OpenChain:
It is an open-source blockchain platform developed by CoinPrism for industries that manage their digital assets. It develops secure and scalable applications and can have a single authority in multiple transactions. Here, the transaction process comes free-of-cost and considered as one of the efficient blockchain platforms.
Use Cases: Keep inter organizational records, develop lightweight fintech systems
4. Stellar:
This blockchain platform is used to develop smart devices, wallets and many more blockchain apps. It is a distributed ledger network which facilitates cross-platform asset transfers. For recording financial transactions, SCP(Stellar consensus protocol) maintain consensus without being rely on a closed system.
Use Cases: SureRemit, Satoshi pay, IBM world wire
5. R3 Corda:
R3 Corda is an innovative blockchain platform which was launched in 2015 and allows institutions to carry out transactions directly from smart contracts, thus reducing the friction of commercial transaction costs. Initially developed for financial institutions, R3 Corda can now be used in applications such as medical care, supply chain, government authorities, and commercial financing.
Use Cases: Manage digital assets, Facilitate global trade
Final Words:
Blockchain technology is predicted to have a huge impact on all business sectors and industries. In the next few years, as the world becomes more and more decentralized and the blockchain adapts as the mainstream, the future is really gonna be definitely unlimited.
Don’t forget to give us your ? !




A comprehensive Guide For All Your Blockchain App Development Needs was originally published in Becoming Human: Artificial Intelligence Magazine on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
3 Major Ways Ai Will Change The World But For Better

The ramifications of late advances in Artificial Intelligence (AI) have prodded warmed discussion internationally. As sci-fi begins to become reality, AI items are gradually penetrating homes and working environments. This is raising worries about the potential impeding impacts of AI hands on advertise, or even about the threats of an AI peculiarity, where aware robots assume control over the world and obliterate people.
While these are largely legitimate conversations, I accept that the focal point of AI ought not be simply on cool home devices or on process enhancement and robotization. Rather, AI can be utilized to generally reevaluate how we take care of the world’s issues.
Artificial intelligence can possibly enormously improve things like social insurance, training, neediness and security. Computer based intelligence machines can do some exceptionally useful things as of now today that people will just always be unable to. On the off chance that we influence that to expand what people progress admirably, AI could decidedly affect society, business, and culture on the request for greatness of the web itself.
I call this utilizing AI to scale the human psyche, not supplant it. The human cerebrum is the most exquisite PC in presence. We process a large number of tangible sources of info consequently and continually, permitting us to learn and react to our condition. In any case, the human cerebrum just contains around 300 million example processors that are answerable for human idea. Imagine a scenario where we could supplement the entirety of our astounding thoughts with more information, yet in addition requests of greatness more information preparing capacity. Envision how we would reexamine each and every difficult that exists today.
Indeed, even with the present crude types of AI, there is sufficient innovation out there to begin doing precisely this. The models beneath draw from an assortment of ventures to represent the greatness of social effect conceivable when we couple AI with human expertise and inventiveness.

1. Exactness Medicine
Computer based intelligence is driving the appropriation and usage of exactness medication: a rising methodology for ailment treatment and counteraction that considers singular inconstancy in qualities, condition, and way of life for every individual. Consider it a kind of clinical personalisation. For instance, around 25,000 individuals in the US are determined to have mind tumors consistently. Customarily, they may all be given a similar course of treatment to perceive what may work in a one-size-fits-all methodology. Exactness medication will permit specialists and analysts to anticipate all the more precisely which treatment and counteraction systems for a specific illness will work in which gatherings of individuals.
A significant number of the appropriate responses lie in the huge measure of clinical information previously gathered. Ayasdi utilizes AI calculations like profound figuring out how to empower specialists and medical clinics to all the more likely dissect their information. Through their work, clinical specialists have had the option to distinguish already obscure diabetes sub-types that could prompt better comprehension of treatments that could work better for specific kinds of patients. Enlitic and IBM are utilizing comparable AI calculations yet to identify tumors in radiology filters all the more precisely and effectively, and even possibly quicken finding a remedy for malignant growth.
2. Cybersecurity
There were around 707 million cybersecurity penetrates in 2015, and 554 million in simply the primary portion of 2016. The effect of only a couple of these assaults, for example, remote governments possibly biasing US presidential decisions, is really frightening.
