Originally from KDnuggets https://ift.tt/3awB5hW
How to Get Your First Job in Data Science without Any Work Experience
Originally from KDnuggets https://ift.tt/2MUI6RC
KDnuggets News 21:n05 Feb 3: How to Get a Job as a Data Scientist; Popular Machine Learning Interview Questions part 2
Originally from KDnuggets https://ift.tt/39GSZiA
Adversarial generation of extreme samples
Originally from KDnuggets https://ift.tt/3aspfoT
Machine Learning- Setting Trends in Science & Technology
A learning machine is any device whose actions are influenced by the past experience — Nils John Nilsson
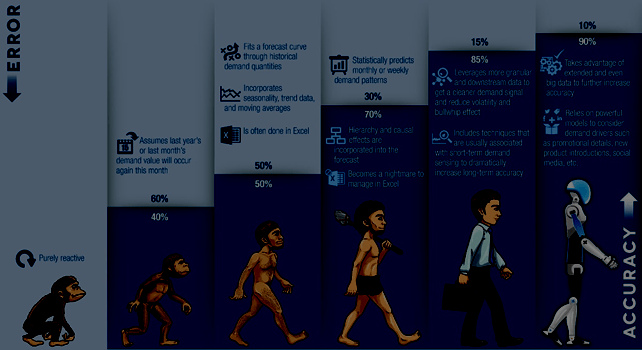
Machine learning is a term incepted by Arthur Samuel in computer learning. It is a technique by which any computer can identify patterns, trends and can store them for its future decisions in similar situations. Machine learning is mostly confused with artificial intelligence but actually, it is not the same.
It is only the current application being used in AI and deals with making machines learn about things on their own. We can save our time in explicitly programming the bots and can work on other areas. This new term has evolved from the study of pattern recognition & computational learning theory.
A computer is made to study the patterns and make note of them so that it might recognize the same style if it sees them again. In simple terms, we say it something learned by the machine. By implementing machine learning tools and applications we can design various algorithms that are crucial for imparting knowledge into the machines.

Imparting knowledge into the machines and making them smarter, is a concept loved by all but still debatable in terms of its limits. Different groups are putting their views about setting some parameters and identifying boundaries for this knowledge transfer. It has been a long-time dream of the humanity to produce something which can give us a feeling of a creator. We are working rigorously to create some really smart beings for whom we can take the full credit. Smart bots are something similar to that only. Machines were created to ease of the human efforts and to make our living more comfortable on this planet.
We want machines to go some extra miles and take the jargon into their own hands. We want machines to be autonomous as well as loyal. We want them to feel, take decisions but those decisions should be the one approved by their master (humans). It is something which is not acceptable by all in a similar manner. Some believe that machines can go a level beyond if they know how to take decisions and can be a danger to our own existence. But others are looking at only the brighter aspects which are making our life easier and less complicated.
As evolution has helped humans to get better with each passing day. We have learned from our past deeds and mistakes. We have even learned a few things from our peers and other’s experience. There are certain ways in which a machine learns. Learning in the case of machines is largely supported by computational statistics. It is highly dependent upon mathematical optimization which provides methods and theories about learning. IT companies all over the world are using these mathematical models to improve learning and extracting maximum information from a small data
a) Learning on examples: Machines are given information to study and understand. It could be patterns, some actions or any other tasks to be done after identifying the certain pattern or listening to a particular command. They are enabled to store that information for their future use so that they can check and follow the same act whenever they see the same thing or pattern.
Trending AI Articles:
2. Generating neural speech synthesis voice acting using xVASynth
b) Learning from experience: Computers do a certain task and gets trapped into an unwanted situation. They are made to learn from their own mistake and expected not to follow the same steps when again they found a similar problem.
c) Self Learning: A method where machines or bots are given enough knowledge to understand what to do and what not to. And then they are being tested upon whether they have some sort of self-learning or not. It could be doing some small things and getting an idea of doing or not doing it. It is generally done by giving data to the machines. They interpret the data and then act accordingly. It is something beneficial to share markets etc.
d) Deep Learning: It is a branch of learning in which computers study about patterns and analyze it for getting a further level of information. Such learning is important in understanding genetic coding and other biological information.
