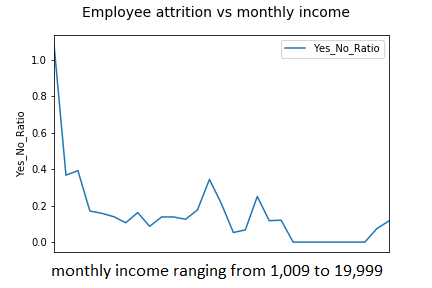
Currently, artificial intelligence and big data are seen as part of the working life in different fields of major enterprises. AI is a groundbreaking technology that has transformed how people utilize computers and perform a business at an accelerated rate of AI growth successes in unmanned air vehicles, chess and poker, digital customer care and analysis systems — are demonstrated.
The appearance of smart computers willing to overcome complex issues in respects that only human beings have been unaware of before. The AI system has developed and strengthened since the day of its discovery. AI is commonly employed in many spheres, due to its capacity to read. Aircraft networks, voice synthesis, computer training, and machine vision are basic implementations of AI.
A quick advance button on medical intelligence (AI) software was pushed by the coronavirus outbreak, and the struggle against both the virus further implemented the technology. Medical imagery AI has taken an important role in support scanning COVID-19 and big data will help monitor the origins of infectious diseases and boost image reader efficiencies based on image processing and other technology. As the pandemic has rounded the globe, creative AI technologies have grown in several places.

Medical AI decision-making processes will also help patients receive better treatment diagnoses
The use of AI technologies in different medical areas is normally referred to in Medical AI. The study says that AI and the industry are one of the first and most significant fields in which large, complicated, and specialized heterogeneous data is integrated. To maximize the processing speed of medical issues, AI may easily use knowledge.
In imports of cold-chain food safety practices, China’s technology firms’ Big Data Shadow,
They partner with local councils to promote the monitoring and safeguarding of manufactured cold chain produce. The method involves the recording of cold food stock, the key feature of the cold chain, the inflowing and outflowing of cold chain food and the manufacturing and selling of manufactured cold chain foods.
Themes such as the growth and Java web development of technology after the pandemic, the interaction between AI and ethics and whether algorithms are going to ‘govern’ people’s lives in the scientific area have been heated.
Trending AI Articles:
1. Preparing for the Great Reset and The Future of Work in the New Normal
In the future let’s look at eagerness based on two factors.
Firstly, data now stream, still AI’s lifeblood. Kaggle is the host of the Covid-19 Free Analysis Dataset, a machine learning and data science website. As is established, Covid-19 compiles related data in one central platform and adds new analysis. The latest data collection is accessible by the machine, which allows it simple to interpret for AI learning purposes. More than 128,000 research papers are written on Covid-19, SARS,
- Coronaviruses and so on.
- Secondly, worldwide medical science and computational scientists today work on these issues laser-focused. It is expected the target of Covid 19 to be up to 200 million medical professionals, researchers, nurses, technologists and engineers. They conduct tens of thousands of tests and exchange knowledge “that we have never seen before with transparency and speed. The study challenge undertaken at Kaggle, Covid-19, seeks to include a large variety of insights into the pandemic, such as its natural background, transfer evidence and diagnostic requirements for the virus and lessons learned from earlier observational studies that enable health organizations in the global community to be better educated and decide on data. On 16 March the challenge came up. In five days, over 500,000 views have been received and over 18,000 downloads have been generated. A new coronavirus can be monitored, mapped, detected and cut off in this world until it was unleashed.
It’s not that far removed as it might sound. We shall soon step into an age of completely autonomous AI when medical technology and computer science merge ever more when we would expect citizens to select wearable, biosensor and intelligent home detectors so that they are kept protected and updated. And with wearable devices and other Internet-of-Things gadgets rising data quality and diversity, a virtuous loop of changes can continue.
Don’t forget to give us your ? !




Does AI Raises Security and Ethics Concerns amid Pandemic was originally published in Becoming Human: Artificial Intelligence Magazine on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.