Security groups battle today to work through the expanding number of cautions created by conventional apparatuses. Oneself learning and computerization capacities empowered by AI can expand adequacy and decrease costs, keeping us a lot more secure from fear based oppression or much littler scope wholesale fraud.
Top 4 Most Popular Ai Articles:
1. Cheat Sheets for AI, Neural Networks, Machine Learning, Deep Learning & Big Data
3. Getting Started with Building Realtime API Infrastructure
4. How I used machine learning as inspiration for physical paintings
Man-made intelligence based arrangements as of now in the market can be progressively proactive and can acquire assaults in the pre-execution state by distinguishing examples and irregularities related with malevolent substance. Secureworks utilizes the prescient capacities of AI for cutting edge risk location on a worldwide scale. SiftScience, Cylance, and Deep Instinct are utilizing it for misrepresentation avoidances and for endpoint security, as cell phones and workstations. These advancements will drastically grow the extension and size of security experts and permit them to distinguish dangers ideally a long time before they really assault.
3. Exactness Farming
The total populace is required to increment essentially throughout the following three decades, however our ability for nourishment creation will battle to keep pace. Simulated intelligence is driving proficiency in our present cultivating techniques to expand creation and diminish wastage without unfavorably influencing the earth.
Frameworks, for example, John Deere’s AutoTrac empower gigantic machines to plant crops in an unquestionably progressively uniform and exact way and can decrease cover in agrarian procedures, for example, working, planting and preparing, which thus lessens the utilization of synthetic compounds and expands profitability.
Cainthus, a machine vision organization, has another methodology. Utilizing profound learning, it has made a facial acknowledgment framework than can distinguish singular dairy animals by their facial highlights in only six seconds, empowering tremendous crowds to be observed with insignificant human contribution. Before long, they will have the option to identify early indications of faltering in a dairy animals dependent on its body shape, and alarm the rancher appropriately.
As sensors multiply on homesteads and automatons catch continuous pictures of the state of immense measures of farmland, AI machines will have the option to enable ranchers to predict what their harvests and homesteads are going to require possibly longer than a year ahead of time, giving them more opportunity to respond to unfavorable conditions.
Simulated intelligence can be applied to a lot more issues and markets. Truth be told, it ought to be thought of as an on a very basic level new way to deal with each issue. Those choices will be made by people who need to change and improve the world, and who presently can scale their psyches to address ever-growing outskirts.
Don’t forget to give us your ? !




3 Major Ways Ai Will Change The World But For Better was originally published in Becoming Human: Artificial Intelligence Magazine on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
Start Your Machine Learning Career in Quarantine
Originally from KDnuggets https://ift.tt/2zqv9bi
Top Stories May 4-10: Deep Learning: The Free eBook; Beginners Learning Path for Machine Learning
Originally from KDnuggets https://ift.tt/2AgpLI9
Machine Learning For Natural Disaster Relief: How Can ML Aid Humanitarian Efforts?

Machine Learning for Natural Disaster Relief
Every year, natural disasters affect approximately 160 million people worldwide.
With more than 400 natural disasters for 2019 alone, relief agencies and governments are struggling to turn these overwhelming amounts of data into actionable insights.
Fortunately, the latest developments in machine learning and artificial intelligence enable researchers, engineers, and scientists to explore and analyze various data sources more efficiently than ever before.
So how can machine learning improve disaster relief efforts?
Appsilon Data Science came up with an innovative solution.