All these types of learning mechanisms are used for training the bots for specific type work. Machines are being made smarter to improve accuracy and reduce human efforts. These smart bots can take some really tiring and high calculative work and give us the results without fatigue. We are constantly upgrading ways to find our some really smart techniques in machine learning which are quick as well as effective. We want these bots to be smart and that too soon keeping in mind that the whole learning process is always under control and bots always abide human instructions.
“Stay Informed and connect to Saavy Relations for the latest updates.”
Your Feedback is Highly Appreciated! We really appreciate the time you took to help us improve.
Don’t forget to give us your ? !




Machine Learning- Setting Trends in Science & Technology was originally published in Becoming Human: Artificial Intelligence Magazine on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
Artificial Intelligence- advances and impact
Artificial Intelligence- Advances and impact
It can be the greatest boon for mankind and have potential risks too

Artificial intelligence is imparting human-like intelligence in machines. With latest advancements in technology, humans have succeeded in imparting a considerable level of knowledge and decision making ability into the machines. These machines are deployed to replace humans from dangerous working conditions and to reduce human efforts for various unproductive activities. These bots are giving reliable assistance to human species.
What does it actually mean??
It is a simulation of human activities by machines, prominently by computers. If we say that we are imparting artificial intelligence in any machine then it means we are making it competent enough to do certain activities. The major processes are reasoning, learning various tasks and doing a self-correction in its own activities.
Numerous benefits from these bots
Numerous companies have started working on artificial intelligence. They are doing a complete revamp of the current working culture in organizations. Companies working in conversational activities, vision, cybersecurity, healthcare, business intelligence etc. are using AI machines and replacing humans with complex activities and reducing their operational costs up to a great extent. Most organizations are using bots for rigorous calculations to avoid human errors and imparting self-rectification skills in these intelligent bots.

Artificial intelligence has contributed considerably in the healthcare industry. Healthcare industries are using these bots for an accurate & faster diagnosis as compared to human specialists. These smart machines are giving a reliable solution for many operational procedures. We are capable enough to introduce these machines in dealing with patients. Chatbots are being deployed to interact with the patients and provide an unmatched response. They have minimized the human efforts and have empowered us to interact with multiple patients simultaneously. These bots can even assist in patient scheduling, follow-ups and billings. A better engagement with patients and reduced human efforts in paperwork have improved the effectiveness of the treatment.
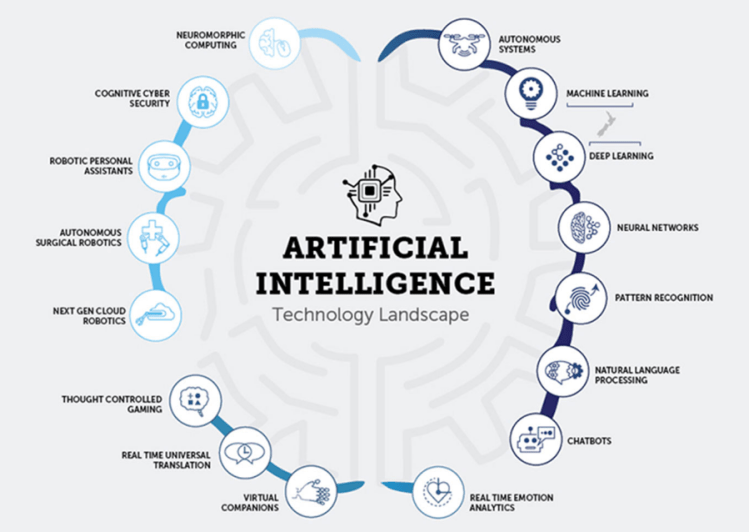
Artificial intelligence has equally contributed to finance sector. The machines are made capable enough to understand and do tedious calculations. These bots are also used in financial applications like Mint or Turbo Tax. They can collect the data and help in making a proper financial plan for the customers. Number of customers can be entertained with an even smaller number of staff without compromising the accuracy. These bots are now being used in trading activities also. Here also these smart bots have proved their mettle.
