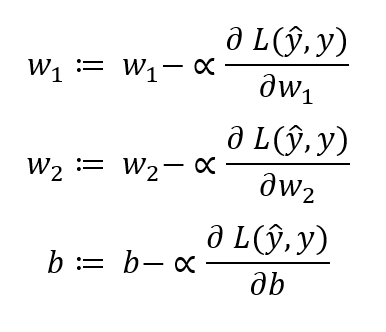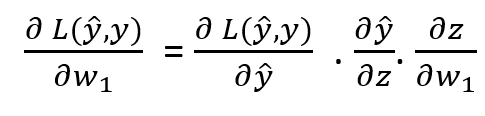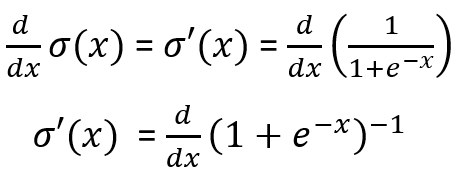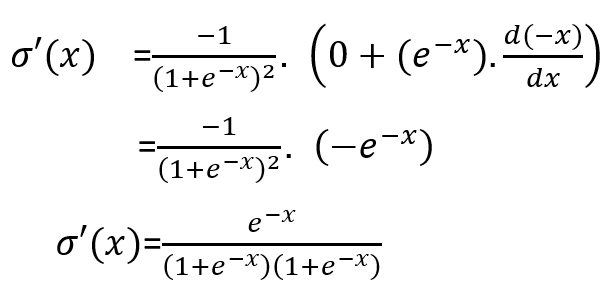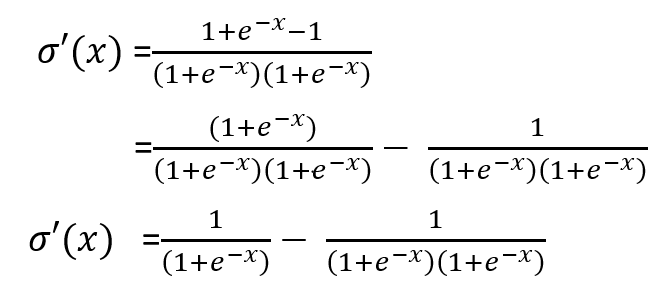Data Annotation — Outsourcing v/s In-house — ROI and Benefits | Analytics Insight
Data Annotation — Outsourcing v/s In-house — ROI and Benefits

A 2018 report revealed that we generated close to 2.5 quintillion bytes of data every single day. Contrary to popular belief, not all the data we generate can be processed for insights. For data that can be used for training machine learning algorithms, the data has to be classified.
If you ask a layman how Artificial Intelligence models and algorithms work, they would tell you that it involves just three steps:
- Data is fed to the algorithms
- The algorithms process the data
- The desired results are obtained
But in reality, this is not how an AI model works and with this outlook, we are completely missing a crucial layer that defines the entire algorithm’s capability to produce efficient and accurate results — data annotation.
In simple words, data annotation or labeling is a process in which humans (inevitable parts of artificial intelligence) tag or label data to make it easier for the algorithms to understand and process. AI experts tag data such as videos, text, audio, images, and other forms of data through specialized tools with human-in-the-loop. Only when the data is tagged can a machine can actually work on it.

However, the actual debate stems at this point as several companies out there have varied opinions on where they would like to get their data annotated. While some companies lean towards having an in-house team or using existing manpower and resources to annotate data, others prefer to outsource data annotation to third party vendors.
Both have their own set of pros and cons and if you’re someone who is stuck at that exact point in the process, this post will help bring you closer to making the right decision for you.
Trending AI Articles:
2. Generating neural speech synthesis voice acting using xVASynth
The Advantages Of Outsourcing Data Annotation Work
Dedicate Your Team For Greater Purposes
Most data scientists will tell you that the most tedious part of their jobs is preparing the data to train their algorithms. Having to do the janitorial work is not only a redundant task for a data science team, but it takes away valuable time and effort that could otherwise be more meaningfully utilized. The redundant task only takes away valuable man-hours and probably stalls the overlapping processes involved in the development cycle, too. But when you outsource the annotation process, both the processes happen simultaneously, eliminating all scopes in project delays.
Moreover, outsourcing the data annotation process enables your data science team to focus on continuing the development of robust algorithms and pushing the brink of innovation further for the company.
Better Quality
Dedicated experts whose only job is to annotate data for machine learning and AI modeling purposes will — any day — do a better job than a team that has to accommodate more than one task in their schedules. Needless to say, This results in better quality output.
Bulk Volumes Of Data Annotated Seamlessly
Though an average AI model development project involves labeling huge chunks of data in the range of thousands, there are specific projects with respect to healthcare, retail, sports, or more than easily add another zero at the end. As the volume of data to be labeled increases, it adds to the burden of your existing in-house team. What’s worse is you might even have to pull engineers and members from other teams to finish the task. However, that’s not the case with outsourcing companies like Shaip, who have niche dedicated teams and members to handle and scale operations regardless of data volumes because that is their one and only goal!.
Eliminate Internal Bias
A fundamental reason why several AI models don’t work the way they are supposed to, is because the teams working on it involuntarily introduce bias, skewing the output and drastically minimizing accuracy. An AI model under development is like a child and similar to a kid that learns from its parents’ behaviors and surroundings, an AI model learns from what it is also fed. That’s why an objective third-party does a better job at annotating the AI training data for optimized accuracy. With assumptions and bias eliminated, the real-world application of the model becomes more effective and impactful.
When Does In-House Data Annotation Make More Sense?
It’s simple. In-house data annotation makes more sense when the data volumes are less and the cost to get it outsourced is more than the project’s scope, budget, and worth.
Also, in-house data annotation is ideal when more internal inputs are required or when a project is super-specific (first-in-market) and only known to the company and its members. In that case, it is time-consuming to train a third-party vendor, orient them and get the job done.
The Data Security Myth
As a project manager, it is common to get concerned about the confidentiality of data being shared. And this is a crucial factor that decides if the annotation project has to be outsourced or retained within teams. Companies are constantly evolving their approach to data privacy and confidentiality. Understanding the importance of the topic’s sensitivity, several outsourcing vendors and companies come prepared to sign confidentiality agreements and clauses and even have security certificates to prove their adherence. For example, if a company is working with highly sensitive healthcare data, the appropriate data vendors are extremely vigilant and would have HIPAA compliance amongst other regulations under their belt. So, if data security is something that has been making you hesitant about outsourcing a complex project, you need not worry about it.
Final Thoughts
It’s safe to say that data annotation is no simple feat. The best option in hand is to get the job done by the pros and veterans. While we at Shaip take care of the tagging processes, you can work on other equally important tasks that would take your project a step closer to completion.
And just like the factors we mentioned, we check all the boxes on data confidentiality, quality, scalability, timely delivery, and more. Our ‘in-house’ teams of annotators have handpicked industry experts who have been working in this spectrum for years. Our super-exclusive tools are also designed to simplify the complexities involved in our projects.
We highly recommend you to get in touch with us for your data annotation needs today.
Author Bio

Vatsal Ghiya is a serial entrepreneur with more than 20 years of experience in healthcare AI software and services. He is a CEO and co-founder of Shaip, which enables the on-demand scaling of our platform, processes, and people for companies with the most demanding machine learning and artificial intelligence initiatives.
Don’t forget to give us your ? !




Data Annotation — Outsourcing v/s In-house — ROI and Benefits | Analytics Insight was originally published in Becoming Human: Artificial Intelligence Magazine on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.