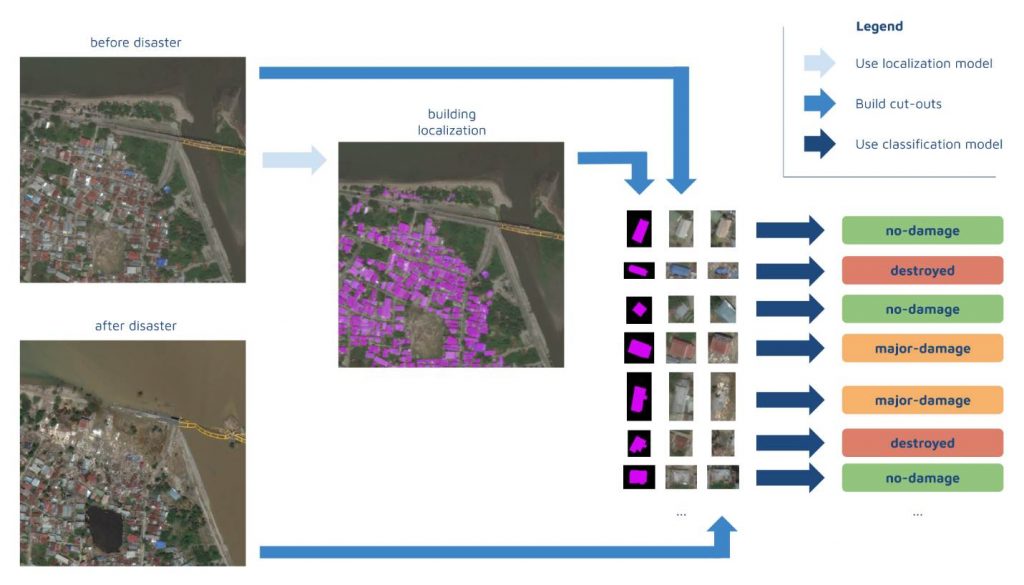
As an entry to the xView2 competition organized by the Defense Innovation Unit at United States Department of Defense, the company created machine learning models to assess structural damage by analyzing before-and-after satellite images of natural disasters. They used PyTorch to build their models and fast.ai to develop their critical parts.
Appsilon’s Machine Learning for Natural Disaster Relief: How does it work?
The Appsilon Data Science Machine Learning team built ML models using the xBD dataset. The dataset comprises data across 8 disaster types, 15 countries, and thousands of square kilometers of imagery. The goal of the ML models was to assess damage to infrastructure to help alleviate human labor and decrease the time for planning an adequate response.
The models not only achieve high accuracy but also boast an intuitive user interface that enables everyone to benefit from its capabilities. The interface was developed and implemented in Shiny using Appsilon’s own shiny.semantic open source package.
Appsilon’s Machine Learning for Natural Disaster Relief: What are the Models’ Technical Specifics?
The Damage Assessment App
Appsilon Data Science implemented their models in a Shiny app that allows users to explore the impact of four real-life natural disasters by running their model on built-in scenarios – Hurricane Florence, Santa Rosa Wildfire, the Midwest Flooding, and the Palu Tsunami.
The latter resulted from the September 2018 earthquake in Indonesia and caused considerable property damage in the area of the capital Palu.
The Dataset
The xBD dataset consists of satellite imagery data for several regions recently harmed by natural disasters. The dataset is quite varied, as it comprises a wide range of affected locations: from remote forests, through industrial areas with large buildings to high-density urban landscapes.
The main challenges the team faced were the diverse locations and building sizes, as well as the variety of disasters.
Apart from the ability to localize the buildings, the model also had to assess structural damage. That meant using one approach for areas destroyed by a fire, and a different one for such destroyed by flood. The disaster types in the dataset included volcanic eruptions, hurricanes, disastrous floods, tsunamis, raging wildfires, tornado damage, and bushfires.
Saving response planners endless hours of searching through thousands of images or conducting face-to-face surveys allows them to focus the limited resources on taking proper action and, consequently, saving more lives.In terms of imagery, the availability of ‘before’ and ‘after’ images of affected areas turned out to be crucial for speeding up humanitarian response.
The Machine Learning Pipeline
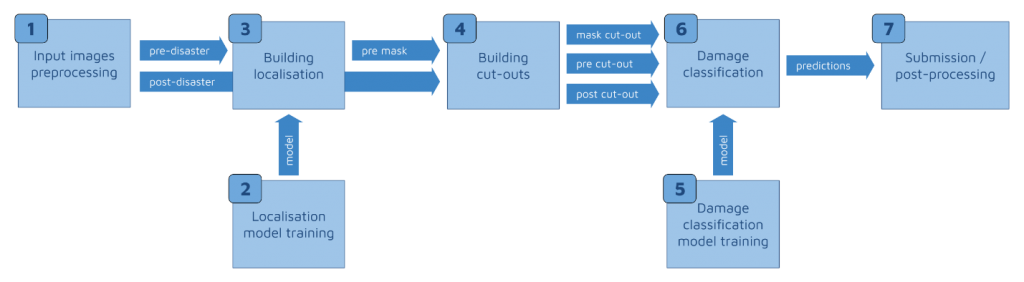
Developing a high-accuracy ML model for satellite imagery analysis requires two components: building localization and damage assessment. Although a single model can do both, Appsilon Data Science decided to build a separate model for each task.