These robots are used in highly iterative tasks in manufacturing and business activities. They can work without fatigue and thus are the preferred choice for most of the industries now. Algorithms are being used in business CRM software for better analysis of data. They can work in a much efficient manner by handling numerous customers and even handling their grievances. AI has enabled machines to replace trainers in the education sector and can even provide additional support to the pupils.
Trending AI Articles:
2. Generating neural speech synthesis voice acting using xVASynth
Risks involved with these intelligent machines
We are largely benefited by Artificial intelligence and our efforts are being replaced by machine iterations. Many tedious and precise jobs have been allocated to these bots. But they have created a sense of insecurity too. Well, with the latest introduction of these smart machines, in various business operations and other segments have replaced humans. The replaced population is mostly unskilled in other segments of the business and thus are unemployable for other skilled jobs. They are facing a situation of financial crisis. But the business houses are enjoying their new cheap and 24X7 working staff, they are asking for minimal benefits from the employers.
Apart from this, many thinkers have doubts about the rapid progressions achieved in this segment. Deploying something more than required, in these machines is the major concern by many eminent professionals. They are seriously against the speed at which intelligence is being imparted to these bots.
Prof Stephen Hawking, one of Britain’s pre-eminent scientists, has said that efforts to create thinking machines pose a threat to our very existence.
Experts differ on the very idea of bots super-seeding the biologically slow evolving human species. Nobody can deny from such future completely. Imparting too much into these bots and giving them the power to replicate and repair can be a catastrophe decision in the future. We have to plan well before executing. Machines were introduced to reduce human efforts but they are simultaneously making humans dumb.
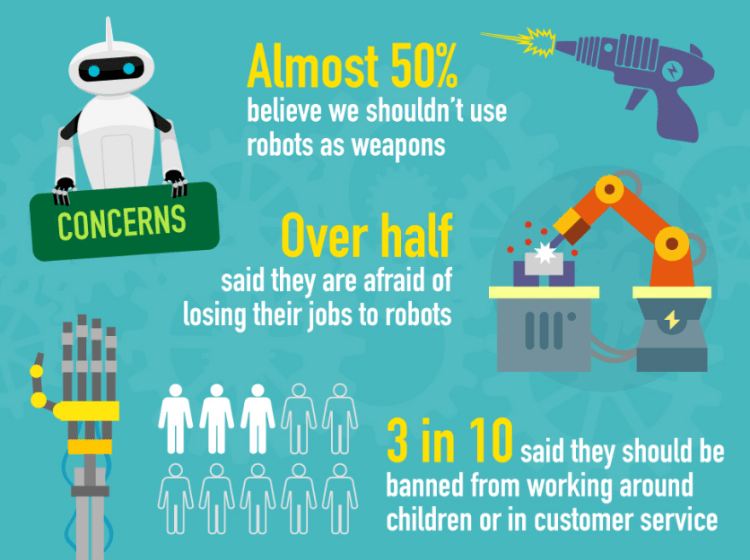
They are doing most of the complex activities by themselves and making humans rely on them heavily. These machines can do complex calculations & precise tasks in a much amicable manner but they can not compete with the creativity of the human brain as of now. Thus we should still take some time before designing our systems.
Are we really ready for the bots??
“Stay Informed and connect to Saavy Relations for the latest updates.”
Your Feedback is Highly Appreciated! We really appreciate the time you took to help us improve.
Don’t forget to give us your ? !




Artificial Intelligence- advances and impact was originally published in Becoming Human: Artificial Intelligence Magazine on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
What is big data? And how does it power todays insights?
By: Sofia Sayyah

We hear the term “big data” all the time. We live in the “era of big data,” companies are learning to “utilize big data,” you can “improve your business model with big data,” yada yada yada. But what is big data? Besides a buzzword, that is.
What is big data?
The phrase “big data” can refer either to the data itself or to the field that undertakes the task of analyzing it. We will discuss what makes data “big” later on, but for now let’s work with the second usage of the term. Big data is a field of work that deals with analyzing and finding insights in data that is too overwhelmingly large or complex for traditional data-processing software to work efficiently.
How big data became the booming field it is today
Data has been leveraged as a resource for decision-making since Ancient Egypt. However, the basis for what would become “big data” began in the 1970s, with database management and data warehousing. These strategies worked with structured data that could be stored in Relational Database Management Systems, and formed the foundation of data mining as we know it, using queries and statistical analysis. Still, it wasn’t until the dot com boom around 1995 that data began to accumulate at a rapidly increasing rate, as it has for the last 20 years.

The expansion of web traffic followed by social media in the 2000s created new opportunities for data analysis, with information such as click-rates and search logs now being collected. Organizations were facing a tsunami of data, data that was semi-structured or unstructured — meaning the data has no pre-defined internal structure and therefore is not stored in a structured database — instead of structured — tabular, and organized in such a way that makes it easily searchable in a database — requiring new techniques for storing, wrangling, and analyzing data in order to make it meaningful.
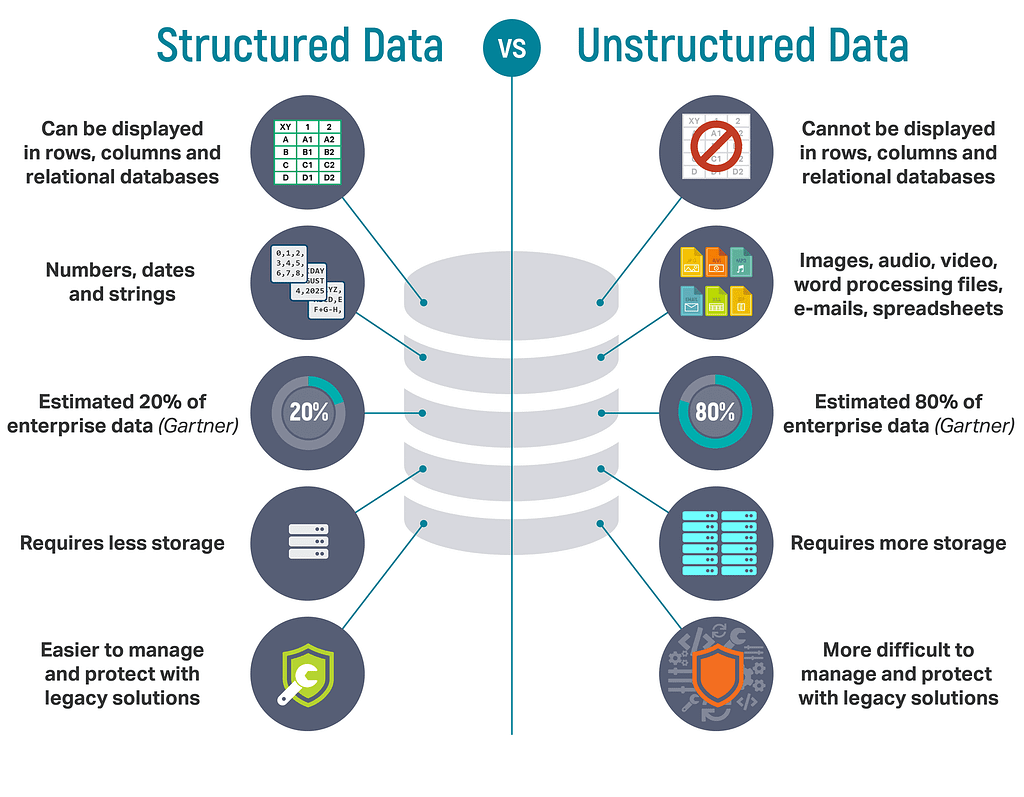
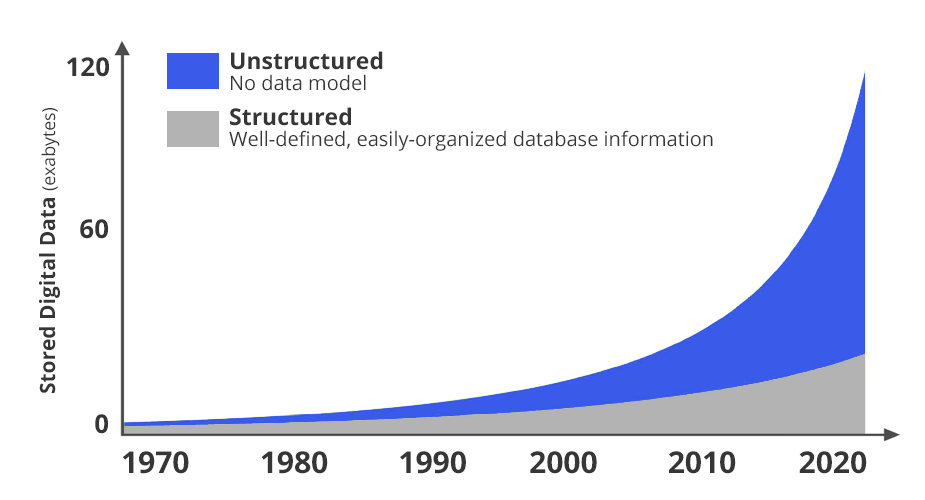
In the last 10 years only, we’ve seen a huge expansion of new types of data collection with the rise of the Internet of Things: smartphones, smart appliances, watches, home assistants, security systems, industrial and commercial sensors, and more have made data collection easy and cheap. There is a wealth of information about our behavior and preferences like never before, if we can just understand all this data.
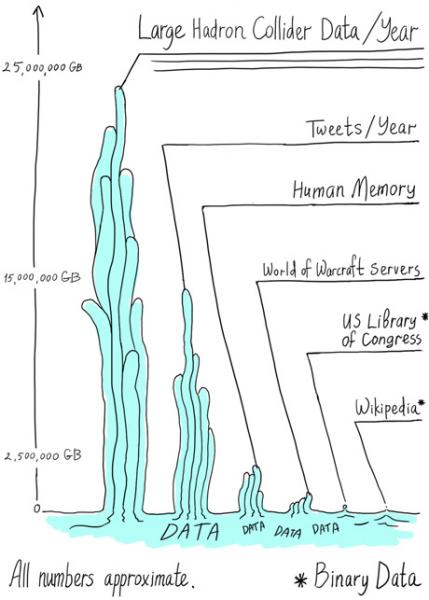
What makes data “big”?
Now that we understand how the field of big data reached its current state, let’s take a look at what technically makes data “big.”
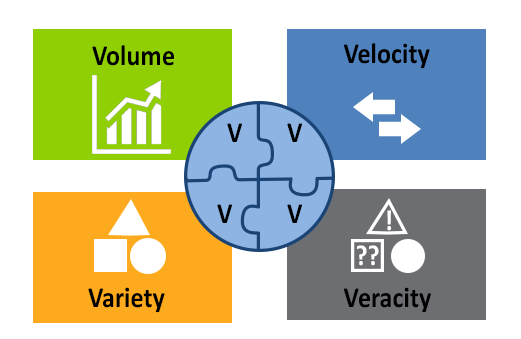
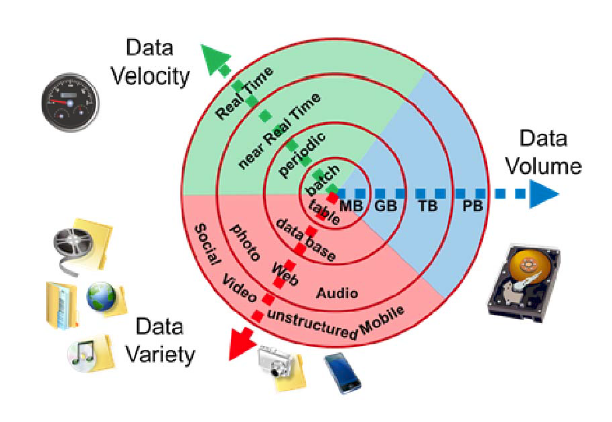
There are three key criteria that define big data: volume, velocity, and variety.