This turned out to be quite challenging, as ‘each model requires a separate training dataset with the same preprocessing schedule’. Preprocessing involves changing the color histograms of the images, cropping, padding, and flipping, among other data augmentation methods. Naturally, the team struggled with managing such a large number of moving parts. Moreover, performing inference on slightly different parameters than the parameters used for model training would result in a very low score.
So how did Appsilon avoid this risk?
By employing an appropriate ML pipeline. This way, the training process remained completely reproducible and, at the same time, efficient. To accomplish that, they based the pipeline on their internal framework. Since it memorized the results of all the steps, they could to reuse them. Besides, it automatically ran the computation in case any hyperparameters or dependencies changed. All of this resulted in a much faster and mistake-free development process.
Here are the specific steps:
But it wasn’t just the ML pipeline, that enabled the team to deliver an accurate model. Two other techniques also helped them achieve that within a limited timeframe – transfer learning for localization and 7-channel input for classification.
Transfer learning for localization
Appsilon chose one of the best models developed for a SpaceNet competition. Then, they used transfer learning to apply it to building damage assessment in natural disaster response.
Localization is of major importance to the model accuracy. After all, the model can’t classify damage to a building, unless it finds it first. In a team member’s own words, ‘the better the localization model, the higher the potential score for damage assessment’.
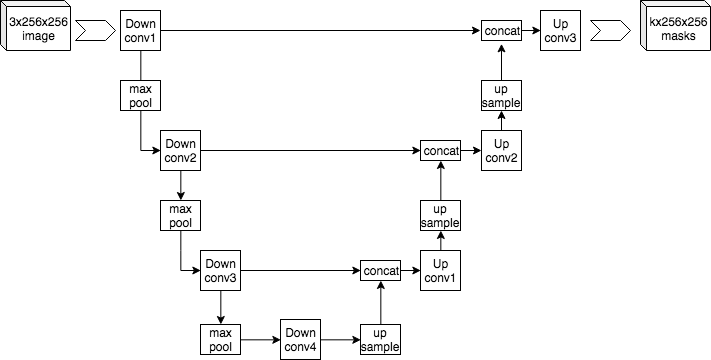
The team used neural networks based on the UNet architecture, as they are suitable for solving such segmentation problems.
UNet architectures first encode the image to a smaller resolution representation; then decode it back to create a segmentation mask. Still, the very process of developing appropriate weights for the segmentation exercise can take a lot of time and effort.
Fortunately, localization of buildings on images is a well-examined issue. So, to build their model, the Appsilon team took existing, cutting-edge ML localization solutions developed through a series of SpaceNet competitions. Specifically, they used XDXD pre-trained weights created for one of the top SpaceNet4 solutions, built using a VGG-16 encoder.
Once the model with pre-existing weights was ready, they continued training it on the xView2 data. Thus, they improved the accuracy, while spending much less time on computation compared to building a model from zero.
7-Channel input for classification
Appsilon further accelerated the training of the damage assessment model by employing a 7th channel for identifying the building location in an image.
The localization model enabled them to identify individual buildings’ locations. How?
They cut each building out of the bigger image along with a small portion of the surrounding area.
That was necessary because the damage score for a building sometimes depended on its surroundings. For example, a building with an undamaged roof was still scored to have sustained significant damage, as it was fully surrounded by floodwater. This means Appsilon Data Science had two cutouts for each building, where its state pre- and post-disaster were depicted (each had 3 channels: RGB).
In addition, they used a 7th channel – a mask highlighting the location of the building within the cutout. The 7th channel allows the classification model to quickly identify the important part of the image – the building itself. It’s true that such an addition increases the size of the model and could slow make the inference process a bit slower. But, even so, it actually accelerates the training of the model because it learns faster where to focus its attention. And, at the end of the day, that results in better accuracy.
Machine Learning for Natural Disaster Relief: How Can You Contribute?
We believe that Appsilon Data Science machine learning solution for disaster relief is a great example of how the data science community can help solve one of the most serious issues in our day. As part of their AI for Good initiative, the company reaches out to the tech community from around the world willing to use their expertise to support those working on the front line of natural disaster management and response to empower them with the latest cutting-edge solutions.
The post Machine Learning For Natural Disaster Relief: How Can ML Aid Humanitarian Efforts? appeared first on 365 Data Science.
from 365 Data Science https://ift.tt/2yLz02I