Volume: The quantity of generated and stored data. Big data usually means you’ll be dealing with large amounts of unstructured data. The size of the data helps to determine the potential insights to be made.
Velocity: The speed at which the data is generated and processed. Big data is often available in real time, and requires immediate evaluation in order to meet the challenges involved in growth and development, and are produced more continually. Velocity can also be further divided into (1) the frequency of generation and (2) the frequency of handling, recording, and publishing.
Variety: The type and nature of the data. Big data draws from many types of data, including text, images, audio, video, and other unstructured or semistructured data. Further, it can fill in the gaps with data fusion. Understanding the variety allows analysts to effectively process the data and create meaningful insights.
Trending AI Articles:
2. Generating neural speech synthesis voice acting using xVASynth
Another factor also considered when determining what is big data is veracity.
Veracity: The data quality and the data value. The quality of captured data can vary greatly, which impacts the quality of analysis and insight. Low quality data is even more challenging to link, clean, and transform across systems, limiting its usefulness.
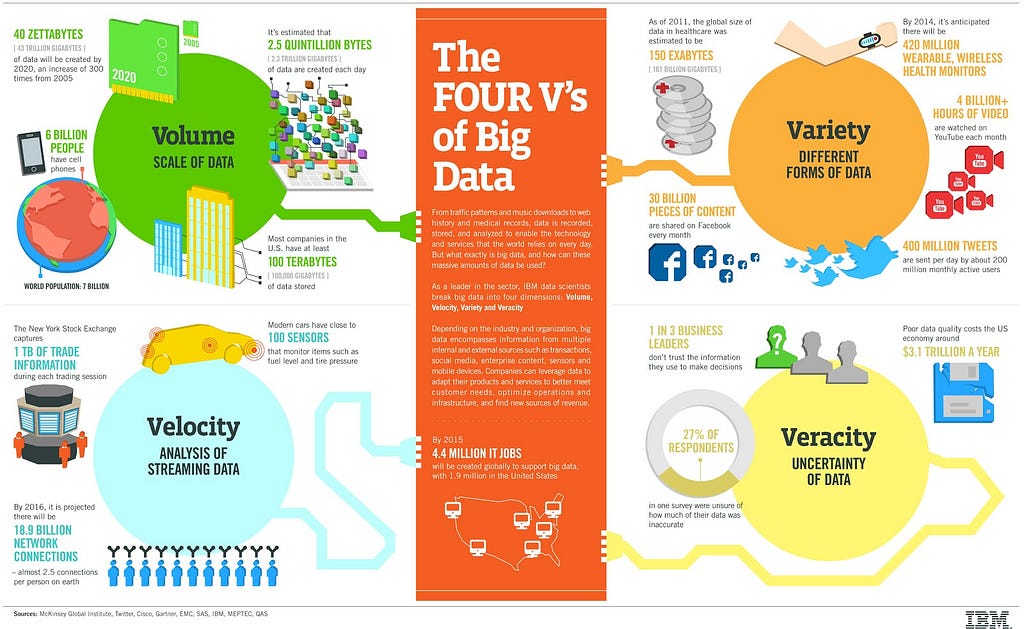
What’s so great about big data?
Big data is a potential gold mine of information for organizations. The sheer quantity and variety of data being collected, often in real time, lead to much greater statistical power. The gains to be made from utilizing big data are substantial, and can include the following:
Improved decision-making capabilities: Organizations have access to more and more information, making for varied and deep insights. By the law of large numbers, as sample size and number of trials increase, sample statistics converge to population parameters; this means that having access to more data, as well as data that is more representative, organizations have much greater statistical power in learning about their subject of interest. Where data was once lacking, there is now a constant flow of information to minimize guesswork involved in decision-making, which has far-reaching implications across an organization.
Increased efficiency: Big data allows an organization to both increase productivity and decrease costs. If the right tools are being used, analysts can analyze more data faster, increasing productivity per analyst. This reduces the effort it takes for an organization to effectively make use of data. In addition to data on their customers and products, organizations can also gather internal data, allowing them to analyze and target operational efficiencies in order to get rid of them.
Greater potential applications: Now that data is being collected about nearly everything we do, the applications of this data are endless. One primary use is improving customer experience; when data is collected from interactions with customers, organizations can make their customer relationships more effective. Other applications include product development, systems maintenance, fraud detection, market disruption, and faster time-to-market, among many others.
What are the challenges associated with big data?
Big data may come with big rewards, but it also comes with big challenges. Many of these challenges have to do with just how big the data is.
Data storage: The New York Stock Exchange generates roughly 1 terabyte of data each day. Facebook ingests 500+ terabytes of data each day. A jet engine can generate 10+ terabytes of data each half hour it is in flight — with hundreds of thousands of flights every day, that is petabytes of data. This leads us to the trillion dollar question — how do we store all of that data?
Data analysis: Say we’ve solved the problem of storing all this data — now we have to sift through it and make something of it. It’s a flood of information, and analysts don’t always know what they’re looking for or how to find it, particularly in data that is unstructured or semi-structured. Finding insights can be like searching for a needle in a very large, very messy haystack.
Data cleaning: Data cleaning is the process of making data uniform and removing or correcting incomplete or inaccurate data. Analysts spend anywhere from 50–80% of their time cleaning data, work that is necessary for any analysis to be done. This should make data analysis easier, but unstructured or semi-unstructured data require much more work to make usable, and data quality can also help or hinder this process. Such a large volume of data makes the task of cleaning an enormous one.
Data maintenance: Now that data has been stored, cleaned, and analyzed, what should be done with it? Do we keep it? Is it still relevant? How do we make room for the data still being collected every minute? How can we keep this data neat as we add to it and update it? All the normal problems faced in data management grow with the size of the data.
The traditional tools used to work with smaller amounts of data are inefficient in handling the same tasks on a much larger scale. Tools that are geared specifically for this challenge, such as Apache Hadoop and Spark, help to manage data that exists on such a large scale (100s GB+), and more tools are constantly in development.
Which industries have benefited the most from the transition?
Healthcare: Big data is completely transforming healthcare. By putting medical records to use, doctors are able to identify illnesses with greater accuracy and treat illnesses with greater precision. This is leading a growing sector focused on personalized medicine, including wearable medical technology. Recently, we’ve also seen how predictive models are helping us to understand the spread of COVID-19.
Retail: The retail market is fast-paced, and retail establishments need to anticipate customers’ wants and provide for them. Big data is helping organizations predict trends, optimize pricing, and match their customers with the products they want.
Finance: Big data is essential to big money trading, particularly in financial models and real time stock market analysis. In addition to these applications, financial institutions are using data to detect fraudulent transactions or manage risk.
Transportation, supply chain, logistics: Organizations are improving their logistics by using big data to map journeys, inform decisions to restock, and prepare for unexpected circumstances. Additionally, sensor data collected from planes, trains, and automobiles can help uncover sources of failure and ways to improve.
Data: Now that big data is so common, an industry devoted to it is quickly growing. There are companies who are built on data, such as Pinterest or Spotify, but have a different end user product. There are also organizations that deal entirely in data, such as providing data management services, or machine learning insights (which is some of what Big Data at Berkeley does for our clients!).
Big data in our daily lives
Big data is in action in our daily lives, whether we see it or not. It is moulding the technologies we use and improving our quality of life. The changes in the healthcare industry mentioned earlier are improving patient outcomes. Our consumption of products is also changing. Amazon, Spotify, and Netflix can tell us what we want to consume before we know it ourselves. Our daily comforts are beginning to rely on big data-utilizing technologies that have integrated seamlessly into our lives without our realizing it.
With these benefits come risks, too. The rise of big data has led to data privacy, security, and misuse concerns. Many people don’t realize how much data on our behavior is being collected — it’s not uncommon for people to skip through the fine print of user agreements. And even more, many organizations are not keeping our data to themselves. Information on our behaviors, preferences, and demographics and constantly being collected and shared; our digital identities reach far beyond where the eye can see. Once this data has been collected, it’s very difficult to take it out of circulation. This makes it hard for some to maintain their desired level of privacy, especially in the case of data breaches, where unauthorized parties gain access to private data, or when organizations are misusing data in ways it wasn’t intended for or that users did not agree to (Read our “Data Science in Social Media” or our “Data Ethics” blogs for more detail).
Just this July, the “Big 4” — Amazon, Apple, Facebook, Google — tech CEOs faced an antitrust congressional hearing. The focus was on the companies trying to stifle competition, and examples of how they did this often had to do with their use of big data. Amazon was accused of lying to lawmakers about tapping data from third party sellers, and all four were accused of putting users’ privacy at risk.
A warning
It’s important to note that innovation prays at the altar of change, more specifically, change for the sake of change. Innovation without the guiding hand of ethics can often pose more harm to our society than good. Big data can make enormous changes to our lives. But this innovation must be wielded with care for those changes to be good.
On the organizational level: While big data might present itself as the best and only way to scale an organization and grow their success, it’s important for organizations to weigh the benefits of big data with their ability to manage the challenges. Organizations should also make sure that their big data strategies align with their overall business strategies and goals. If big data is not being managed or utilized effectively, the costs may outweigh the benefits, whether that be in legal fees or company culture.
On the individual level: Users of products and services may want to read the fine print to better understand how their data is being used, and if it is in their best interest to allow their data to be used in certain ways. They may want to limit their exposure to data misuse or security issues.
On the governmental level: Recent laws and regulations are slowly giving consumers more rights in limiting their exposure with regards to private data. The California Consumer Privacy Act allows consumers to demand to see the information a company has saved about them, as well as a list of third parties that information has been shared with. It also allows consumers to opt-out of unnecessary data collection. In the European Union, “right to be forgotten” laws have been passed that allow users to ask that their personal information be made unsearchable. While the right to be forgotten faces an uphill battle in the United States, where first amendment free speech rights are regarded very highly, the EU’s laws provide one example for how to approach data privacy concerns.
Now what?
The technologies that have been created and the gains that have been made in the last 20 years are greater than anyone would have imagined prior. Today we can’t even imagine life without them. The pace of technological innovations has been rapidly increasing, and we expect they will continue to do so in the next decade as well. Understanding innovations such as big data can help guide our use of it, and make sure that we are headed in the right direction.
Sources
- “Big Data: What It Is and Why It Matters.” SAS, SAS Institue Inc., www.sas.com/en_us/insights/big-data/what-is-big-data.html.
- Espinosa, J. Albert, et al. Big Data Redux: New Issues and Challenges Moving Forward. University of Hawai’i at Manoa, 2019, scholarspace.manoa.hawaii.edu/bitstream/10125/59546/0106.pdf.
- “How Is Big Data Transforming Business?” Bernard Marr, www.bernardmarr.com/default.asp?contentID=767.
- “A Short History of Big Data: Big Data Framework.” Big Data Framework©, 26 Mar. 2019, www.bigdataframework.org/short-history-of-big-data/.
- “What Is BIG DATA? Introduction, Types, Characteristics, Example.” Guru99, www.guru99.com/what-is-big-data.html.
- “What Is Big Data?” Oracle, Oracle, www.oracle.com/big-data/what-is-big-data.html.
Feel free to reach out to us if you have any feedback, or if you want to know more about the major. Also, follow us on Instagram @bigdata.berkeley and visit our website at bd.berkeley.edu if you want to learn more about Big Data at Berkeley!
Don’t forget to give us your ? !




What is “big data”? And how does it power today’s insights? was originally published in Becoming Human: Artificial Intelligence Magazine on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
Does Data Science Make You Happy?
Originally from KDnuggets https://ift.tt/36zkiJT
source https://365datascience.weebly.com/the-best-data-science-blog-2020/does-data-science-make-you-happy
Vision Transformers: Natural Language Processing (NLP) Increases Efficiency and Model Generality
Originally from KDnuggets https://ift.tt/2MqNHz4
Top Stories Jan 25-31: Want to Be a Data Scientist? Dont Start With Machine Learning; The Ultimate Scikit-Learn Machine Learning Cheatsheet
Originally from KDnuggets https://ift.tt/39E7bsH
